Question: So Please complete the following code : #Author: #File: #Date Created: #Short Description: # # # Motion: # [0,0] - stay # [0,1] - right
![#Short Description: # # # Motion: # [0,0] - stay # [0,1]](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f3aaae2a9ed_97366f3aaad9a826.jpg)
![- right # [0,-1] - left # [1,0] - down # [-1,0]](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f3aaaf0efaa_97466f3aaae79116.jpg)


![float(len(colors)) / float(len(colors[0])) p = [[pinit for row in range(len(colors[0]))] for col](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f3aab1a3b01_97766f3aab10deb1.jpg)
![in range(len(colors))] # >>> Insert your code here def show(p): rows =](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f3aab282091_97866f3aab203534.jpg)
So Please complete the following code :
#Author: #File: #Date Created: #Short Description: # #
# Motion: # [0,0] - stay # [0,1] - right # [0,-1] - left # [1,0] - down # [-1,0] - up
def localize(colors,measurements,motions,sensor_right,p_move): # initializes p to a uniform distribution over a grid of the same dimensions as colors pinit = 1.0 / float(len(colors)) / float(len(colors[0])) p = [[pinit for row in range(len(colors[0]))] for col in range(len(colors))] # >>> Insert your code here
def show(p): rows = ['[' + ','.join(map(lambda x: '{0:.5f}'.format(x),r)) + ']' for r in p] print '[' + ', '.join(rows) + ']' ############################################################# # For the following test case, your output should be # [[0.01105, 0.02464, 0.06799, 0.04472, 0.02465], # [0.00715, 0.01017, 0.08696, 0.07988, 0.00935], # [0.00739, 0.00894, 0.11272, 0.35350, 0.04065], # [0.00910, 0.00715, 0.01434, 0.04313, 0.03642]] # (within a tolerance of +/- 0.001 for each entry)
colors = [['R','G','G','R','R'], ['R','R','G','R','R'], ['R','R','G','G','R'], ['R','R','R','R','R']] measurements = ['G','G','G','G','G'] motions = [[0,0],[0,1],[1,0],[1,0],[0,1]] p = localize(colors,measurements,motions,sensor_right = 0.7, p_move = 0.8) show(p) # displays your answer
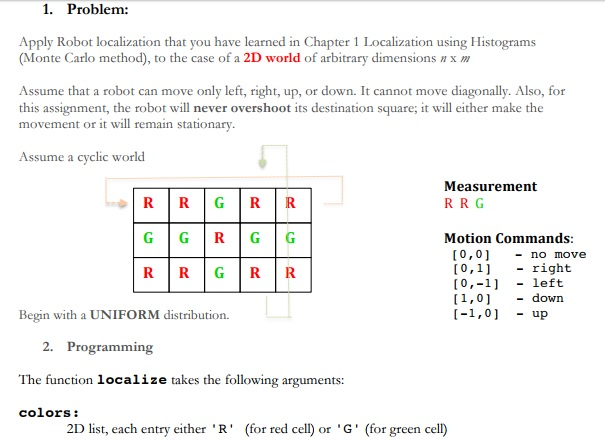
1. Problem: Apply Robot localization that you have learned in Chapter 1 Localization using Histograms (Monte Carlo method), to the case of a 2D world of arbitrary dimensions nx m Assume that a robot can move only left, right, up, or down. It cannot move diagonally. Also, for this assignment, the robot will never overshoot its destination square; it will either make the movement or it will remain stationary Assume a cyclic world Measurement RR G RRG R R Motion Commands [0,0 - no move 0,1 - right [0,1 - left 1,0 - down [-1,0 - up Begin with a UNIFORM distribution. 2. Programming The function localize takes the followi ng arguments: colors: 21) list, each entry either . R ' (for red cell) or G" (for green cell)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


