Question: solve with matlab code Part 2) It is asked to solve for the dynamics of the model in part 1 with respect to time, using
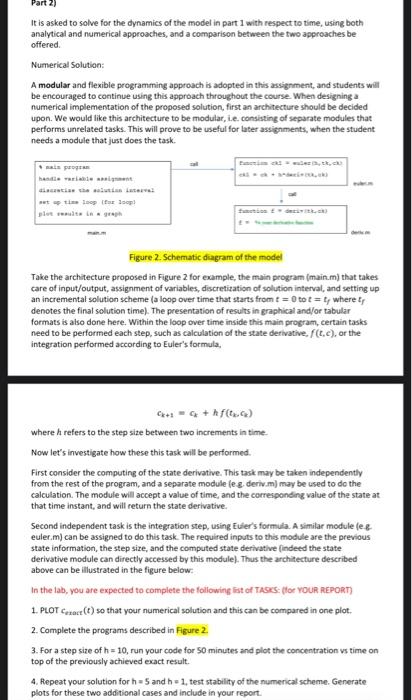
Part 2) It is asked to solve for the dynamics of the model in part 1 with respect to time, using both analytical and numerical approaches, and a comparison between the two approaches be offered. Numerical Solution: A modular and flexible programming approach is adopted in this assignment, and students will be encouraged to continue using this approach throughout the course. When designing a numerical implementation of the proposed solution, first an archinecture should be decided upon. We would like this architecture to be modular, i.e. consisting of separate modules that performs unrelated tasks. This will prove to be useful for later assignments, when the student needs a module that just does the task. Figure 2. Schematic diagram of the model Take the architecture proposed in Figure 2 for example, the main program (main.m) that takes care of input/output, assignment of variables, discretization of solution interval, and setting up an incremental solution scheme (a loop over time that starts from t=0 to t=tf where tf denotes the final solution time). The presentation of results in graphical and/or tabular formats is atso done here. Within the loop over time inside this main program, certain tasks need to be performed each step, such as calculation of the state dertvative, f(t,c), or the integration performed according to Euler's formula, ck+1=ck+hf(tk,ck) where h refers to the step size between two increments in time. Now let's investigate how these this task will be performed. First consider the computing of the state derivative. This task may be taken independently from the rest of the program, and a separate module (es. derivm) may be used to do the calculation. The module will accept a value of time, and the corresponding value of the state at that time instant, and will return the state derivative. Second independent task is the integration step, using Euler's formula. A similar module (e. \& . euler.m) can be assigned to do this task. The required inputs to this module are the previous state information, the step size, and the computed state derivative findeed the state derivative module can directly accessed by this module). Thus the architecture described above can be illustrated in the figure below: In the lab, you are expected to complete the following list of TAGES: (for YOUR REPORT) 1. PLOT cexace(t) so that your numerical solution and this can be compared in one plot. 2. Complete the programs described in Figure 2. 3. For a step size of h=10, run your code for 50 minutes and plot the concentration vs time on top of the previously achieved exact result. 4. Repeat your solution for h=5 and h=1, test stability of the numerical scheme, Generate plots for these two additional cases and include in your report
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


