Question: Solve the following questions 9. Use this aggregate demandaggregate supply schedule for a hypothetical economy to answer the following questions. Real domestic Real domestic output
Solve the following questions
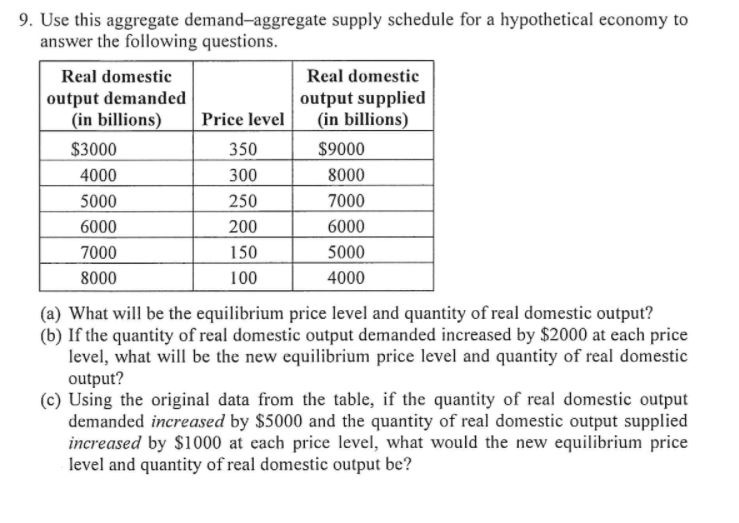



9. Use this aggregate demandaggregate supply schedule for a hypothetical economy to answer the following questions. Real domestic Real domestic output demanded output supplied (in billions Price level (in billions) $3000 350 $9000 4000 000 T000 0000 00 '3'000 3000 00 {a} What will be the equilibrium price level and quantity of real domestic output? {b} If the quantity of real domestic output demanded increased by $2000 at each price level, what will be the new equilibrium price level and quantity of real domestic output? (c) Using the original data from the table, if the quantity of real domestic output demanded increased by $5000 and the quantity of real domestic output supplied increased by $l000 at each price level, what would the new equilibrium price level and quantity of real domestic output be? 2. There are two types of residents in Long Island City (LIC), those who own a pet and those who do not. Long Island City is proposing to add a new public park in town. The benefit (inverse demand) of a new park to pet owners is given by P = 10 -Q where Q is number of square miles of the new park. The benefit to non-pet owners is P = 10-2Q. Assume that there are 1,000 of each type of resident. (a) What is the total benefit to LIC residents for a new park that is 2 square miles? (b) If the cost of adding a new park in terms of square miles is C(Q) = 10000" + 2000, what size of park would maximize social surplus? (e) If LIC funded the park by donations from their residents, would you expect the size of the park financed by the donations to be smaller or larger than optimal park size found in part (b)? Explain.my is described... SmartSite@UCDavis : EC... https:/smartsite.ucdavis... Suppose that velocity of money is constant, the growth rate of money is 5 percent per year (9M = 0.05), and the long-run real interest rate is 2 percent (r = 0.02). Using the Solow-Romer model for output growth, the quantity theory of money for inflation (the growth rate of prices), and the Fisher effect for the relationship between nominal and real interest rates, answer each of the following questions below: A. (1 point) What is the growth rate of real GDP in this economy along the balanced growth path in the baseline case described above? B. (1 point) What is the rate of inflation in the baseline case described above? C. (1 point) What is the nominal interest rate in the baseline case described above? D. (3 points) Suppose the growth rate of money rises to 10 percent per year, what specifically happens to inflation and nominal interest rates? Does the classical dichotomy hold in this case? Briefly explain Inflation (4 points) There are two quotes in Chapter 8:3. Consider an open economy characterized by the following equations C = co + cl 1: (Y T) I'M = le X = x1!" where m1 and x1 are propensities to import and export. Assume that the real exchange rate is xed at a value of 1 and treat foreign income Y* as xed. Note that in this example imports and exports do not depend on the real exchange rate like we saw in class. This is because in the case we are assuming it is equal to 1. Also assume that investment (I) and taxes (T) are xed and that government purchases (G) are exogenous (i.e., decided by the government). We explore the effectiveness of changes in G under alternative assumptions about the propensity to import. a) What should the sign of m1 and 11 be to be consistent with the behavior of the import IZM(Y) and export X(Y*) functions we saw in class? b) Using the fact that Y=C+I+G+NX solve for Y. c) Suppose government purchases increase by one unit. What is the effect on output? d) How do net exports change when government purchases increase by one unit? Now consider two economies, one with m1 = 0.5 and the other one with m1 = 0.1. Both economies have c1 = 0.6. e) Calculate your answers to parts (0) and (d) for each economy by substituting the appropriate parameter values. 1) In which economy will scal policy have a larger effect on output? In which economy will scal policy have a larger effect on net exports
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


