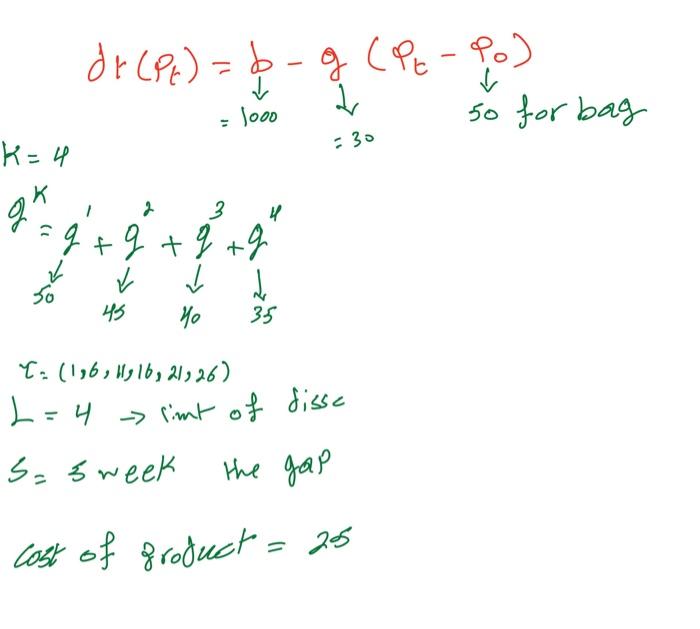Question: Solve using excel Consider these numbers that we assume Problem Statement The manager of an fast moving consuming good (FMCG) category in a grocery retailer
Solve using excel
Consider these numbers that we assume
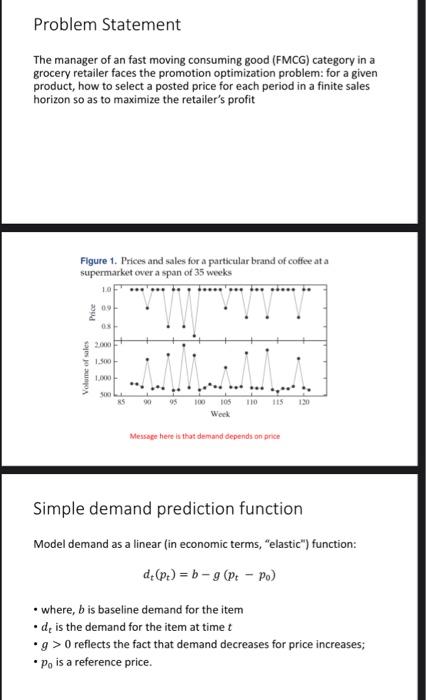
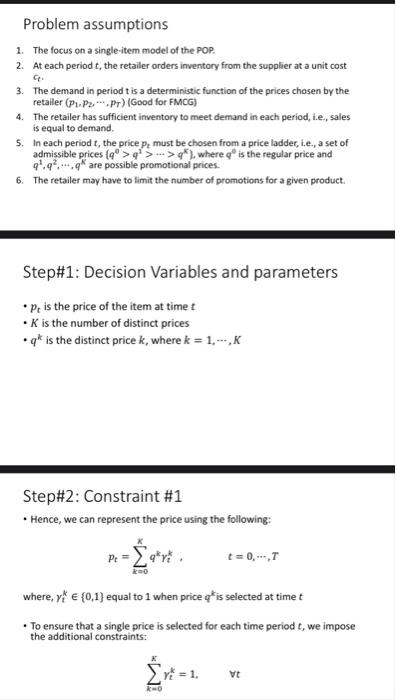
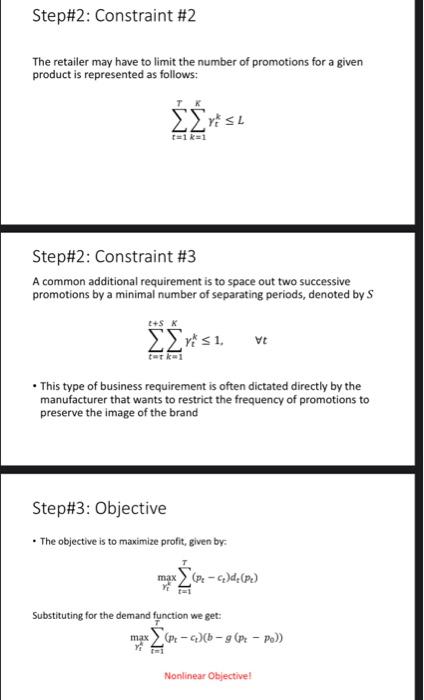
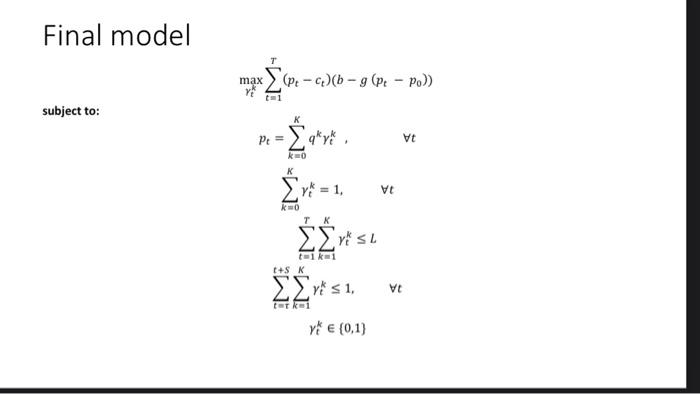
Problem Statement The manager of an fast moving consuming good (FMCG) category in a grocery retailer faces the promotion optimization problem: for a given product, how to select a posted price for each period in a finite sales horizon so as to maximize the retailer's profit Figure 1. Prices and sales for a particular brand of coffee at a supermarket over a span of 35 weeks ... 10 00 Price 2 TIS Volume of sales 1.000 .. SOLL RS 90 95 100 110 115 130 105 Week Message here is that demand depends on price Simple demand prediction function Model demand as a linear (in economic terms, "elastic") function: d (P) = b -9 P- Po) where, b is baseline demand for the item .de is the demand for the item at timet .g > reflects the fact that demand decreases for price increases; Po is a reference price. a Problem assumptions 1. The focus on a single-item model of the POP. 2. At each period t, the retailer orders inventory from the supplier at a unit cost 3. The demand in period tis a deterministic function of the prices chosen by the retailer (P1P2,--.Pr) (Good for FMCG) 4. The retailer has sufficient inventory to meet demand in each period, i.e., sales is equal to demand. 5. In each period t, the price p, must be chosen from a price ladder, i.e., a set of admissible prices (q >> >), where is the regular price and 94.4,.q are possible promotional prices 6. The retailer may have to limit the number of promotions for a given product. Step#1: Decision Variables and parameters P, is the price of the item at timet K is the number of distinct prices .qis the distinct price k, where k = 1.-,K Step#2: Constraint #1 Hence, we can represent the price using the following: PE t = 0, -,T where, vt (0.1) equal to 1 when price q* is selected at timet To ensure that a single price is selected for each time period t, we impose the additional constraints: Vt ko Step#2: Constraint #2 The retailer may have to limit the number of promotions for a given product is represented as follows: