Question: Set - Covering Problem ( SCP ) Given a set of elements { 1 , 2 , dots, n } ( called the universe )
SetCovering Problem SCP
Given a set of elements dots,called the universe and a collection of subsets whose union equals
the universe, the set cover problem is to identify the smallest subcollection of whose union equals the
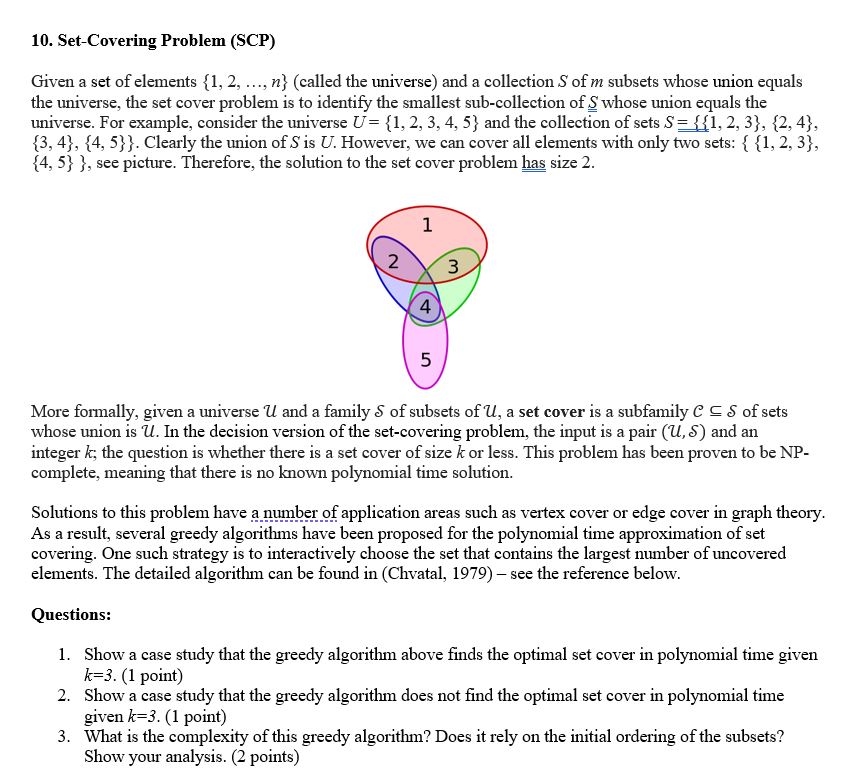
universe. For example, consider the universe and the collection of sets
Clearly the union of is However, we can cover all elements with only two sets:
see picture. Therefore, the solution to the set cover problem has size
More formally, given a universe and a family of subsets of a set cover is a subfamily CsubeS of sets
whose union is In the decision version of the setcovering problem, the input is a pair and an
integer ; the question is whether there is a set cover of size or less. This problem has been proven to be NP
complete, meaning that there is no known polynomial time solution.
Solutions to this problem have a number of application areas such as vertex cover or edge cover in graph theory.
As a result, several greedy algorithms have been proposed for the polynomial time approximation of set
covering. One such strategy is to interactively choose the set that contains the largest number of uncovered
elements. The detailed algorithm can be found in Chvatal see the reference below.
Questions:
Show a case study that the greedy algorithm above finds the optimal set cover in polynomial time given
point
Show a case study that the greedy algorithm does not find the optimal set cover in polynomial time
given point
What is the complexity of this greedy algorithm? Does it rely on the initial ordering of the subsets?
Show your analysis. points
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


