Question: Solution must be written in Haskell. 4. createLevelTree, listify, isbalanced - 28% Consider the following type for a binary tree that stores values both at
Solution must be written in Haskell.
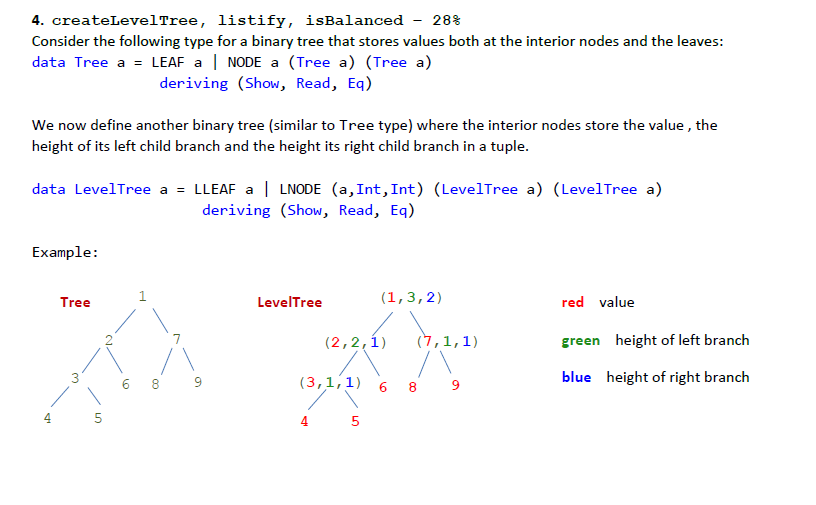



4. createLevelTree, listify, isbalanced - 28% Consider the following type for a binary tree that stores values both at the interior nodes and the leaves: data Tree a = LEAF a | NODE a (Tree a) (Tree a) deriving (Show, Read, Eq) We now define another binary tree (similar to Tree type) where the interior nodes store the value, the height of its left child branch and the height its right child branch in a tuple. data LevelTree a = LLEAF a | LNODE (a, Int, Int) (LevelTree a) (LevelTree a) deriving (Show, Read, Eq) Example: Tree 1 LevelTree (1,3,2) red value (2,2,1) (7,1,1) green height of left branch 3 3 (3,1,1) 6 8 9 blue height of right branch 4 5 (a) createLevelTree - 12% Write a recursive function createLevelTree that takes a Tree value as input and turns it to a LevelTree. The function should calculate the heights of the children branches for each interior node. You can assume that the height of a LEAF is 1. The type of the createLevelTree function should be: createLevelTree :: Tree a -> LevelTree a Examples: treel = NODE "grand-grand-mom" (NODE "grand-mom" (LEAF "aunt") (NODE "mom" (LEAF "me") (LEAF "brother"))) (LEAF "grand-uncle") tree2 = NODE 1 (NODE 2 (NODE 3 (LEAF 4) (LEAF 5)) (LEAF 6)) (NODE 7 (LEAF 8) (LEAF 9)) > createLevelTree tree1 LNODE (1,3,2) (LNODE (2,2,1) (LNODE (3,1,1) (LLEAF 4) (LLEAF 5)) (LLEAF 6)) (LNODE (7,1,1) (LLEAF 8) (LLEAF 9)) > createLevelTree tree2 LNODE ("grand-grand-mom",3,1) (LNODE ("grand- mom",1,2) (LLEAF "aunt") (LNODE ("mom",1,1) (LLEAF "me") (LLEAF "brother"))) (LLE AF "grand-uncle") (b) listify - 68 Write a recursive function listify that takes a levelTree value and turns it into a list of tuples. Your function should traverse the tree in pre-order (i.e., parent, left child, right child). The type of the listify function should be: listify :: LevelTree a -> [(a, Int, Int)] For example: (1,3,2) listify returns : (2,2,1) (7,1,1) [(1,3,2),(2,2,1),(3,1,1),(4,0,0),(5,0,0),(6,0,0), (7,1,1),(8,0,0), (9,0,0)] (3,1,1) 6 8 9 4 5 leveltreel = LNODE ("grand-grand-mom",3,1) (LNODE ("grand- mom",1,2) (LLEAF "aunt") (LNODE ("mom",1,1) (LLEAF "me") (LLEAF "brother"))) (LLE AF "grand-uncle") leveltree2 = LNODE (1,3,2) (LNODE (2,2,1) (LNODE (3,1,1) (LLEAF 4) (LLEAF 5)) (LL EAF 6)) (LNODE (7,1,1) (LLEAF 8) (LLEAF 9)) > listify leveltree1 [("grand-grand-mom",3,1), ("grand-mom",1,2), ("aunt",0,0), ("mom",1,1), ("me",0,0), ("brother",0,0), ("grand-uncle",0,0)] > listify leveltree2 [(1,3,2), (2,2,1),(3,1,1),(4,0,0), (5,0,0), (6,0,0), (7,1,1), (8,0,0), (9,0,0)] (c) isBalanced 10% Write a recursive function isBalanced that takes a LevelTree and returns True if the tree is balance, and returns False otherwise. A LevelTree is balanced if, for every interior node, the difference between the heights of left and right children are at most 1. Assume that an LLEAF node is always balanced. The type of the isBalanced function should be: isBalanced :: LevelTree a -> Bool For example: (1,3,2) isBalanced on the left tree returns