Question: solve for table 3.2 with the given data. you do not need to solve from assay 1 to 6, but at least show how you
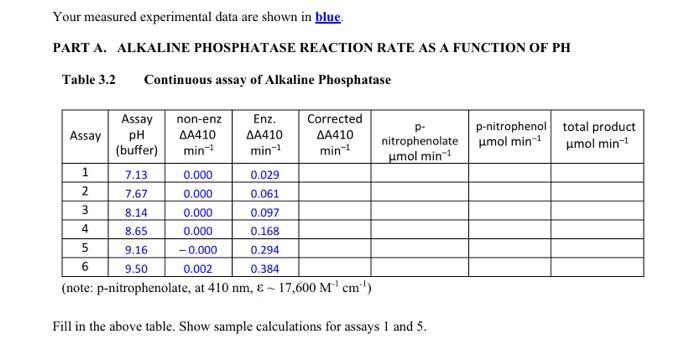
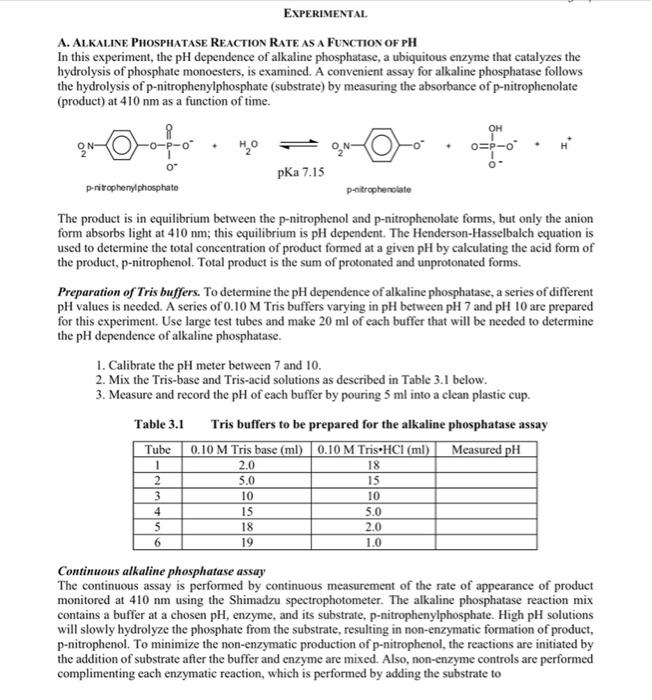

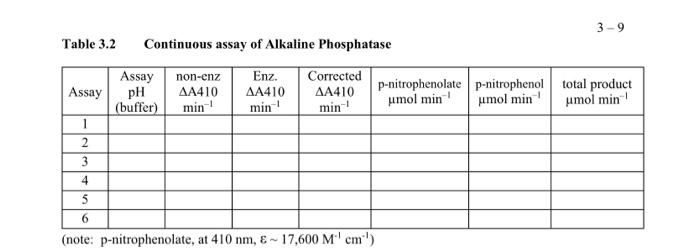
Your measured experimental data are shown in blue PART A. ALKALINE PHOSPHATASE REACTION RATE AS A FUNCTION OF PH Table 3.2 Continuous assay of Alkaline Phosphatase nitrophenolate umol min-1 p-nitrophenol total product umol min-1 umol min-1 Assay non-enz Enz. Corrected Assay pH 410 410 410 (buffer) min-1 min-1 min-1 1 7.13 0.000 0.029 2 7.67 0.000 0.061 3 8.14 0.000 0.097 4 8.69 0.000 0.168 5 9.16 -0.000 0.294 6 9.50 0.002 0.384 (note: p-nitrophenolate, at 410 nm, & - 17,600 M'cm') Fill in the above table. Show sample calculations for assays 1 and 5. 0 EXPERIMENTAL A. ALKALINE PHOSPHATASE REACTION RATE AS A FUNCTION OF PH In this experiment, the pH dependence of alkaline phosphatase, a ubiquitous enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of phosphate monoesters, is examined. A convenient assay for alkaline phosphatase follows the hydrolysis of p-nitrophenylphosphate (substrate) by measuring the absorbance of p-nitrophenolate (product) at 410 nm as a function of time. o=p-o pka 7.15 D-ritrophenylphosphate pritrophenolate The product is in equilibrium between the p-nitrophenol and p-nitrophenolate forms, but only the anion form absorbs light at 410 nm; this equilibrium is pH dependent. The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation is used to determine the total concentration of product formed at a given pH by calculating the acid form of the product, p-nitrophenol. Total product is the sum of protonated and unprotonated forms. Preparation of Tris buffers. To determine the pH dependence of alkaline phosphatase, a series of different pH values is needed. A series of 0.10 M Tris buffers varying in pH between pH 7 and pH 10 are prepared As for this experiment. Use large test tubes and make 20 ml of each buffer that will be needed to determine the pH dependence of alkaline phosphatase. 1. Calibrate the pH meter between 7 and 10. 2. Mix the Tris-base and Tris-acid solutions as described in Table 3.1 below. 3. Measure and record the pH of each buffer by pouring 5 ml into a clean plastic cup. Table 3.1 Tris buffers to be prepared for the alkaline phosphatase assay Tube 0.10 M Tris base (ml) 0.10 M Tris.HCI (ml) Measured pH 2.0 5.0 10 15 18 19 1 2 3 4 5 6 18 15 10 5.0 2.0 1.0 Continuous alkaline phosphatase assay The continuous assay is performed by continuous measurement of the rate of appearance of product monitored at 410 nm using the Shimadzu spectrophotometer. The alkaline phosphatase reaction mix contains a buffer at a chosen pH, enzyme, and its substrate, p-nitrophenylphosphate. High pH solutions will slowly hydrolyze the phosphate from the substrate, resulting in non-enzymatic formation of product, p-nitrophenol. To minimize the non-enzymatic production of p-nitrophenol, the reactions are initiated by the addition of substrate after the buffer and enzyme are mixed. Also, non-enzyme