Question: Solve using excel and solver and show all work in excel. Textiles, Ltd . , is a Hong Kong based firm that distributes textiles world
Solve using excel and solver and show all work in excel. Textiles, Ltd is a Hong Kongbased firm that distributes textiles world wide. The company is owned by the Lao family. Should the Peoples Republic of China continue its economic renaissance, the company hopes to use its current base to expand operations to the mainland. International Textile has mills in the Bahamas, Hong Kong, Korea, Nigeria, and Venezuela, each weaving fabrics out of two or more raw fibers: cotton, polyester, andor silk. The mills service eight company distribution centers located near the customers geographical centers of activity.
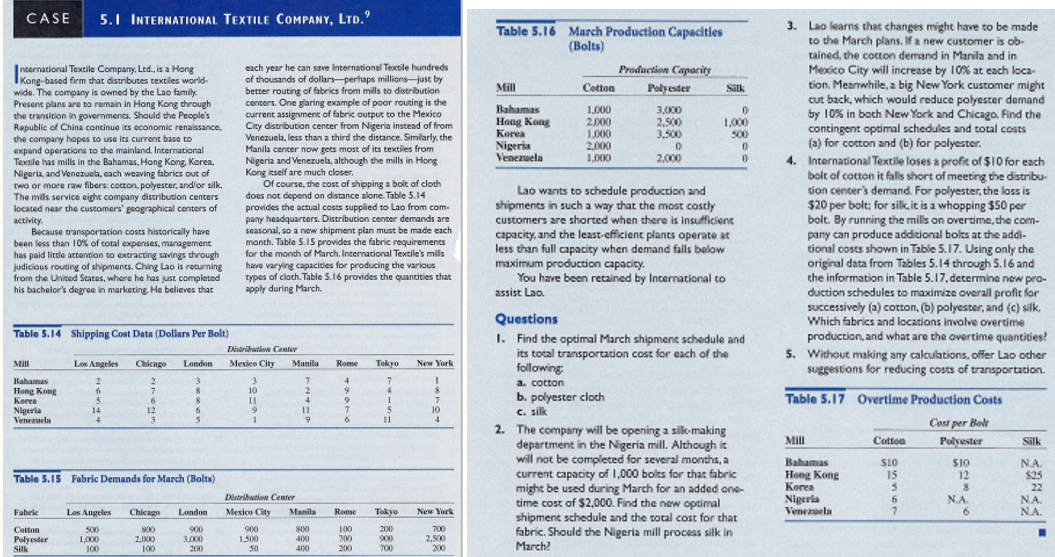
Because transportation costs historically have been less than of total expenses, management has paid little attention to extracting savings through judicious routing of shipments. Ching Lao is returning from the United States, where he has just completed his bachelors degree in business. He believes that each year he can save New Horizon hundreds of thousands dollars perhaps millions by better routing of fabrics from mills to distribution centers. One glaring example of poor routing is the current assignment of fabric output to the Mexico City distribution center from Nigeria instead of from Venezuela, less than a third the distance. Similarly, the Manila center now gets most of its textiles from Nigeria and Venezuela, although the mills in Hong Kong itself are much closer.
Of course, the cost of shipping a bolt of cloth does not depend on distance alone. Table provides the actual costs supplied to Lao from company headquarters. Distribution center demands are seasonal, so a new shipment plan must be made each month. Table provides the fabric requirements for the month of March. New Horizons mills have varying capacities for producing the various types of cloth. Table provides the capacities that apply during March.
Lao wants to schedule production and shipments in such a way that the most costly customers are shorted when there is insufficient capacity, and the leastefficient plants operate at less than full capacity when demand falls below maximum production capacity.
You have been retained by International to assist Lao.
Questions
Find the optimal March shipment schedule and its total transportation cost for each of the following: a cotton, b polyester, c silk
The company will be opening a silkmaking department in the Nigeria mill. Although it will not be completed for several months, a current capacity of bolts for that fabric might be used during March for an added onetime cost of $ Find the new optimal shipment schedule and the total cost for that fabric. Should the Nigeria mill process silk in March?
Lao learns that changes might have to be made to the March plans. If a new customer is obtained, the cotton demand in Manila and in Mexico City will increase by at each location. Meanwhile, a big New York customer might cut back, which would reduce polyester demand by in both New York and Chicago. Find the contingent optimal schedules and total costs a for cotton and b for polyester.
New Horizon loses a profit of $ for each bolt of cotton it falls short of meeting the distribution centers demand. For polyester, the loss is $ per bolt; for silk, it is a whopping $ per bolt. By running the mills on overtime, the company can produce additional bolts at the additional costs shown in Table Using only the original data from Tables through and the information in Table determine new production schedules to maximize overall profit for successively a cotton, b polyester, and c silk. Which fabrics and locations involve overtime production, and what are the overtime quantities?
Offer Lao other suggestions for reducing costs of transportation. You dont have to do any more calculations.
Show the complete formulation clearly.
Table Shipping Cost Data Dollars Per Bolt
Distribution Center
Mill Los Angeles Chicago London Mexico City Manila Rome Tokyo New York
Bahamas
Hong Kong
Korea
Nigeria
Venezuela
Table Fabric Demands For March Bolts
Distribution Center
Fabric Los Angeles Chicago London Mexico City Manila Rome Tokyo New York
Cotton
Polyester
Silk
Table March Production Capacities
Production Capacity Bolts
Mill Cotton Polyester Silk
Bahamas
Hong Kong
Korea
Nigeria
Venezuela
Table Overtime Production Costs
Cost Per Bolt
Mill Cotton Polyester Silk
Bahamas $ $ NA
Hong Kong $ $ $
Korea $ $ $
Nigeria $ NA NA
Venezuela $ $ NA
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


