Question: Solve (Question 1) ONLY.. which is ((Developing a plan (i.e. a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) to guide the contractor on the assembly of the various
Solve (Question 1) ONLY.. which is ((Developing a plan (i.e. a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) to guide the contractor on the assembly of the various construction elements to realize the project.))

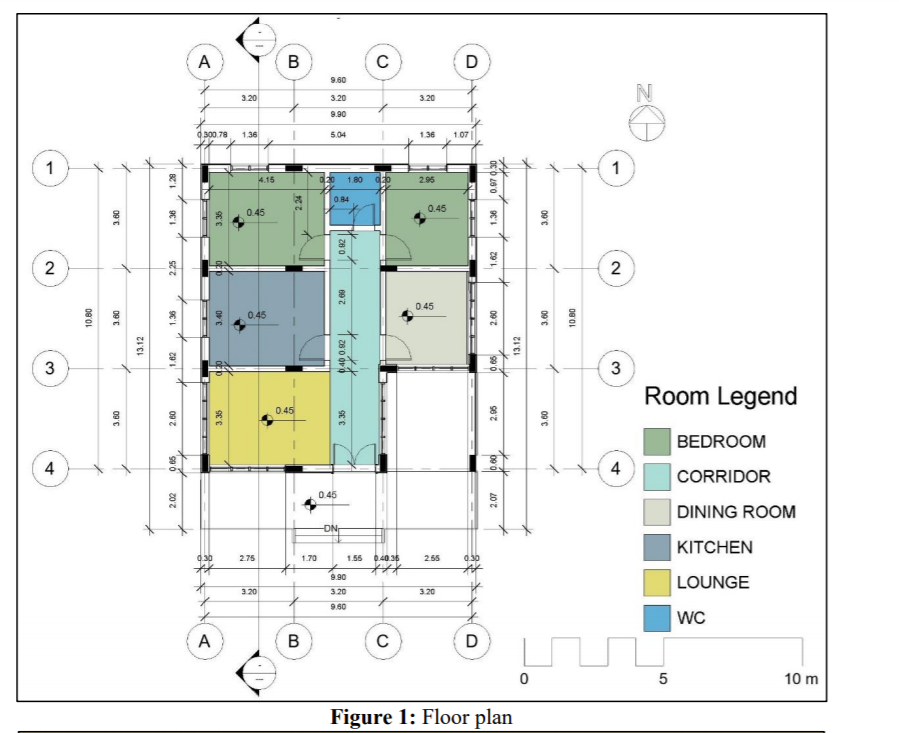
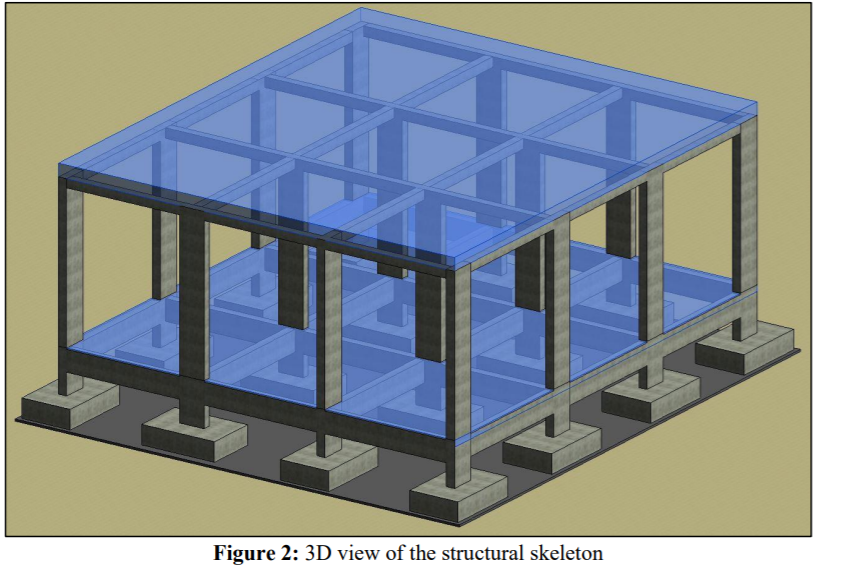
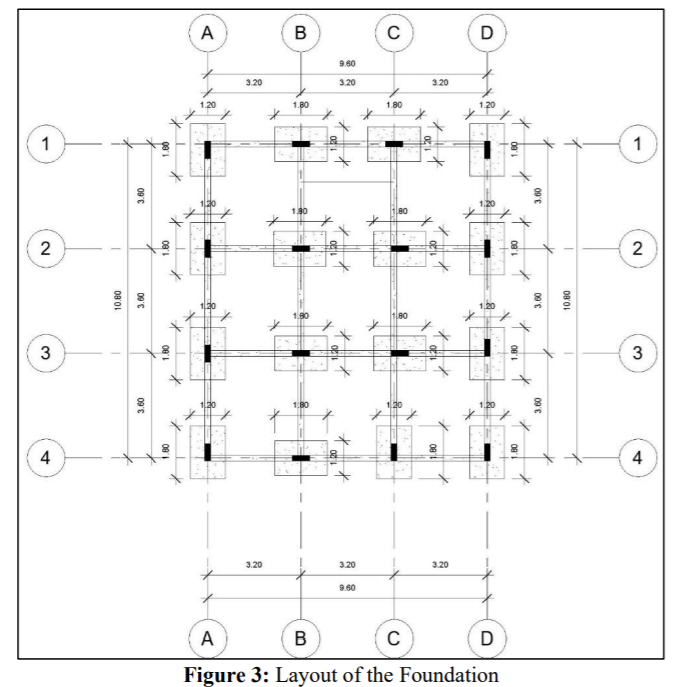
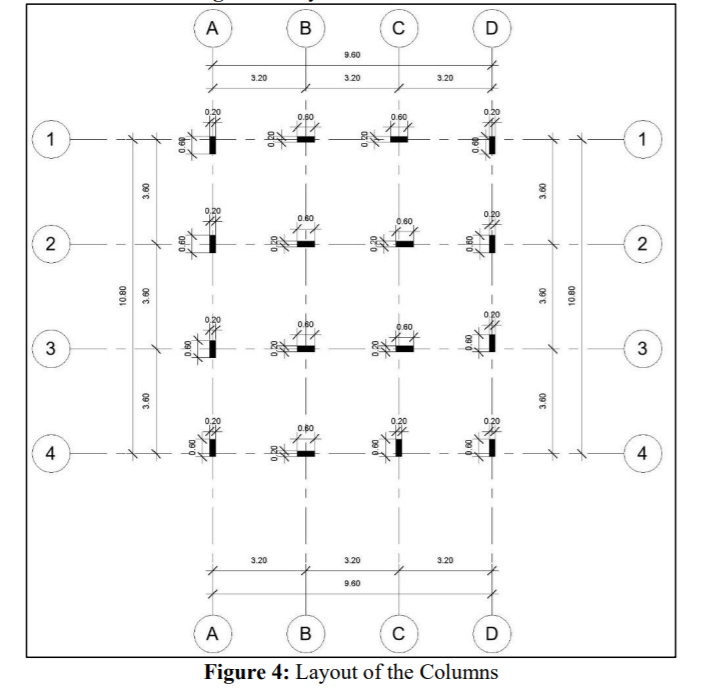
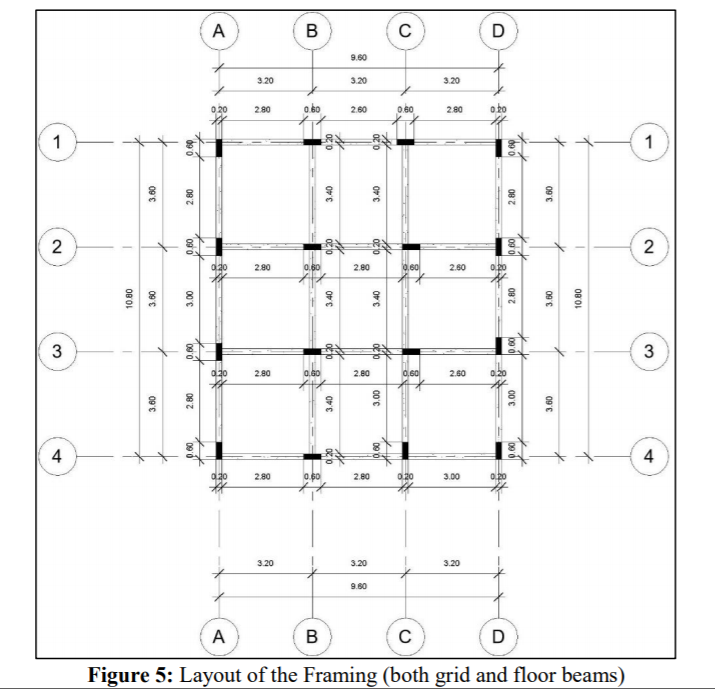
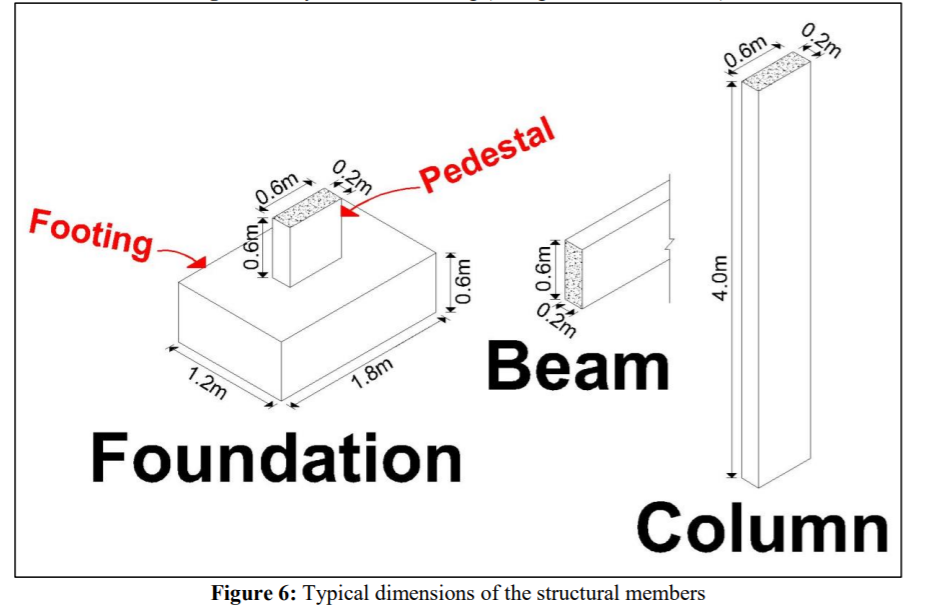
Building construction is a process that requires: 1. Developing a plan (i.e. a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) to guide the contractor on the assembly of the various construction elements to realize the project. 2. Developing a schedule of the construction activities, based on the identified elements of the WBS. Given the illustrated one-storey building (9.6m X 10.8m), the owner wants to construct its structural skeleton, within a period that does not exceed 3 months, and a budget that does not exceed SR 40,000. You