True. (2,2,1) (7,1,1) (3,1,1) 6 8 9 4 5 >isBalanced leveltreel False >isBalanced leveltree2 True 4. createLevelTree, listify, isbalanced - 28% Consider the following type for a binary tree that stores values both at the interior nodes and the leaves: data Tree a = LEAF a | NODE a (Tree a) (Tree a) deriving (Show, Read, Eq) We now define another binary tree (similar to Tree type) where the interior nodes store the value, the height of its left child branch and the height its right child branch in a tuple. data LevelTree a = LLEAF a | LNODE (a, Int, Int) (LevelTree a) (LevelTree a) deriving (Show, Read, Eq) Example: Tree 1 LevelTree (1,3,2) red value (2,2,1) (7,1,1) green height of left branch 3 3 (3,1,1) 6 8 9 blue height of right branch 4 5 (a) createLevelTree - 12% Write a recursive function createLevelTree that takes a Tree value as input and turns it to a LevelTree. The function should calculate the heights of the children branches for each interior node. You can assume that the height of a LEAF is 1. The type of the createLevelTree function should be: createLevelTree :: Tree a -> LevelTree a Examples: treel = NODE "grand-grand-mom" (NODE "grand-mom" (LEAF "aunt") (NODE "mom" (LEAF "me") (LEAF "brother"))) (LEAF "grand-uncle") tree2 = NODE 1 (NODE 2 (NODE 3 (LEAF 4) (LEAF 5)) (LEAF 6)) (NODE 7 (LEAF 8) (LEAF 9)) > createLevelTree tree1 LNODE (1,3,2) (LNODE (2,2,1) (LNODE (3,1,1) (LLEAF 4) (LLEAF 5)) (LLEAF 6)) (LNODE (7,1,1) (LLEAF 8) (LLEAF 9)) > createLevelTree tree2 LNODE ("grand-grand-mom",3,1) (LNODE ("grand- mom",1,2) (LLEAF "aunt") (LNODE ("mom",1,1) (LLEAF "me") (LLEAF "brother"))) (LLE AF "grand-uncle") (b) listify - 68 Write a recursive function listify that takes a levelTree value and turns it into a list of tuples. Your function should traverse the tree in pre-order (i.e., parent, left child, right child). The type of the listify function should be: listify :: LevelTree a -> [(a, Int, Int)] For example: (1,3,2) listify returns : (2,2,1) (7,1,1) [(1,3,2),(2,2,1),(3,1,1),(4,0,0),(5,0,0),(6,0,0), (7,1,1),(8,0,0), (9,0,0)] (3,1,1) 6 8 9 4 5 leveltreel = LNODE ("grand-grand-mom",3,1) (LNODE ("grand- mom",1,2) (LLEAF "aunt") (LNODE ("mom",1,1) (LLEAF "me") (LLEAF "brother"))) (LLE AF "grand-uncle") leveltree2 = LNODE (1,3,2) (LNODE (2,2,1) (LNODE (3,1,1) (LLEAF 4) (LLEAF 5)) (LL EAF 6)) (LNODE (7,1,1) (LLEAF 8) (LLEAF 9)) > listify leveltree1 [("grand-grand-mom",3,1), ("grand-mom",1,2), ("aunt",0,0), ("mom",1,1), ("me",0,0), ("brother",0,0), ("grand-uncle",0,0)] > listify leveltree2 [(1,3,2), (2,2,1),(3,1,1),(4,0,0), (5,0,0), (6,0,0), (7,1,1), (8,0,0), (9,0,0)] (c) isBalanced 10% Write a recursive function isBalanced that takes a LevelTree and returns True if the tree is balance, and returns False otherwise. A LevelTree is balanced if, for every interior node, the difference between the heights of left and right children are at most 1. Assume that an LLEAF node is always balanced. The type of the isBalanced function should be: isBalanced :: LevelTree a -> Bool For example: (1,3,2) isBalanced on the left tree returns True. (2,2,1) (7,1,1) (3,1,1) 6 8 9 4 5 >isBalanced leveltreel False >isBalanced leveltree2 True
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


