Question: Solve the initial value problem y + 8y + 16y = 0, y(-1) = 2, y' ( -1) = 2. y(t) = : 12e-4(2+1) +
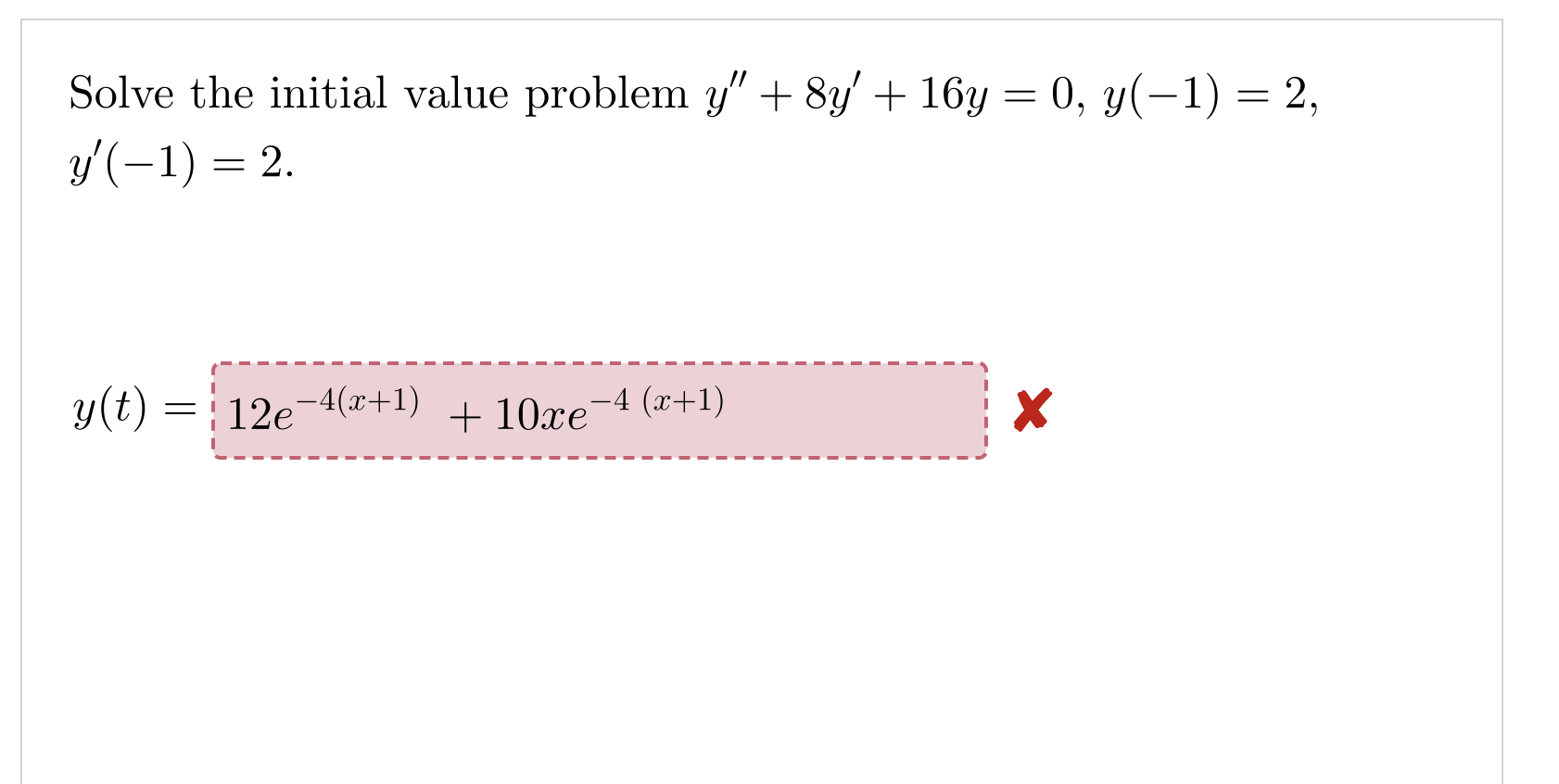

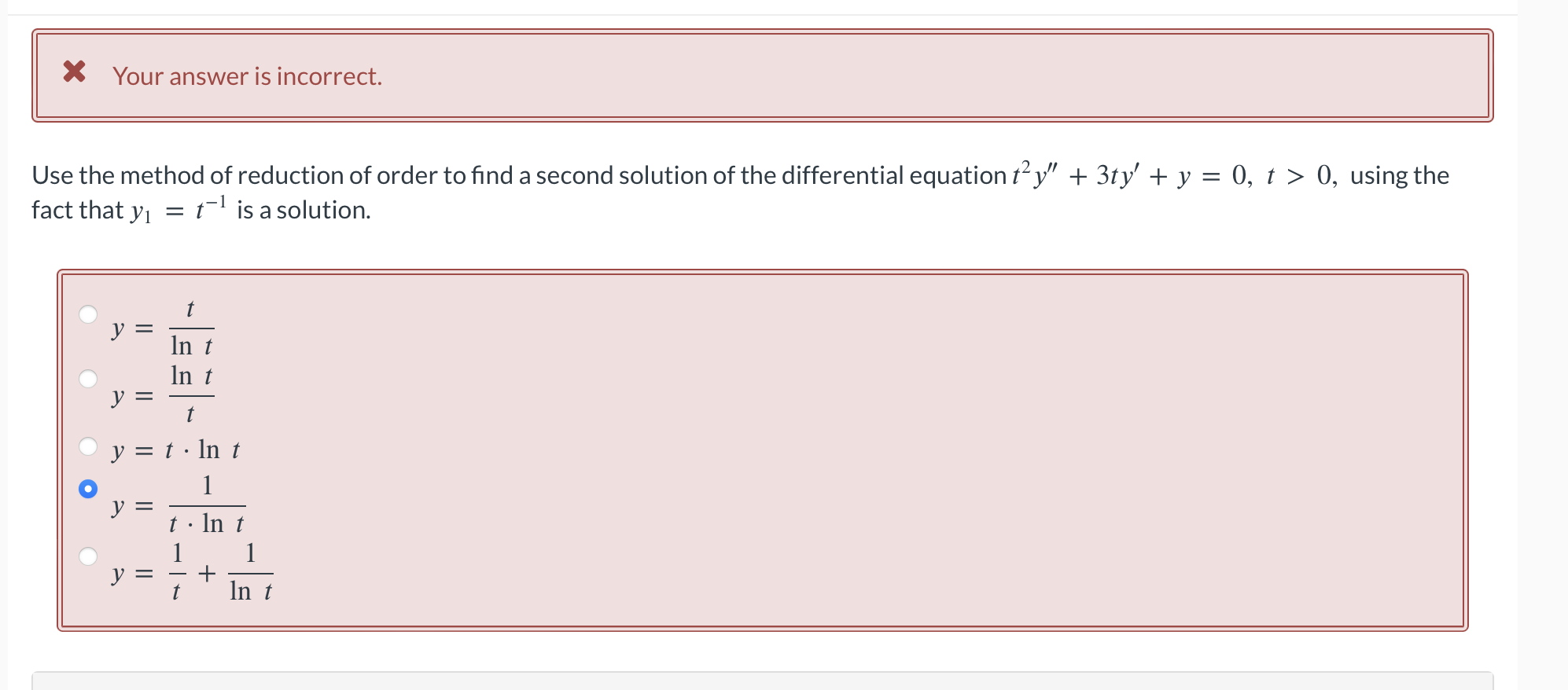
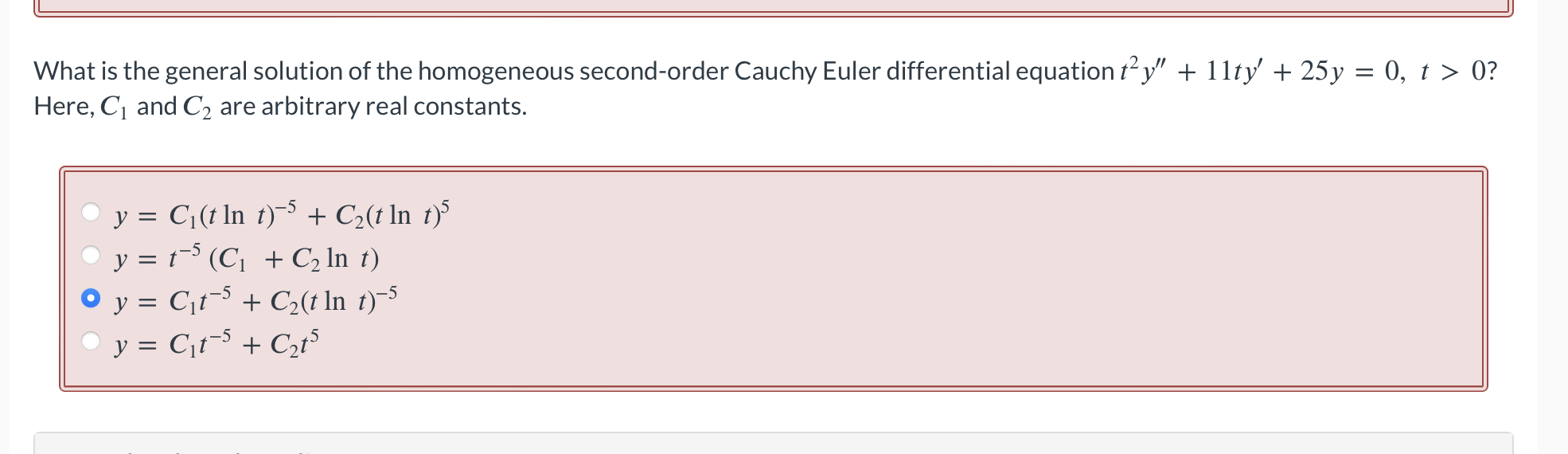
Solve the initial value problem y" + 8y + 16y = 0, y(-1) = 2, y' ( -1) = 2. y(t) = : 12e-4(2+1) + 10re -4 (x+1) XUse the method of reduction of order to find a second solution of the differential equation thy" + 18ty' + 16y =0, t> 0; yi(t) =t-1 NOTE: Use t as the independent variable. Do not use arbitrary constants. y2 (t) =X Your answer is incorrect. Use the method of reduction of order to find a second solution of the differential equation ty" + 3ty' + y = 0, t > 0, using the fact that y1 = tis a solution. V = In t In t t Oy= t . Int O V = t . In t 1 y + t In tWhat is the general solution of the homogeneous second-order Cauchy Euler differential equation ty" + 1lty' + 25y = 0, t > 0? Here, C1 and C2 are arbitrary real constants. O y = Ci(t In t)-5 + C2(t In t)5 Oy = t's (C1 + C2 In t) O y = Cit-5 + C2(t In t)-5 O y = Cit-5 + Cats
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


