Question: seminar question first need to prepare job description for the following jobs then answered the questions down. I uploaded the slides that me help you












seminar question first need to prepare job description for the following jobs then answered the questions down. I uploaded the slides that me help you for answers
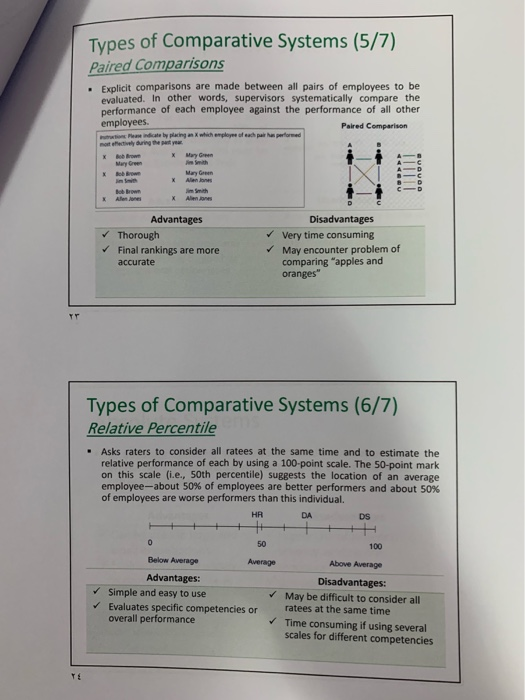
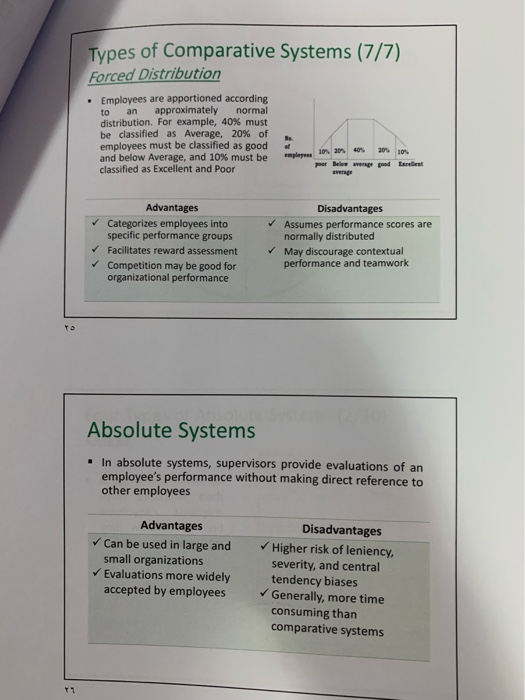
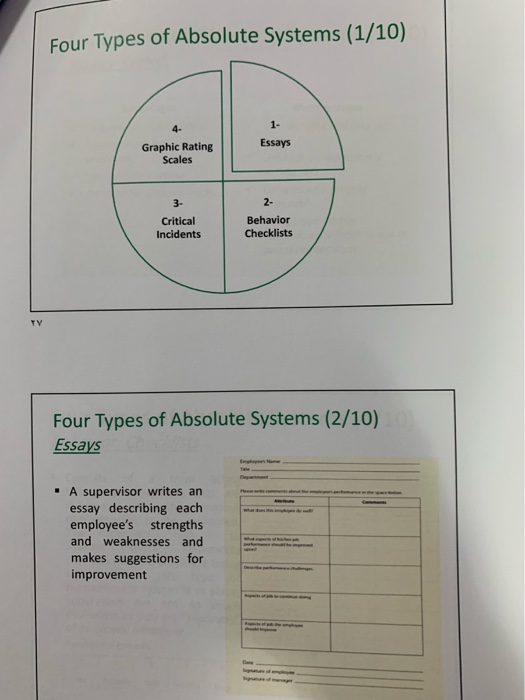
Seminar Question After Preparing a job description document for the allocated job title, A. Receptionist at a Private Hospital (Group A) B. Customer Service Representative at Bupa (Group B) C. Financial manager at a Public Hospital (Group C) D. Social Media Specialist at Hail Health Directorate (Group D) Each group has to 1. Define the key performance criteria/standards: Setting 10 key performance standards/criteria for this job title 2. Measurement System: Choosing the most relevant measurement system. Justify your choice; you can choose more than one. Performance Criteria/Standards (1/7) 1- Behavior Approach Competencies Approach an 2- 3- Trait Approach Results Approach Performance Criteria/Standards (2/7) Behaviour Approach Behaviors are typically viewed as resulting from life experiences. A behavior may have been learned from parents, significant friends, or from a certain work environment. A behavior can be changed but traits are usually more established. Often a young who joins the military will have many behavioral changes take place prior to returning to civilian life. An appropriate behavior to evaluate for a manager might be leadership style. For individuals working in teams, developing others, teamwork and cooperation, or customer service orientation might be appropriate. Desired behaviors may be appropriate as evaluation criteria because if they are recognized and rewarded, employees tend to repeat them. If certain behaviors result in desired outcomes, there is merit in using them in the evaluation process. Performance Criteria/Standards (3/7). Behaviour Approach-contd. . emphasizes what employees do on the job and does not consider employees' traits or the outcomes resulting from their behaviours. Process-oriented approach that emphasizes how an employee does the job The behaviour approach is most appropriate under the following circumstances: The link between behaviours and results is not obvious Outcomes occur in the distant future Poor results are due to causes beyond the performer's control Performance Criteria/Standards (4/7) Results Approach (Goal Achievement) . If organizations consider the ends more important than the means. then using only goal achievement as an outcome might be appropriate. The outcomes established should be within the control of the individual or team and should be those results that lead to the firm's success. At upper levels, the goals might be profit and market share. At lower organizational levels, the outcomes might be meeting the customer's quality requirements and delivering according to the promised schedule. Emphasizes the outcomes and results produced by the employees. It does not consider the traits that employees may possess or how employees do the job. This is a bottom-line approach - not concerned about employee behaviours and processes but instead focuses on what is produced. It is also cost effective data resulting from a results approach are objective and intuitively appealing Performance Criteria/Standards (5/7) Results Approach (Goal Achievement-contd. . Advantages: Less time Lower cost Data appear objective . The results approach is most appropriate under the following circumstances: Workers are skilled in the needed behaviours Behaviours and results are obviously related Results show consistent improvement over time There are many to do the job right Performance Criteria/Standards (6/7) Trait Approach Traits are usually thought of as resulting from biology. A personality trait is more Ingrained as with a person being introverted or extroverted. Certain employee traits such as appearance and cognitive aptitude may be the basis for some evaluations. . Emphasizes the individual performer and ignores the specific situation, behaviours, and results. Raters evaluate relatively stable traits. This approach is justified based on the positive relationship found between abilities and personality traits and desirable work-related behaviours. The trait-oriented approach can be most useful as: Part of a business strategy to anticipate drastic structural changes for reorganization of most functions and the resulting reallocation of employees CHALLENGES/DISADVANTAGE: traits are not under the control of individuals and in most cases they are fairly stable over one's life span. They