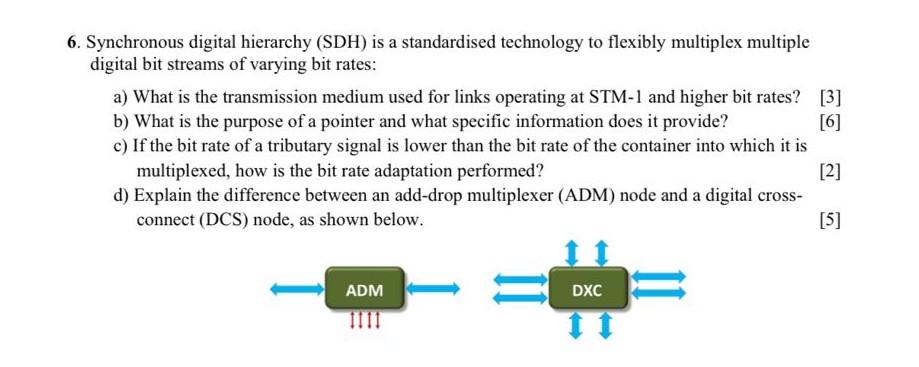
Question: solve C and D part 6. Synchronous digital hierarchy (SDH) is a standardised technology to flexibly multiplex multiple digital bit streams of varying bit rates:
solve C and D part
6. Synchronous digital hierarchy (SDH) is a standardised technology to flexibly multiplex multiple digital bit streams of varying bit rates: a) What is the transmission medium used for links operating at STM-1 and higher bit rates? [3] b) What is the purpose of a pointer and what specific information does it provide? [6] c) If the bit rate of a tributary signal is lower than the bit rate of the container into which it is multiplexed, how is the bit rate adaptation performed? [2] d) Explain the difference between an add-drop multiplexer (ADM) node and a digital cross- connect (DCS) node, as shown below. [5] ADM DXC =
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


