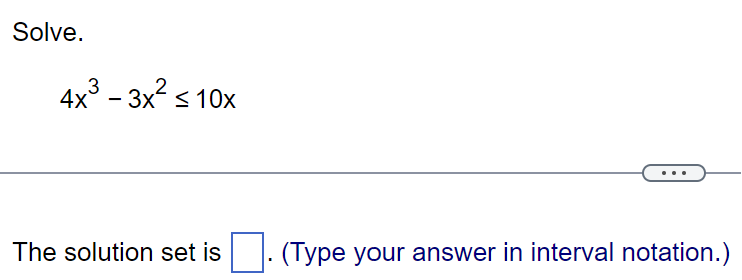
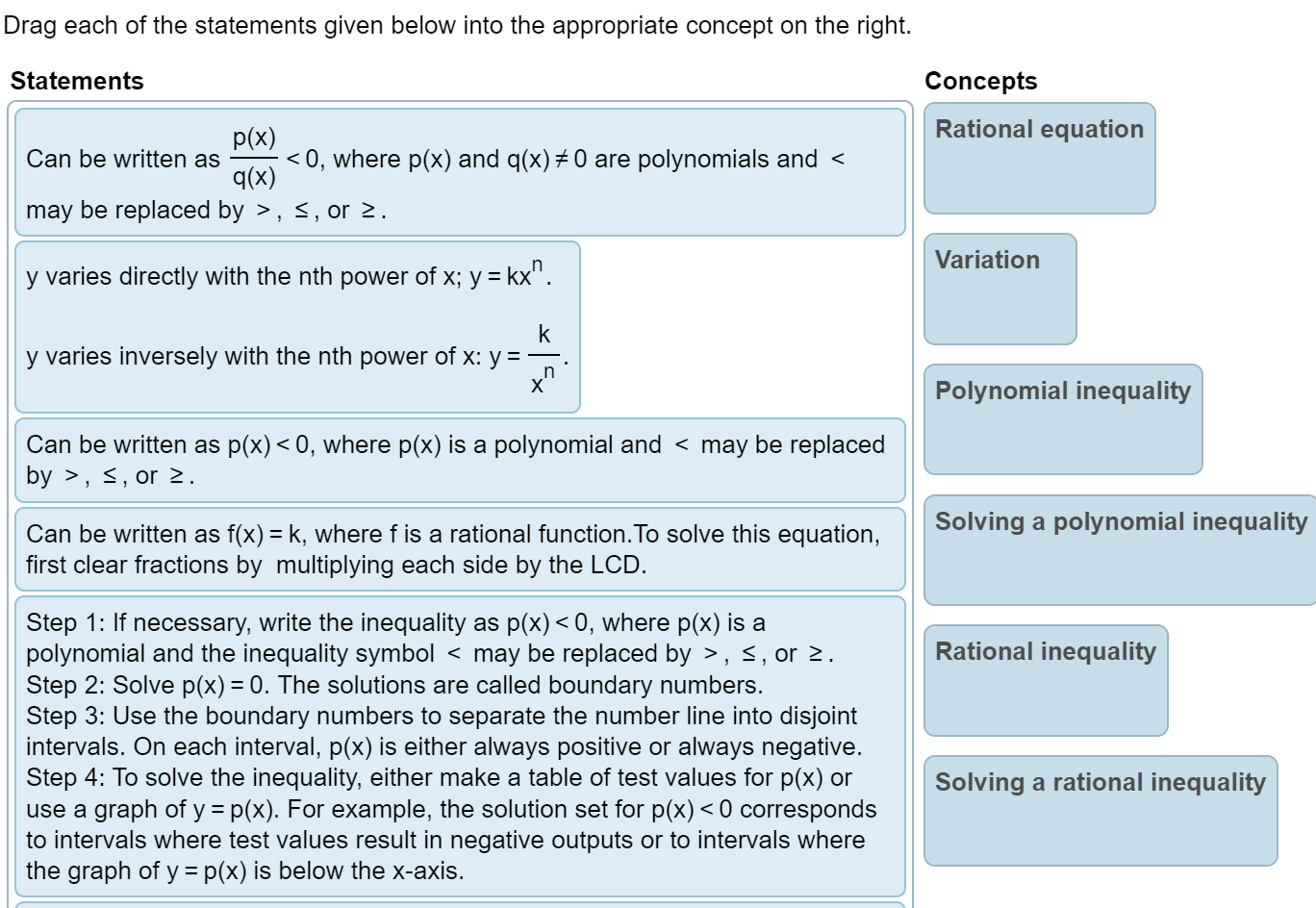
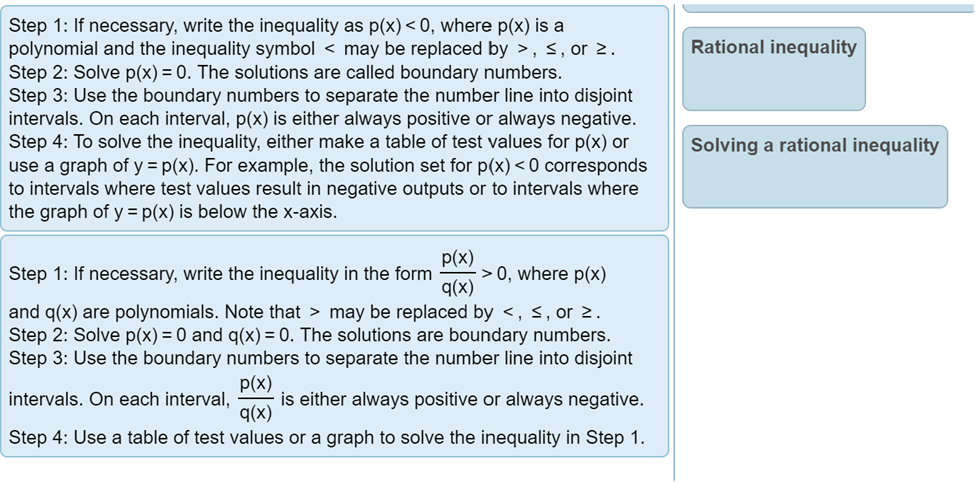
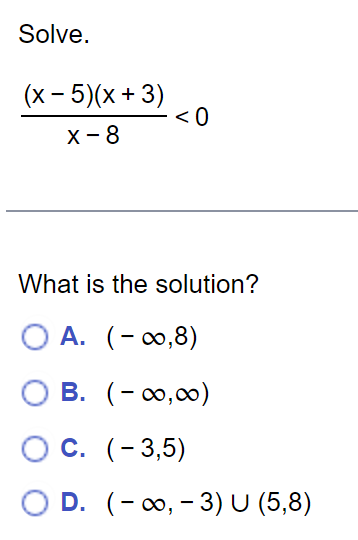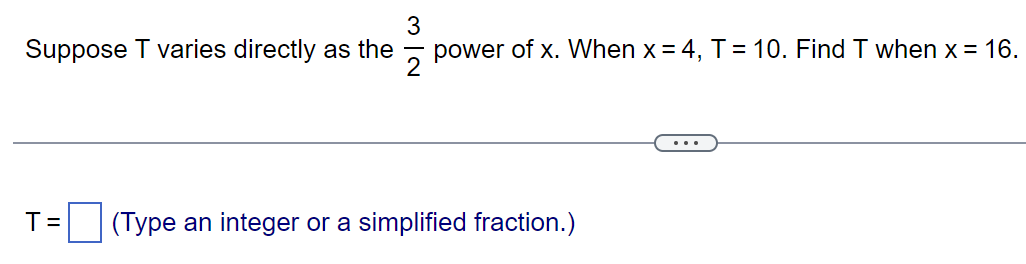Question: Solve the polynomial inequality symbolically. x39x20 The solution is E. (Type your answer in interval notation.) Solve. 4x3 3x2 s 10x E) The solution set
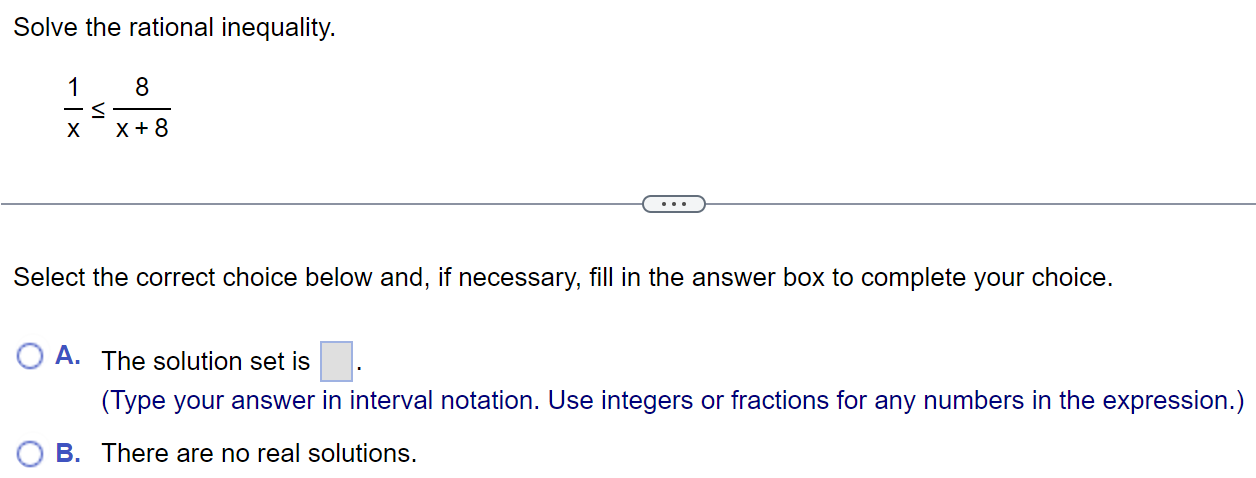
Solve the polynomial inequality symbolically. x39x20 The solution is E. (Type your answer in interval notation.) Solve. 4x3 3x2 s 10x E) The solution set is E. (Type your answer in interval notation.) Solve the rational inequality. ( x + 2)2 SO x - 5 . . . Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer box to complete your choice. O A. The solution set is (Type your answer in interval notation.) O B. There are no real solutions.Solve the polynomial inequality. (x - 8)(X - 9)(X - 10) 20 Choose