Question: Solve questions 1-4 without using excel. I just need to know if the numbers i produced in excel were correct for said problems. I provided

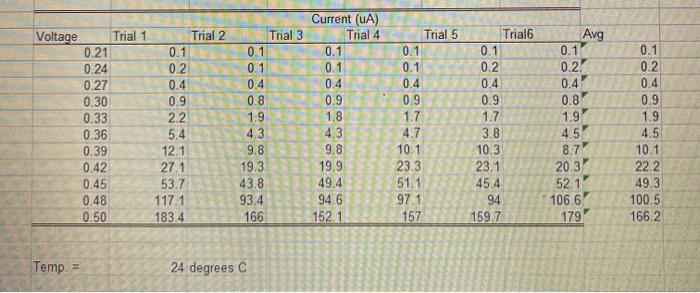

1. 2. Using Excel, calculate your best-estimate for the diode current at each voltage setting, along with its uncertainty (the SDOM). Use Excel to plot values of In(1) vs. V. Find the best fit straight line slope and y-intercept. Do this two ways using Excel: (1) have Excel display the equation of its linear trendline, and (2) use the Linest function as an array function" to calculate and display the values and uncertainties for the slope and y-intercept To use the Linest function in an array: Use the mouse to select a convenient 2x2 set of cells in your worksheet Type the following: -Linest(known y-values, known x-values, true, true) To enter this as an array function" use CTRL-SHIFT-ENTER Four numbers will be displayed in your 2x2 array: best-fit slope best-fit intercept slope S.D. intercept S.D. Compare your calculated values with those returned by Excel. From the slope and its uncertainty, determine the value ku for your graph. Use these to determine your best estimate of the value and uncertainty of ku, and compare your value with the accepted value. From the y-intercept value and its uncertainty, determine the value and uncertainty of the leakage eur- rent for the diode 3. 0.1 0.2 0.4 0.9 Current (UA) Trial 3 Trial 4 0.1 0.1 0.1 0.1 0.4 0.4 0.8 0.9 1.9 1.8 4.3 4.3 9.8 9.8 19.3 19.9 43.8 49.4 93.4 94.6 166 152.1 Voltage Trial 1 Trial 2 0.21 0.1 0.24 0.2 0.27 0.4 0.30 0.9 0.33 2.2 0.36 5.4 0.39 12.1 0.42 27.1 0.45 53.7 0.48 117.1 0.50 183.4 1.9 Trial 5 0.1 0.1 0.4 0.9 1.7 4.7 10.1 23.3 51.1 97.1 157 Avg 0.1 0.21 0.4 0.8 1.9 4.5 8.7 Trial 0.1 0.2 0.4 0.9 1.7 3.8 10.3 23.1 45.4 94 159.7 20.3 4.5 10.1 22.2 49.3 100.5 166.2 52.1 106,6 179 Temp. = 24 degrees C which create an excess or deficiency of charge carriers. These semiconductors are called p-type (where excess positive charges are present), or n-type (where excess negative charges are present). A diode consists of a pn- junction, where p-type and n-type materials are placed next to each other. At the boundary, there is a tendency of electrons to move to the p-side, and positive charges to move to the n-side. When enough charges have moved, a barrier is formed which prevents additional charges from changing side. To overcome this potential barrier, a voltage Vo is required. If a battery with a voltage of Vis connected to the diode, the probability an elec- tron will have enough energy to cross the barrier is proportional to: exp(-e(Vo-V)/(kgT)) In this case, the barrier is reduced an electrons can flow freely, and the diode is said to be forward biased. If a potential is applied in the opposite direction, the barrier would be increase, and no current could flow. The diode would be reverse biased in this case. For the forward biased condition, the current through the diode is given by: eV exp .)-1) Tere la represents the leakage current of the diode, e is the charge of an electron, Tis the temperature, V is the oltage across the diode, and ka is Boltzmann's constant. In this situation, the exponential term will be much arger than 1, and so we can safely neglect that in the above equation. If we then take the log of both sides, we et: In(1)=In(1.)+e_v k T 1. 2. Using Excel, calculate your best-estimate for the diode current at each voltage setting, along with its uncertainty (the SDOM). Use Excel to plot values of In(1) vs. V. Find the best fit straight line slope and y-intercept. Do this two ways using Excel: (1) have Excel display the equation of its linear trendline, and (2) use the Linest function as an array function" to calculate and display the values and uncertainties for the slope and y-intercept To use the Linest function in an array: Use the mouse to select a convenient 2x2 set of cells in your worksheet Type the following: -Linest(known y-values, known x-values, true, true) To enter this as an array function" use CTRL-SHIFT-ENTER Four numbers will be displayed in your 2x2 array: best-fit slope best-fit intercept slope S.D. intercept S.D. Compare your calculated values with those returned by Excel. From the slope and its uncertainty, determine the value ku for your graph. Use these to determine your best estimate of the value and uncertainty of ku, and compare your value with the accepted value. From the y-intercept value and its uncertainty, determine the value and uncertainty of the leakage eur- rent for the diode 3. 0.1 0.2 0.4 0.9 Current (UA) Trial 3 Trial 4 0.1 0.1 0.1 0.1 0.4 0.4 0.8 0.9 1.9 1.8 4.3 4.3 9.8 9.8 19.3 19.9 43.8 49.4 93.4 94.6 166 152.1 Voltage Trial 1 Trial 2 0.21 0.1 0.24 0.2 0.27 0.4 0.30 0.9 0.33 2.2 0.36 5.4 0.39 12.1 0.42 27.1 0.45 53.7 0.48 117.1 0.50 183.4 1.9 Trial 5 0.1 0.1 0.4 0.9 1.7 4.7 10.1 23.3 51.1 97.1 157 Avg 0.1 0.21 0.4 0.8 1.9 4.5 8.7 Trial 0.1 0.2 0.4 0.9 1.7 3.8 10.3 23.1 45.4 94 159.7 20.3 4.5 10.1 22.2 49.3 100.5 166.2 52.1 106,6 179 Temp. = 24 degrees C which create an excess or deficiency of charge carriers. These semiconductors are called p-type (where excess positive charges are present), or n-type (where excess negative charges are present). A diode consists of a pn- junction, where p-type and n-type materials are placed next to each other. At the boundary, there is a tendency of electrons to move to the p-side, and positive charges to move to the n-side. When enough charges have moved, a barrier is formed which prevents additional charges from changing side. To overcome this potential barrier, a voltage Vo is required. If a battery with a voltage of Vis connected to the diode, the probability an elec- tron will have enough energy to cross the barrier is proportional to: exp(-e(Vo-V)/(kgT)) In this case, the barrier is reduced an electrons can flow freely, and the diode is said to be forward biased. If a potential is applied in the opposite direction, the barrier would be increase, and no current could flow. The diode would be reverse biased in this case. For the forward biased condition, the current through the diode is given by: eV exp .)-1) Tere la represents the leakage current of the diode, e is the charge of an electron, Tis the temperature, V is the oltage across the diode, and ka is Boltzmann's constant. In this situation, the exponential term will be much arger than 1, and so we can safely neglect that in the above equation. If we then take the log of both sides, we et: In(1)=In(1.)+e_v k T
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


