Question: Solve using MATLAB 1 Introduction In this project, you are to simulate the trajectory of several satellites as they maneuver into their new orbits. At
Solve using MATLAB
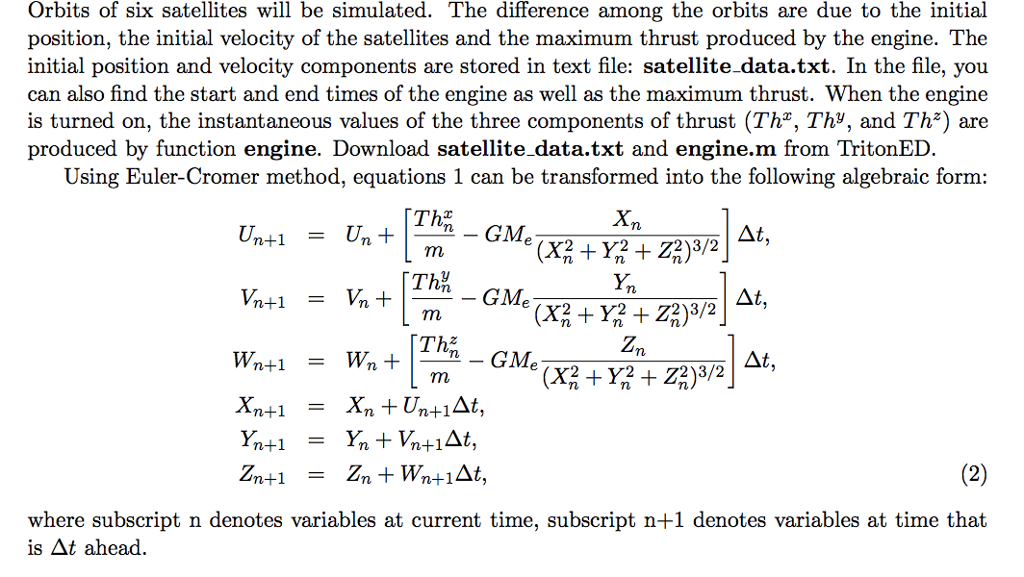
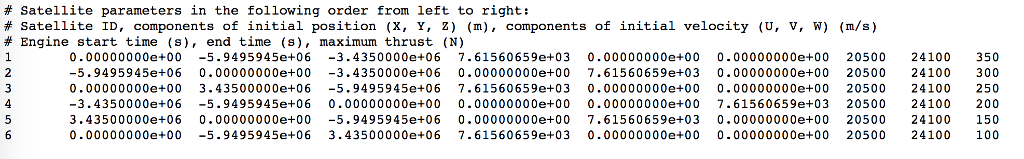

1 Introduction In this project, you are to simulate the trajectory of several satellites as they maneuver into their new orbits. At initial time, the satellite trajectories are produced by the gravitational force from Earth. An engine will be turned on for a short period of time to produce a thrust needed for the satellites to move to higher orbits. You will simulate and analyze the trajectories of the satellites before, during and after the maneuver. From Newton's second law, the orbital motion of the satellites can be described by the following differential equations GM, Ot av Z2)32 GM, Ot OY Ot where t is time (in seconds); X, Y, and Z are position (in meters) of the satellites relative to the center of Earth in rectilinear coordinate. U, V, and W are the velocity components (in meters per second) in the X, Y and Z directions, respectively. Th", Th' and Th2 are three components of thrust (in N) produced by the engine. Earth is assumed to be stationary in this project. The parameters in the equation 1 above are given as follows Radius of Earth: Re-637 106 (m) Mass of the Earth: Me 5.97x 1024 (kg) Gravitational constant : G = 6.67408 10-11 (m3 kg-1 8-2) o Mass of the satellites: m 1500 (kg): Furthermore, the following quantities will be of interest while analyzing the satellite orbits Altitude of the satellites (m): h = X2 + Y2 Z2-Re * Speed of the satellites (ms'): Vmag VU2 + V2 + w2 Acceleration of the satellites (m 8-2): Acc = d(Wnagydt 1 Introduction In this project, you are to simulate the trajectory of several satellites as they maneuver into their new orbits. At initial time, the satellite trajectories are produced by the gravitational force from Earth. An engine will be turned on for a short period of time to produce a thrust needed for the satellites to move to higher orbits. You will simulate and analyze the trajectories of the satellites before, during and after the maneuver. From Newton's second law, the orbital motion of the satellites can be described by the following differential equations GM, Ot av Z2)32 GM, Ot OY Ot where t is time (in seconds); X, Y, and Z are position (in meters) of the satellites relative to the center of Earth in rectilinear coordinate. U, V, and W are the velocity components (in meters per second) in the X, Y and Z directions, respectively. Th", Th' and Th2 are three components of thrust (in N) produced by the engine. Earth is assumed to be stationary in this project. The parameters in the equation 1 above are given as follows Radius of Earth: Re-637 106 (m) Mass of the Earth: Me 5.97x 1024 (kg) Gravitational constant : G = 6.67408 10-11 (m3 kg-1 8-2) o Mass of the satellites: m 1500 (kg): Furthermore, the following quantities will be of interest while analyzing the satellite orbits Altitude of the satellites (m): h = X2 + Y2 Z2-Re * Speed of the satellites (ms'): Vmag VU2 + V2 + w2 Acceleration of the satellites (m 8-2): Acc = d(Wnagydt
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


