Question: - Several months ago, Buddy Inc. issued a unique fixed income security. As of today, the security is maturing in 11 months. The security pays
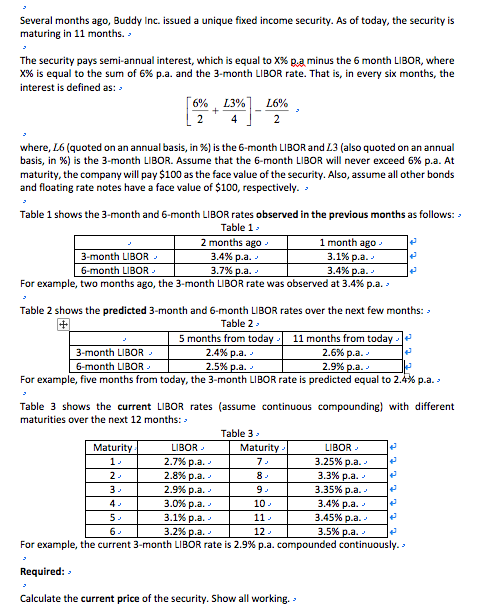
- Several months ago, Buddy Inc. issued a unique fixed income security. As of today, the security is maturing in 11 months. The security pays serni-annual interest, which is equal to XXR.a minus the 5 month LIBOR, where X% is equal to the sum of 6% p.a. and the 3-month LIBOR rate. That is, in every six months, the interest is defined as: 6% L3% 26% + 4 2 - where, L. (quoted on an annual basis, in %) is the 6-month LIBOR and 23 (also quoted on an annual basis, in %) is the 3-month LIBOR. Assume that the 6-month LIBOR will never exceed 6% p.a. At maturity, the company will pay $100 as the face value of the security. Also, assume all other bonds and floating rate notes have a face value of $100, respectively. Table 1 shows the 3-month and 6-month LIBOR rates observed in the previous months as follows: Table 1 2 months ago 1 month ago 3-month LIBOR- 3.4% p.a. 3.1% p.a. 6-month LIBOR 3.7% p.a. - 3.4%p.a. For example, two months ago, the 3-month LIBOR rate was observed at 3.4% p.a. - Table 2 shows the predicted 3-month and 6-month LIBOR rates over the next few months: 3 Table 2 5 months from today 11 months from today 3-month LIBOR- 2.4% p.a. 2.6% p.a. 6-month LIBOR 2.5% p.a. 2.9% p.a. For example, five months from today, the 3-month LIBOR rate is predicted equal to 2.4% p.a. Table 3 shows the current LIBOR rates (assume continuous compounding) with different maturities over the next 12 months: Table 3 Maturity LIBOR Maturity LIBOR- 1- 2.7% p.a. 7. 3.25% p.a. 2- 2.8% p.a. 8 - 3.3% p.a. - 2.9% p.a. 3.35% p.a. - 3.0% p.a. 10 3.4% p.a. 5 3.1% p.a. 11 - 3.45% p.a. 3.2% p.a. - 12 - 3.5% p.a. For example, the current 3-month LIBOR rate is 2.9% p.a. compounded continuously. - t t 3 Required: Calculate the current price of the security. Show all working. - - Several months ago, Buddy Inc. issued a unique fixed income security. As of today, the security is maturing in 11 months. The security pays serni-annual interest, which is equal to XXR.a minus the 5 month LIBOR, where X% is equal to the sum of 6% p.a. and the 3-month LIBOR rate. That is, in every six months, the interest is defined as: 6% L3% 26% + 4 2 - where, L. (quoted on an annual basis, in %) is the 6-month LIBOR and 23 (also quoted on an annual basis, in %) is the 3-month LIBOR. Assume that the 6-month LIBOR will never exceed 6% p.a. At maturity, the company will pay $100 as the face value of the security. Also, assume all other bonds and floating rate notes have a face value of $100, respectively. Table 1 shows the 3-month and 6-month LIBOR rates observed in the previous months as follows: Table 1 2 months ago 1 month ago 3-month LIBOR- 3.4% p.a. 3.1% p.a. 6-month LIBOR 3.7% p.a. - 3.4%p.a. For example, two months ago, the 3-month LIBOR rate was observed at 3.4% p.a. - Table 2 shows the predicted 3-month and 6-month LIBOR rates over the next few months: 3 Table 2 5 months from today 11 months from today 3-month LIBOR- 2.4% p.a. 2.6% p.a. 6-month LIBOR 2.5% p.a. 2.9% p.a. For example, five months from today, the 3-month LIBOR rate is predicted equal to 2.4% p.a. Table 3 shows the current LIBOR rates (assume continuous compounding) with different maturities over the next 12 months: Table 3 Maturity LIBOR Maturity LIBOR- 1- 2.7% p.a. 7. 3.25% p.a. 2- 2.8% p.a. 8 - 3.3% p.a. - 2.9% p.a. 3.35% p.a. - 3.0% p.a. 10 3.4% p.a. 5 3.1% p.a. 11 - 3.45% p.a. 3.2% p.a. - 12 - 3.5% p.a. For example, the current 3-month LIBOR rate is 2.9% p.a. compounded continuously. - t t 3 Required: Calculate the current price of the security. Show all working
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


