Question: solve these problems Consider a small ferry that can accommodate cars and buses. The toll for cars is $3, and the toll for buses is
solve these problems
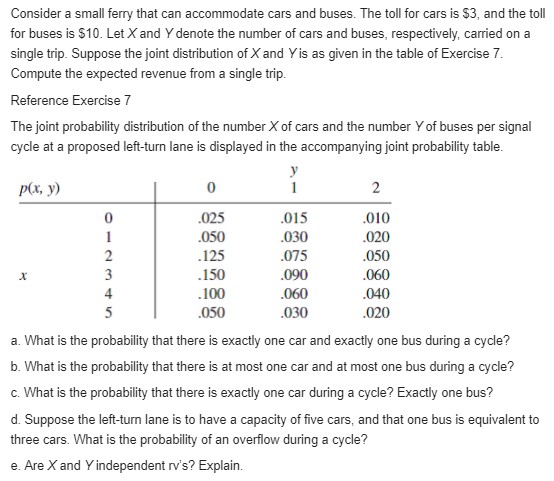






Consider a small ferry that can accommodate cars and buses. The toll for cars is $3, and the toll for buses is $10. Let X and Y denote the number of cars and buses, respectively, carried on a single trip. Suppose the joint distribution of X and Yis as given in the table of Exercise 7. Compute the expected revenue from a single trip. Reference Exercise 7 The joint probability distribution of the number X of cars and the number Y of buses per signal cycle at a proposed left-turn lane is displayed in the accompanying joint probability table. p(x, y) 0 .025 .015 010 .050 .030 020 .125 .075 050 .150 .090 .060 .100 .060 040 .050 .030 .020 a. What is the probability that there is exactly one car and exactly one bus during a cycle? b. What is the probability that there is at most one car and at most one bus during a cycle? c. What is the probability that there is exactly one car during a cycle? Exactly one bus? d. Suppose the left-turn lane is to have a capacity of five cars, and that one bus is equivalent to three cars. What is the probability of an overflow during a cycle? e. Are X and Y independent rv's? Explain.In Exercise 66, the weight of the beam itself contributes to the bending moment. Assume that the beam is of uniform thickness and density so that the resulting load is uniformly distributed on the beam. If the weight of the beam is random, the resulting load from the weight is also random; denote this load by W (kip-ft). a. If the beam is 12 ft long, Whas mean 1.5 and standard deviation .25, and the fixed loads are as described in part (a) of Exercise 66, what are the expected value and variance of the bending moment? [Hint: If the load due to the beam were w kip-ft, the contribution to the bending moment would be w xdx.] ] b. If all three variables (X1, X2, and W) are normally distributed, what is the probability that the bending moment will be at most200 kip-ft? Reference Exercise 66 If two loads are applied to a cantilever beam as shown in the accompanying drawing, the bending moment at 0 due to the loads is a, X, + a,X2. (0, 1)- (x, 1 - x) a. Suppose that X1 and X2 are independent rv's with means 2 and 4 kips, respectively, and standard deviations .5 and 1.0 kip, respectively. If a, = 5 ft and a2 _ 10 ft, what is the expected bending moment and what is the standard deviation of the bending moment? b. If X1 and X2 are normally distributed, what is the probability that the bending moment will exceed 75 kip-ft? c. Suppose the positions of the two loads are random variables. Denoting them by A, and A2, assume that these variables have means of 5 and 10 ft, respectively, that each has a standard deviation of .5, and that all Aj's and Xi's are independent of one another. What is the expected moment now? d. For the situation of part (c), what is the variance of the bending moment? e. If the situation is as described in part (a) except that Corr(X,, X2) = .5 (so that the two loads are not independent), what is the variance of the bending moment?a. Let X, have a chi-squared distribution with parameter v1 (see Section 4.4), and let X, be independent of X, and have a chi-squared distribution with parameter v2- Use the technique of Example 5.21 to show that X, + X, has a chi-squared distribution with parameter V1 _ V2- b. In Exercise 71 of Chapter 4, you were asked to show that if Z is a standard normal rv, then Zz has a chi-squared distribution with v = 1. Let Z,, Z 2. .. .. Z, ben independent standard normal ry's. What is the distribution of X? Justify your answer. c. Let X1, . . . . X, be a random sample from a normal distribution with mean m and variance of. What is the distribution of the sum 1 ? Justify your answer. Reference example 5.21 Service time for a certain type of bank transaction is a random variable having an exponential distribution with parameter I. Suppose X1 and X2 are service times for two different customers, assumed independent of each other. Consider the total service time To = X1 + X2 for the two customers, also a statistic. The cdf of 7, is, for f 2 0, X2 Reference exercise 7 in chapter 4 The time X (min) for a lab assistant to prepare the equipment for a certain experiment is believed to have a uniform distribution with A = 25 and B =35. a. Determine the pdf of X and sketch the corresponding density curve. b. What is the probability that preparation time exceeds 33 min? c. What is the probability that preparation time is within 2 min of the mean time? [Hint. Identify u from the graph of f(x).] d. For any a such that 25 .044 is equivalent to what inequalities involving x (see Example 8.4)?] e. Using the test procedure of (d), what would you conclude if 6 of the 25 queried favored company 1
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


