Question: Software Dev. & Problem Solving II Graphs & Breadth-First Search Goals of the Assignment Practice using graphs and searches with graphs. This assignment will

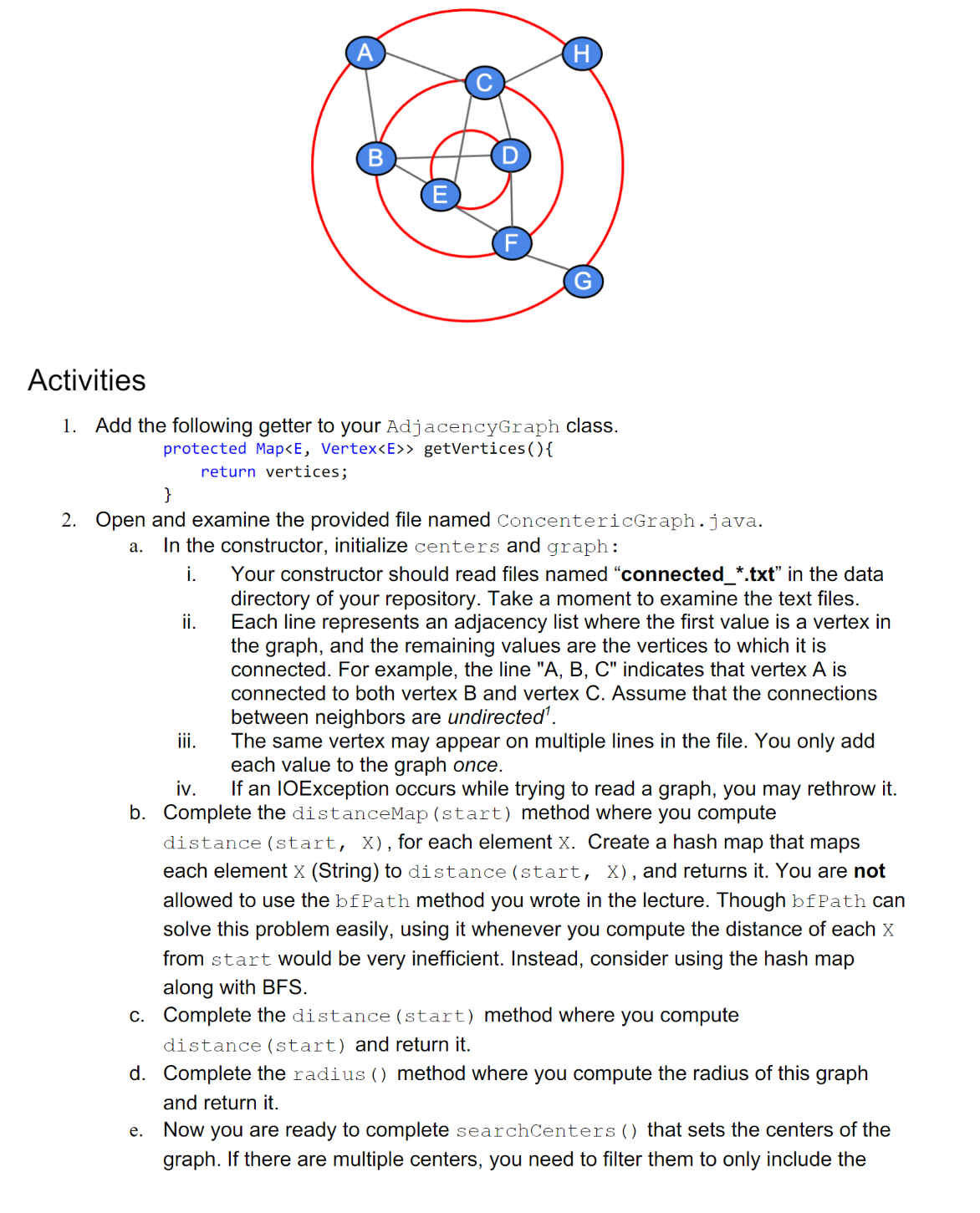



Software Dev. & Problem Solving II Graphs & Breadth-First Search Goals of the Assignment Practice using graphs and searches with graphs. This assignment will require the Graph interface and the Vertex and AdjacencyGraph classes implemented during class as well as the implementation of the BFS algorithm. JUnit unit testing is not expected for this assignment. Read this document in its entirety before asking for help from the course staff. The following terminologies will be used in the assignment: Background Let G be a graph, and A and B be two vertices in G. We have learned that BFS can be used to find one of the shortest paths from A to B. We will call such a path a BFS path. distance (A, B) is the number of edges along a BFS path from A to B. distance (A) is the maximum distance of A to any vertices in G. That is distance (A) = max{distance (A, X), for any vertex X in G} A vertex C is called a center of G if distance (C) A Activities 1. Add the following getter to your AdjacencyGraph class. protected Map getVertices() { return vertices; ii. B } 2. Open and examine the provided file named ConcentericGraph.java. a. In the constructor, initialize centers and graph: i. e. H iii. The same vertex may appear on multiple lines in the file. You only add each value to the graph once. iv. If an IOException occurs while trying to read a graph, you may rethrow it. b. Complete the distanceMap (start) method where you compute distance (start, X), for each element X. Create a hash map that maps each element X (String) to distance (start, X), and returns it. You are not allowed to use the bf Path method you wrote in the lecture. Though bf Path can solve this problem easily, using it whenever you compute the distance of each X from start would be very inefficient. Instead, consider using the hash map along with BFS. Your constructor should read files named "connected_*.txt" in the data directory of your repository. Take a moment to examine the text files. Each line represents an adjacency list where the first value is a vertex in the graph, and the remaining values are the vertices to which it is connected. For example, the line "A, B, C" indicates that vertex A is connected to both vertex B and vertex C. Assume that the connections between neighbors are undirected'. c. Complete the distance (start) method where you compute distance (start) and return it. d. Complete the radius () method where you comp and return it. the radius of this graph Now you are ready to complete search Centers () that sets the centers of the graph. If there are multiple centers, you need to filter them to only include the ones that have the most neighbors. There could be still multiple centers of the graph after filtering. f. (10% bonus credit) Override the toString method that returns a concentric view of the graph. Refer to the sample output in the next section. Hint: Use BFS starting from centers to build a string representation. 3. Sample One public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { ConcentricGraph cGraph = new ConcentricGraph("data/connected_3.txt");//example System.out.println("Distance of each vertex from A:"); } System.out.println(cGraph.distanceMap("A")); System.out.println("distance (A): +cGraph.distance("A")); System.out.println("Graph radius: " +cGraph.radius()); System.out.println("Graph Centers: " + cGraph.getCenters()); System.out.println("Concentric Graph: " + cGraph); // Bonus credit Distance of each vertex from A: {A=0, B=1, C=1, D=2, E=2, F=3, G=4, H=2} distance (A): 4 Graph radius: 2 Graph Centers: [D, E] Concentric Graph: Ring 0: [D, E] Ring 1: [C, F, B] Ring 2: [H, A, G] 4. Sample Two public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { ConcentricGraph cGraph = new ConcentricGraph("data/connected_usa.txt"); System.out.println("Distance of each state from New York: "); System.out.println(cGraph.distanceMap ("New York")); System.out.println("distance (New York): " + cGraph.distance("New York")); System.out.println("Graph radius: " +cGraph.radius()); System.out.println("Graph Centers: " + cGraph.getCenters()); System.out.println("Concentric Graph: " + cGraph); // Bonus Credit Distance of each state from New York: {North Carolina=4, Indiana=3, Wyoming=6, Utah=7, Arizona=7, Montana=6, Kentucky-3, Kansas=5, California=8, Delaware=2, Florida=6, Pennsylvania=1, Mississippi-5, Iowa-5, Illinois-4, Texas=6, Connecticut=1, Georgia=5, Maryland=2, Virginia=3, Idaho=7, Vermont=1, Oregon=8, Maine=3, Tennessee-4, Oklahoma=5, Alabama=5, Arkansas=5, South Carolina-5, Washington-8, Nebraska=5, West Virginia=2, Arkanssas-6, Massachusetts=1, Colorado-6, Missouri=4, North Dakota=5, Wisconsin-4, Nevada=8, New York=0, Rhode Island=1, South Dakota=5, Minnesota=4, New Jersey=1, Michigan=3, New Mexico=6, New Hampshire=2, Louisiana=6, Ohio=2} distance (New York): 8 Graph radius: 6 Graph Centers: Concentric Graph:
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