the correct solution below. O A. (- 00,8)U(10,00) O B. (8,9) OC. O O D. [8,9][10,00)Find the constant of proportionality k. K y= -, and y = 5 when x = 3 X K = (Type an integer or a simplified fraction.)Solve the rational inequality (a) symbolically and (b) graphically. (a) The solution set is E. (Type your answer in interval notation.) Solve. (x - 5)(x + 3) T : E (Type an integer or a simplified fraction.) Complete parts (a) through (c). (a) Identify where f(x) is undefined or f(x) = 0. (b) Solve f(x) > 0. (c) Solve f(x) , s, or 2. . . . n Variation y varies directly With the nth power of x; y = kx . k y varies inversely with the nth power of x: y = n. X Polynomial inequality Can be written as p(x) , s, or 2. Can be written as f(x) = k, where f is a rational function.To solve this equation, Solving a polynomial inequality first clear fractions by multiplying each side by the LCD. Step 1: If necessary, write the inequality as p(x) , s, or 2. Rational inequality Step 2: Solve p(x) =0. The solutions are called boundary numbers. Step 3: Use the boundary numbers to separate the number line into disjoint intervals. On each interval, p(x) is either always positive or always negative. Step 4: To solve the inequality. either make a table of test values for p(x) or Solving a rational inequality use a graph of y = p(x). For example, the solution set for p(x) , S,or 2. Step 2: Solve p(x) = 0. The solutions are called boundary numbers. Step 3: Use the boundary numbers to separate the number line into disjoint intervals. On each interval, p(x) is either always positive or always negative. Step 4: To solve the inequality, either make a table of test values for p(x) or use a graph of y = p(x). For example, the solution set for p(x) 0, where p{x} (400 and q(x) are polynomials. Note that > may be replaced by