Question: SISTEM PENGENDALIAN / OPERATING SYSTEM Example: In non - preemptive scheduling, once the CPU cycle is allocated to process, the process holds it till it
SISTEM PENGENDALIAN OPERATING SYSTEM
Example:
In nonpreemptive scheduling, once the CPU cycle is allocated to process, the process holds it till it reaches a waiting state or terminated.
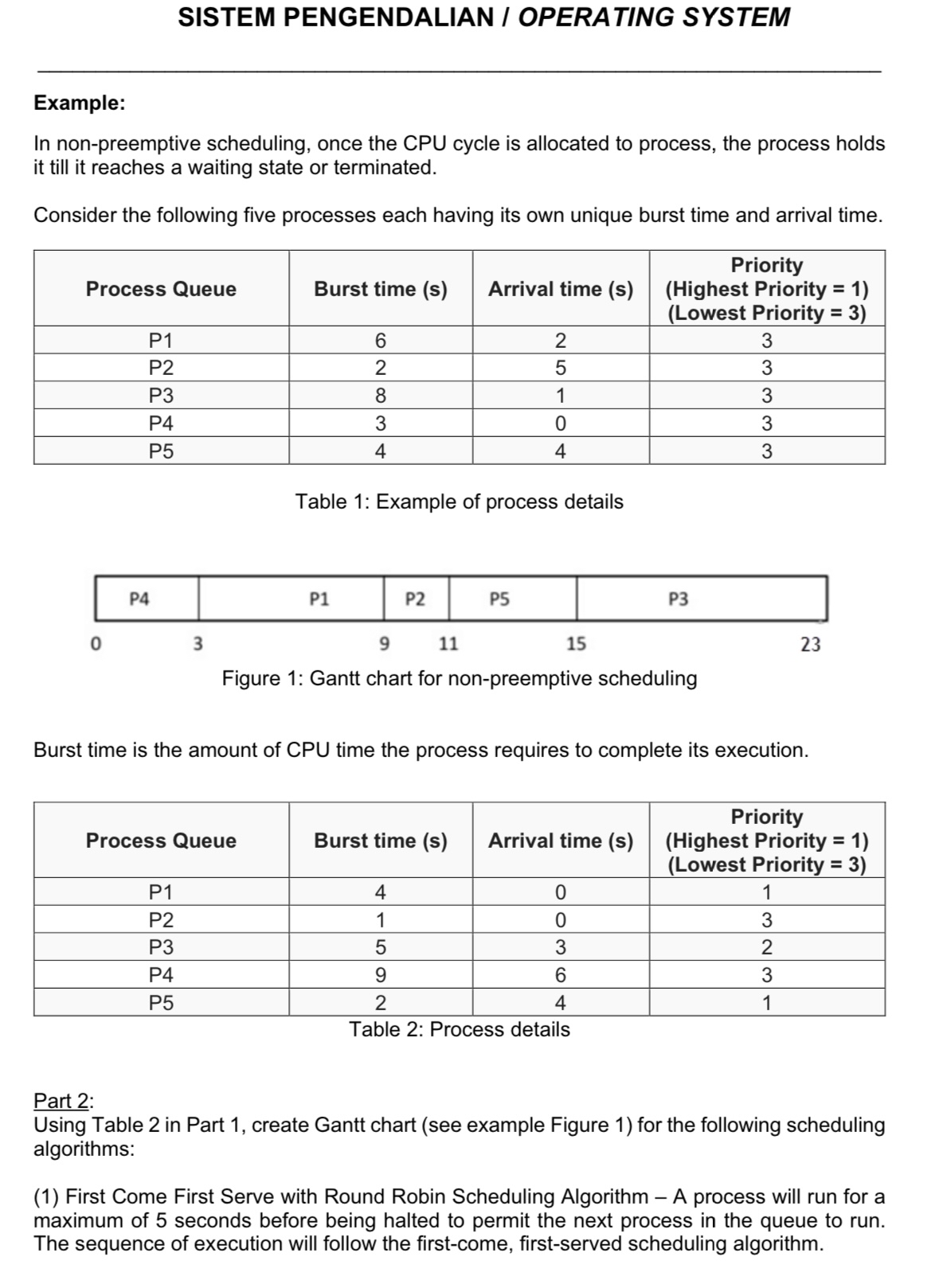
Consider the following five processes each having its own unique burst time and arrival time.
tableProcess Queue,Burst time sArrival time stablePriorityHighest Priority Lowest Priority PPPPP
Table : Example of process details
tablePPPPP
Burst time is the amount of CPU time the process requires to complete its execution.
tableProcess Queue,Burst time sArrival time stablePriorityHighest Priority Lowest Priority PPPPP
Table : Process details
Part :
Using Table in Part create Gantt chart see example Figure for the following scheduling algorithms:
First Come First Serve with Round Robin Scheduling Algorithm A process will run for a maximum of seconds before being halted to permit the next process in the queue to run. The sequence of execution will follow the firstcome, firstserved scheduling algorithm.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