are not likely to change even if an individual is willing to exert substantial effort to do so (development of these traits are beyond their control). The fact that an individual possesses a certain trait does not mean that this trait will necessarily lead to desired results and behaviours. Performance Criteria/Standards (7/7) Competencies Approach Competencies include a broad range of knowledge, skills, traits, and behaviors that are needed to perform a job successfully. They may be technical in nature, relate to interpersonal skills, or are business-oriented. For example, analytical thinking and achievement orientation might be essential in professional jobs. . In leadership jobs, relevant competencies might include developing talent, delegating authority, and people management skills. The competencies selected for evaluation purposes should be those that are closely associated with job success. Performance Measurement System . Comparative system: Compares employees with one another Absolute system: Measuring an employees performance against some established Standards Advantages and Disadvantages of Comparative Systems Advantages Disadvantages - Easy to explain Rankings may not be . Straightforward specific enough for: - Identifies top as well as Useful feedback underperformers Protection from legal Better control for biases and challenge errors found in absolute No information on relative systems distance between Leniency employees Severity Specific issues with forced Central tendency distribution method Five Types of Comparative Systems (1/7) Forced Distribution Simple Rank Order Relative Percentile Alternation Rank Order Paired Comparisons Types of Comparative Systems (2/7) Simple Rank Order - Simple rank order system is used, employees are simply ranked from best performer to worst performer Advantages: Simple and easy to do Results are clear Disadvantages: Judges performance based on one dimension only May be difficult to rank similar performance levels Types of Comparative Systems (3/7) Alternation Rank Order ALTERNATION RANGING SCALE For her you all the employees you want to put the g employe e the lowering employee's name for highest rang online 2. the new est ranking on line 19. and so on Continue on the wa Highening employee i ng the names Lowering employee Types of Comparative Systems (4/7) Alternation Rank Order-contd. The supervisor initially lists all employees. Then, the supervisor selects the best performer (#1), then the worst performer (#n), then the second best (#2), then the second worst (#n-1), and so forth, alternating from the top to the bottom of the list until all employees have been ranked. Advantages Simple and easy to do Results are clear Uses two anchors (best and worst) Disadvantages Judges performance based on one dimension only May be difficult to rank similar performance levels Does not specify threshold for acceptable performance Types of Comparative Systems (5/7) Paired Comparisons Explicit comparisons are made between all pairs of employees to be evaluated. In other words, supervisors systematically compare the performance of each employee against the performance of all other employees. Paired Comparison es te by placing an x which aployee of the performed mote ly during you X Mary Green Mary Green Be X Mary Green Alan Jones Advantages Thorough Final rankings are more accurate Disadvantages Very time consuming May encounter problem of comparing "apples and oranges" Types of Comparative Systems (6/7) Relative Percentile Asks raters to consider all ratees at the same time and to estimate the relative performance of each by using a 100-point scale. The 50-point mark on this scale (i.e., 50th percentile) suggests the location of an average employee-about 50% of employees are better performers and about 50% of employees are worse performers than this individual. HA DA DS 50 Below Average Average Advantages: Simple and easy to use Evaluates specific competencies or overall performance 100 Above Average Disadvantages: May be difficult to consider all ratees at the same time Time consuming if using several scales for different competencies Types of Comparative Systems (7/7) Forced Distribution Employees are apportioned according to an approximately normal distribution. For example, 40% must be classified as Average, 20% of employees must be classified as good and below Average, and 10% must be classified as Excellent and Poor pley 1020% 40% pour Beloe vera 20% good rest Advantages Categorizes employees into specific performance groups Facilitates reward assessment Competition may be good for organizational performance Disadvantages Assumes performance scores are normally distributed May discourage contextual performance and teamwork Absolute Systems . In absolute systems, supervisors provide evaluations of an employee's performance without making direct reference to other employees Advantages Can be used in large and small organizations Evaluations more widely accepted by employees Disadvantages Higher risk of leniency, severity, and central tendency biases Generally, more time consuming than comparative systems Four Types of Absolute Systems (1/10) Essays Graphic Rating Scales 3- Critical Incidents Behavior Checklists Four Types of Absolute Systems (2/10) Essays . A supervisor writes an essay describing each employee's strengths and weaknesses and makes suggestions for improvement Four Types of Absolute Systems (3/10) Essays- contd. Advantages Simplest absolute method Individualized for each employee Can be done anytime Potential for detailed feedback Disadvantages Unstructured and may lack detail Depends on supervisor's writing skill Comparisons virtually impossible Lack of quantitative information; difficult to use in personnel decisions Four Types of Absolute Systems (4/10) Behavior Checklists Consists of a form listing behavioral statements that are indicators of the various competencies to be measured. The supervisor's task is to indicate ("check") statements that describe the employee being rated. When this type of measurement system is in place, supervisors are not so much evaluators as they are "reporters" of employee behaviour. Four Types of Absolute Systems (5/10) Behavior Checklists- contd. Advantages Easy to use and understand Provides quantitative information Widespread use More objective than other systems Disadvantages May feel impersonal and disconnected Scale points used are often arbitrary Difficult to get detailed and useful feedback Four Types of Absolute Systems (6/10) Critical Incidents Involves gathering reports of situations in which employees exhibited behaviors that were especially effective or ineffective in accomplishing their jobs Instructions for each description of work behavior, circle the number that best describes how frequently the employee engages in that behavior 1. The incumbent removes manure and unconsumed food from the animal enclosures Almost never sometimes fairly often Very atten 2. The incumbent haphazardly measures the feed items when placing them in the animal enclosures Never Almost never sometimes fairly often Very often 1. The incumbent leaves refuse dropped by visitors on and around the public walkway Almost never Sometimes Fairly often Very often 4 The incumbent skily identifies instances of abnormal behavior among the animals, which represent signs of liness Never Almost ever sometimes fairly otten Veryohen Four Types of Absolute Systems (7/10) Critical Incidents- contd. Advantages Focus on actual job behavior Provides specific examples Employees identify with rating Disadvantages Collecting critical incidents can be very time consuming Quantification is difficult Four Types of Absolute Systems (8/10) Graphic Rating Scales Project management awareness is the knowledge of project management planning, updating status, working within budget and delivering praxton time and within budget. Rate 's project management awarness using the following scale Uw not interested e additional Aware of responsibilities Bent knowledge and performance of Superior performance of ability to Example of a Graphic Rating Scale question How would you rate the individual in terms of quality of work, neatness and accuracy? 1. Non-Existen Careless Worker. Tends to repeat similar mistakes 2. Average Work is sometimes unsatisfactory due to undness 3. Good: Work is acceptable. Not many errors 4. Very Goodwale worker. Good Glity of work. Checks work and b e SExcellent work is of high quality Errors are any. Letle wanted effort Four Types of Absolute Systems (9/10) Graphic Rating Scales- contd. Traits or behaviours that are important for effective performance are listed out and each employee is rated against these traits. The rating helps employers to quantify the behaviours displayed by its employees Behaviorally Anchored Rating Scales (BARS), is one graphic rating scales types. It uses critical incidents as anchors. Involves multiple groups of employees in development Identify important job elements Describe critical incidents at various levels of performance Check for inter-rater reliability Scales should be behaviourally based. Ambiguous behaviours definitions, such as loyalty, honesty etc. should be avoided Ratings should be relevant to the behaviour being measured. For example, to measure "English Speaking Skill" rates should be fluent, hesitant, and laboured instead of excellent, average and poor. Four Types of Absolute Systems (10/10) Graphic Rating Scales- contd. Advantages