are requested to: Develop an initial cost estimate for the construction of the structural skeleton. Develop a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) for the structural skeleton. Based on the developed WBS, identify the activities (with their individual durations, sequencing logie, and cost estimates) that need to be scheduled to construct this structure. Based on the developed list of activities, develop a network diagram to determine the critical path and the total duration of the project. Assumptions: 1. The unit price for the cubic meter of reinforced-concrete ranges between SR 250 - SR 300 (this includes the material, labor, equipment (including machines and formwork] and the contractor's fee). 2. The excavation cost will range between SR3,000 to SR4,000. 3. The typical dimensions of the structural members are as follows: Foundation: Footing - 1.8m 1.2m x 0.6m o Pedestal = 0.6m x 0.2m x 0.6m Beams' cross section = 0.2m x 0.6m Columns - 0.6m 0.2m x 4.0m Slab depth = 0.25m Plain concrete depth = 0.05m 4. Assume close durations to the ones provide to you in the example. 5. Assume any other missing information you may need. D B D 9.60 N 3.20 3.20 3.20 9.90 0 300.78 1.36 5.04 1.36 107 1 1 23 4.15 1.80 2.95 c 200 0.84 0.45 3.60 0.45 1.36 1.36 09 ZBO 1.62 2 $ N 2.69 0.45 10.80 OP 095 3 0.45 09Z 09 10.00 13.12 28000 .62 13.12 3 0.66 de 3 Room Legend 0.45 3.60 2.60 3.35 982 3.60 4 0.65 10.60 4 0.45 2.02 2.07 BEDROOM CORRIDOR DINING ROOM KITCHEN LOUNGE 2.75 1.70 1.55 0.40.36 2.55 9.90 3.20 3.20 3.20 9.60 WC A B B D 0 5 01 10 m Figure 1: Floor plan Figure 2: 3D view of the structural skeleton D B B D 9.60 3.20 3.20 3.20 0.60 0.60 1 1 3.60 3.00 0.80 0.20 2 0.60 0,20 100 - 2 1 10.80 3.60 09 10.80 020 3 o'o 3 3.60 3.60 0.20 0.60 4 4 3.20 3.20 3.20 9.60 A B D Figure 4: Layout of the Columns A B D 9.60 3.20 3.20 3.20 2.80 0.60 2.60 0.60 2.80 o ko 1 0.20 0.20 1 3.60 2.80 3.40 3.40 2.80 3.60 2 0.60 020 0120 0.60 2 010 2.80 2.80 2.60 0.20 10.80 3.60 00 3.40 3.40 2.80 3.60 10.80 3 000 0410 020 0.60 3 2.80 0.60 2.80 0,60 2.60 0.20 3.60 2.80 3.40 3.00 3.00 3.60 4 090 020 4 2.80 2.80 0.20 3.00 3.20 3.20 3.20 9.80 A B B D Figure 5: Layout of the Framing (both grid and floor beams) 0.2m 0.6m 0.2m 1.6m Pedestal Footing *ugo" 0.6m 40.6m, 4.Om 0.2m 1.2m 1.8m Beam Foundation Column Figure 6: Typical dimensions of the structural members