controls are performed complimenting each enzymatic reaction, which is performed by adding the substrate to only buffer and monitoring the "rate" as with the enzyme catalyzed reactions. The six enzyme-catalyzed reactions and the six non-enzyme control reactions are to be recorded for 1 minute each. 1. Obtain 500 ul of 0.125 mg/ml alkaline phosphatase enzyme: keep this stock sample on ice. Also, obtain 3 ml of 10 mM p-nitrophenylphosphate; keep this stock at room temperature. 2. The concentrations of the alkaline phosphatase reaction mixture in a I ml final volume are: 0.075 M buffer and 2.0 mM p-nitrophenylphosphate 50 ul of alkaline phosphatase (alkaline phosphatase stock concentration is 0.125 mg/ml) the reaction is started by adding the appropriate volume of 10 mM p-nitrophenylphosphate Calculate the volume of the buffer required per 1 ml continuous assay volume: Calculate the volume of the substrate required per 1 ml continuous assay volume: 3. Set parameters for kineties on the spectrophotometer as follows: Select: #4. Kinetics, from the Mode Menu screen. Select: #2. Kinetic rate, from the Kinetics screen. 1.2. - 410 nm 2. Measured time: 60 sec: Cycle: 0.1 sec; and Interval: 10 sec 3. Rec range: 0.000 A - 1.500 A 4. Time scale: sec 5. Discriminator: 10% (default, leave alone) 4. Obtain two 1.5 ml plastic cuvettes. Auto-zero with H2O, then discard the H2O in the sample cuvette, 5. Just prior to performing the assay, (a) Turn the printer ON. (b) Transfer the appropriate volume of the 0.1 M Tris buffer to the sample cuvette; then add 50 ml of alkaline phosphatase, mix gently. 6. The reaction is started by adding the appropriate volume of the 10 mM p-nitrophenylphosphate to the cuvette. Immediately and quickly mix by inverting the cuvette (covered with Parafilm) only once, and insert it into the spectrophotometer and press: Start. The spectrophotometer will record the reaction in real time every 10 seconds and print out: Time (sec), Abs, and AAbs 7. When the run is finished, select the F2 key to see the kinetic curve. Press the print key to Print the curve. 8. When the printing is finished, select the Return key. The machine is ready to run another sample. 9. For proper controls, all six reactions are repeated as above in the absence of enzyme. Mix 800 ul of buffer and 200 ul substrate in the sample cuvette, quickly insert it into the spectrophotometer and press: Start. Any observed rate of absorbance is must be subtracted from the observed enzymatic derived rate of absorbance obtained above, which is the corrected rate. 10. Keep all raw data generated from the spectrophotometer, and record pertinent data in Table 3.2. For valid reactions (ie linear rates): calculate the AAbs min': Abs at 60 sec - Abs 0.0 sec. 3-9 Table 3.2 Continuous assay of Alkaline Phosphatase Enz. Assay Assay pH (buffer) non-enz AA410 min' AA410 min' Corrected AA410 min' p-nitrophenolate p-nitrophenol total product umol min' umol min' umol min 1 2 3 4 5 6 (note: p-nitrophenolate, at 410 nm, & - 17,600 Mem')
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