Meanings, interpretations, and dimensions being rated are clear Useful and accurate Most popular tool Disadvantages Time consuming and resource-laden to develop Lacks individualized feedback and recommendations Seminar Question After Preparing a job description document for the allocated job title, A. Receptionist at a Private Hospital (Group A) B. Customer Service Representative at Bupa (Group B) C. Financial manager at a Public Hospital (Group C) D. Social Media Specialist at Hail Health Directorate (Group D) Each group has to 1. Define the key performance criteria/standards: Setting 10 key performance standards/criteria for this job title 2. Measurement System: Choosing the most relevant measurement system. Justify your choice; you can choose more than one. Performance Criteria/Standards (1/7) 1- Behavior Approach Competencies Approach an 2- 3- Trait Approach Results Approach Performance Criteria/Standards (2/7) Behaviour Approach Behaviors are typically viewed as resulting from life experiences. A behavior may have been learned from parents, significant friends, or from a certain work environment. A behavior can be changed but traits are usually more established. Often a young who joins the military will have many behavioral changes take place prior to returning to civilian life. An appropriate behavior to evaluate for a manager might be leadership style. For individuals working in teams, developing others, teamwork and cooperation, or customer service orientation might be appropriate. Desired behaviors may be appropriate as evaluation criteria because if they are recognized and rewarded, employees tend to repeat them. If certain behaviors result in desired outcomes, there is merit in using them in the evaluation process. Performance Criteria/Standards (3/7). Behaviour Approach-contd. . emphasizes what employees do on the job and does not consider employees' traits or the outcomes resulting from their behaviours. Process-oriented approach that emphasizes how an employee does the job The behaviour approach is most appropriate under the following circumstances: The link between behaviours and results is not obvious Outcomes occur in the distant future Poor results are due to causes beyond the performer's control Performance Criteria/Standards (4/7) Results Approach (Goal Achievement) . If organizations consider the ends more important than the means. then using only goal achievement as an outcome might be appropriate. The outcomes established should be within the control of the individual or team and should be those results that lead to the firm's success. At upper levels, the goals might be profit and market share. At lower organizational levels, the outcomes might be meeting the customer's quality requirements and delivering according to the promised schedule. Emphasizes the outcomes and results produced by the employees. It does not consider the traits that employees may possess or how employees do the job. This is a bottom-line approach - not concerned about employee behaviours and processes but instead focuses on what is produced. It is also cost effective data resulting from a results approach are objective and intuitively appealing Performance Criteria/Standards (5/7) Results Approach (Goal Achievement-contd. . Advantages: Less time Lower cost Data appear objective . The results approach is most appropriate under the following circumstances: Workers are skilled in the needed behaviours Behaviours and results are obviously related Results show consistent improvement over time There are many to do the job right Performance Criteria/Standards (6/7) Trait Approach Traits are usually thought of as resulting from biology. A personality trait is more Ingrained as with a person being introverted or extroverted. Certain employee traits such as appearance and cognitive aptitude may be the basis for some evaluations. . Emphasizes the individual performer and ignores the specific situation, behaviours, and results. Raters evaluate relatively stable traits. This approach is justified based on the positive relationship found between abilities and personality traits and desirable work-related behaviours. The trait-oriented approach can be most useful as: Part of a business strategy to anticipate drastic structural changes for reorganization of most functions and the resulting reallocation of employees CHALLENGES/DISADVANTAGE: traits are not under the control of individuals and in most cases they are fairly stable over one's life span. They are not likely to change even if an individual is willing to exert substantial effort to do so (development of these traits are beyond their control). The fact that an individual possesses a certain trait does not mean that this trait will necessarily lead to desired results and behaviours. Performance Criteria/Standards (7/7) Competencies Approach Competencies include a broad range of knowledge, skills, traits, and behaviors that are needed to perform a job successfully. They may be technical in nature, relate to interpersonal skills, or are business-oriented. For example, analytical thinking and achievement orientation might be essential in professional jobs. . In leadership jobs, relevant competencies might include developing talent, delegating authority, and people management skills. The competencies selected for evaluation purposes should be those that are closely associated with job success. Performance Measurement System . Comparative system: Compares employees with one another Absolute system: Measuring an employees performance against some established Standards Advantages and Disadvantages of Comparative Systems Advantages Disadvantages - Easy to explain Rankings may not be . Straightforward specific enough for: - Identifies top as well as Useful feedback underperformers Protection from legal Better control for biases and challenge errors found in absolute No information on relative systems distance between Leniency employees Severity Specific issues with forced Central tendency distribution method Five Types of Comparative Systems (1/7) Forced Distribution Simple Rank Order Relative Percentile Alternation Rank Order Paired Comparisons Types of Comparative Systems (2/7) Simple Rank Order - Simple rank order system is used, employees are simply ranked from best performer to worst performer Advantages: Simple and easy to do Results are clear Disadvantages: Judges performance based on one dimension only May be difficult to rank similar performance levels Types of Comparative Systems (3/7) Alternation Rank Order ALTERNATION RANGING SCALE For her you all the employees you want to put the g employe e the lowering employee's name for highest rang online 2. the new est ranking on line 19. and so on Continue on the wa Highening employee i ng the names Lowering employee Types of Comparative Systems (4/7) Alternation Rank Order-contd. The supervisor initially lists all employees. Then, the supervisor selects the best performer (#1), then the worst performer (#n), then the second best (#2), then the second worst (#n-1), and so forth, alternating from the top to the bottom of the list until all employees have been ranked. Advantages Simple and easy to do Results are clear Uses two anchors (best and worst) Disadvantages Judges performance based on one dimension only May be difficult to rank similar performance levels Does not specify threshold for acceptable performance Types of Comparative Systems (5/7) Paired Comparisons Explicit comparisons are made between all pairs of employees to be evaluated. In other words, supervisors systematically compare the performance of each employee against the performance of all other employees. Paired Comparison es te by placing an x which aployee of the performed mote ly during you X Mary Green Mary Green Be X Mary Green Alan Jones Advantages Thorough Final rankings are more accurate Disadvantages Very time consuming May encounter problem of comparing "apples and oranges" Types of Comparative Systems (6/7) Relative Percentile Asks raters to consider all ratees at the same time and to estimate the relative performance of each by using a 100-point scale. The 50-point mark on this scale (i.e., 50th percentile) suggests the location of an average employee-about 50% of employees are better performers and about 50% of employees are worse performers than this individual. HA DA DS 50 Below Average Average Advantages: Simple and easy to use Evaluates specific competencies or overall performance 100 Above Average Disadvantages: May be difficult to consider all ratees at the same time Time consuming if using several scales for different competencies Types of Comparative Systems (7/7) Forced Distribution Employees are apportioned according to an approximately normal distribution. For example, 40% must be classified as Average, 20% of employees must be classified as good and below Average, and 10% must be classified as Excellent and Poor pley 1020% 40% pour Beloe vera 20% good rest Advantages Categorizes employees into specific performance groups Facilitates reward assessment Competition may be good for organizational performance Disadvantages Assumes performance scores are normally distributed May discourage contextual performance and teamwork Absolute Systems . In absolute systems, supervisors provide evaluations of an employee's performance without making direct reference to other employees Advantages Can be used in large and small organizations Evaluations more widely accepted by employees Disadvantages