Question: sing the method of morphological box, analyze various objects (for example, printed publications, household items, stationery, etc.). Create a matrix of search for new variants

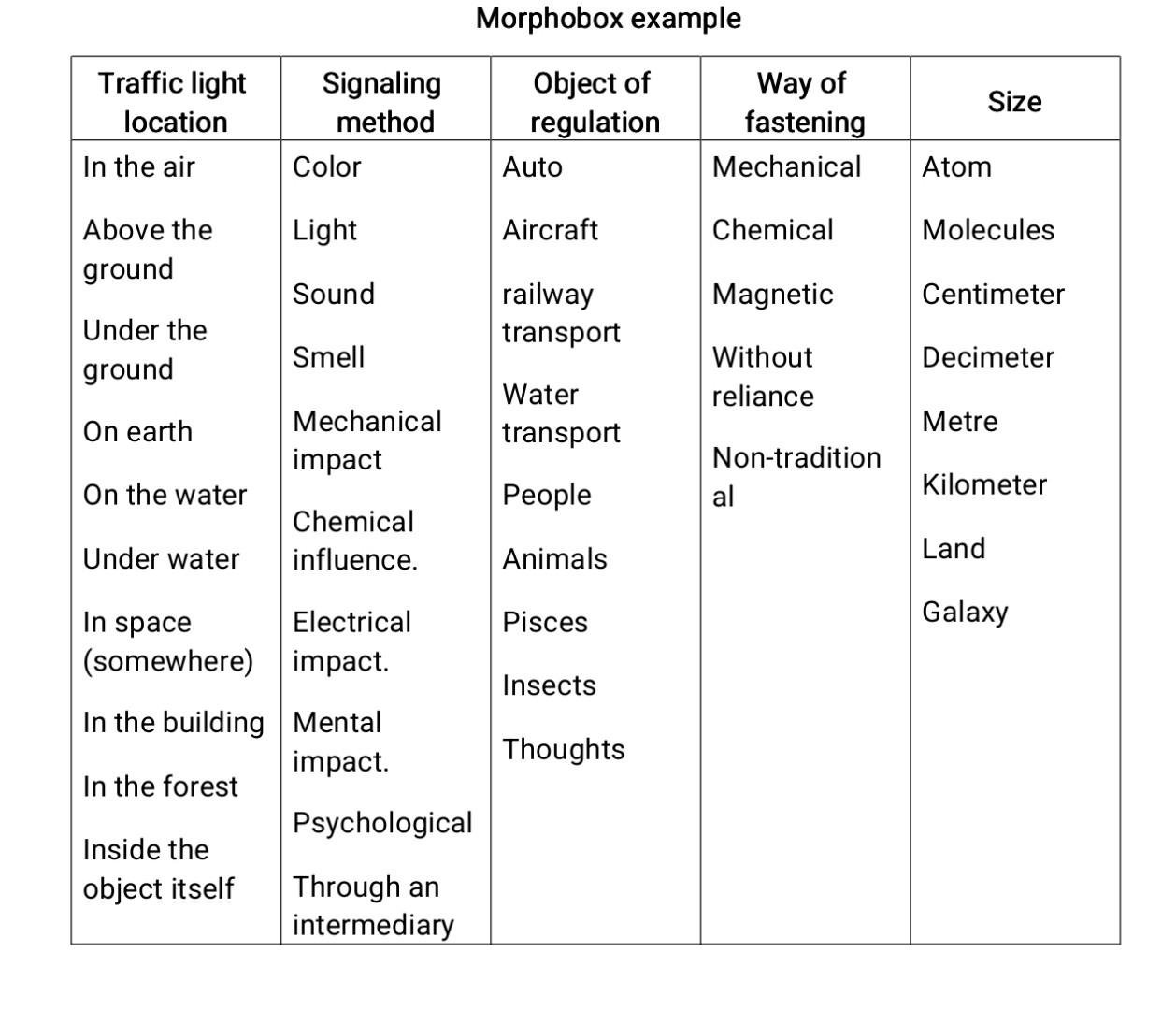
sing the method of morphological box, analyze various objects (for example, printed publications, household items, stationery, etc.). Create a matrix of search for new variants of their fulfillment, a tree of classification of decisions. Sequence of morphological analysis: 1. Choose the system you are interested in, determine what is required from it - set a goal. 2. Identify the components and properties of this system (elements, functions, etc.), thereby obtain a set of axes of morphological box. If the choice of axes is not obvious, it is advisable: - Look at three or four variants of such systems. For example, if the system is a tree, then different types of trees should be considered. - Compare how these options differ. For example, let's compare two trees - an apple tree and a birch tree. Then the difference: leaf shape and size, height, trunk shape and size, root system, lifespan, etc. Significant changing factors will be axes at your morpho box. 3. Determine possible options of significant components identified in point # 2, and input them to the axis of morpho box. 4. If necessary, add universal axes from the following list: system composition, system state, system direction, energy supply, measurement method, scope, management, purpose, goal of existence. You can add a functional axis that contains: "zoom-out zoom-in", "connect-disconnect", "antiproperty-property", "acceleration - deceleration", "time set back - forward", "constant - variable time properties". Separate a function from an object, change the relationship to the environment, including a complete environment replacement. Input the data to the form of a table and/or a decision tree. 5. Select combinations. 6. Describe the new system based on the selected combinations. Morphobox example sing the method of morphological box, analyze various objects (for example, printed publications, household items, stationery, etc.). Create a matrix of search for new variants of their fulfillment, a tree of classification of decisions. Sequence of morphological analysis: 1. Choose the system you are interested in, determine what is required from it - set a goal. 2. Identify the components and properties of this system (elements, functions, etc.), thereby obtain a set of axes of morphological box. If the choice of axes is not obvious, it is advisable: - Look at three or four variants of such systems. For example, if the system is a tree, then different types of trees should be considered. - Compare how these options differ. For example, let's compare two trees - an apple tree and a birch tree. Then the difference: leaf shape and size, height, trunk shape and size, root system, lifespan, etc. Significant changing factors will be axes at your morpho box. 3. Determine possible options of significant components identified in point # 2, and input them to the axis of morpho box. 4. If necessary, add universal axes from the following list: system composition, system state, system direction, energy supply, measurement method, scope, management, purpose, goal of existence. You can add a functional axis that contains: "zoom-out zoom-in", "connect-disconnect", "antiproperty-property", "acceleration - deceleration", "time set back - forward", "constant - variable time properties". Separate a function from an object, change the relationship to the environment, including a complete environment replacement. Input the data to the form of a table and/or a decision tree. 5. Select combinations. 6. Describe the new system based on the selected combinations. Morphobox example
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