Higher risk of leniency, severity, and central tendency biases Generally, more time consuming than comparative systems Four Types of Absolute Systems (1/10) Essays Graphic Rating Scales 3- Critical Incidents Behavior Checklists Four Types of Absolute Systems (2/10) Essays . A supervisor writes an essay describing each employee's strengths and weaknesses and makes suggestions for improvement Four Types of Absolute Systems (3/10) Essays- contd. Advantages Simplest absolute method Individualized for each employee Can be done anytime Potential for detailed feedback Disadvantages Unstructured and may lack detail Depends on supervisor's writing skill Comparisons virtually impossible Lack of quantitative information; difficult to use in personnel decisions Four Types of Absolute Systems (4/10) Behavior Checklists Consists of a form listing behavioral statements that are indicators of the various competencies to be measured. The supervisor's task is to indicate ("check") statements that describe the employee being rated. When this type of measurement system is in place, supervisors are not so much evaluators as they are "reporters" of employee behaviour. Four Types of Absolute Systems (5/10) Behavior Checklists- contd. Advantages Easy to use and understand Provides quantitative information Widespread use More objective than other systems Disadvantages May feel impersonal and disconnected Scale points used are often arbitrary Difficult to get detailed and useful feedback Four Types of Absolute Systems (6/10) Critical Incidents Involves gathering reports of situations in which employees exhibited behaviors that were especially effective or ineffective in accomplishing their jobs Instructions for each description of work behavior, circle the number that best describes how frequently the employee engages in that behavior 1. The incumbent removes manure and unconsumed food from the animal enclosures Almost never sometimes fairly often Very atten 2. The incumbent haphazardly measures the feed items when placing them in the animal enclosures Never Almost never sometimes fairly often Very often 1. The incumbent leaves refuse dropped by visitors on and around the public walkway Almost never Sometimes Fairly often Very often 4 The incumbent skily identifies instances of abnormal behavior among the animals, which represent signs of liness Never Almost ever sometimes fairly otten Veryohen Four Types of Absolute Systems (7/10) Critical Incidents- contd. Advantages Focus on actual job behavior Provides specific examples Employees identify with rating Disadvantages Collecting critical incidents can be very time consuming Quantification is difficult Four Types of Absolute Systems (8/10) Graphic Rating Scales Project management awareness is the knowledge of project management planning, updating status, working within budget and delivering praxton time and within budget. Rate 's project management awarness using the following scale Uw not interested e additional Aware of responsibilities Bent knowledge and performance of Superior performance of ability to Example of a Graphic Rating Scale question How would you rate the individual in terms of quality of work, neatness and accuracy? 1. Non-Existen Careless Worker. Tends to repeat similar mistakes 2. Average Work is sometimes unsatisfactory due to undness 3. Good: Work is acceptable. Not many errors 4. Very Goodwale worker. Good Glity of work. Checks work and b e SExcellent work is of high quality Errors are any. Letle wanted effort Four Types of Absolute Systems (9/10) Graphic Rating Scales- contd. Traits or behaviours that are important for effective performance are listed out and each employee is rated against these traits. The rating helps employers to quantify the behaviours displayed by its employees Behaviorally Anchored Rating Scales (BARS), is one graphic rating scales types. It uses critical incidents as anchors. Involves multiple groups of employees in development Identify important job elements Describe critical incidents at various levels of performance Check for inter-rater reliability Scales should be behaviourally based. Ambiguous behaviours definitions, such as loyalty, honesty etc. should be avoided Ratings should be relevant to the behaviour being measured. For example, to measure "English Speaking Skill" rates should be fluent, hesitant, and laboured instead of excellent, average and poor. Four Types of Absolute Systems (10/10) Graphic Rating Scales- contd. Advantages Meanings, interpretations, and dimensions being rated are clear Useful and accurate Most popular tool Disadvantages Time consuming and resource-laden to develop Lacks individualized feedback and recommendations
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


