Question: (Solving a comprehensive problem) Use the end-of-year stock price data in the popup window, , to answer the following questions for the Harris and Pinwheel
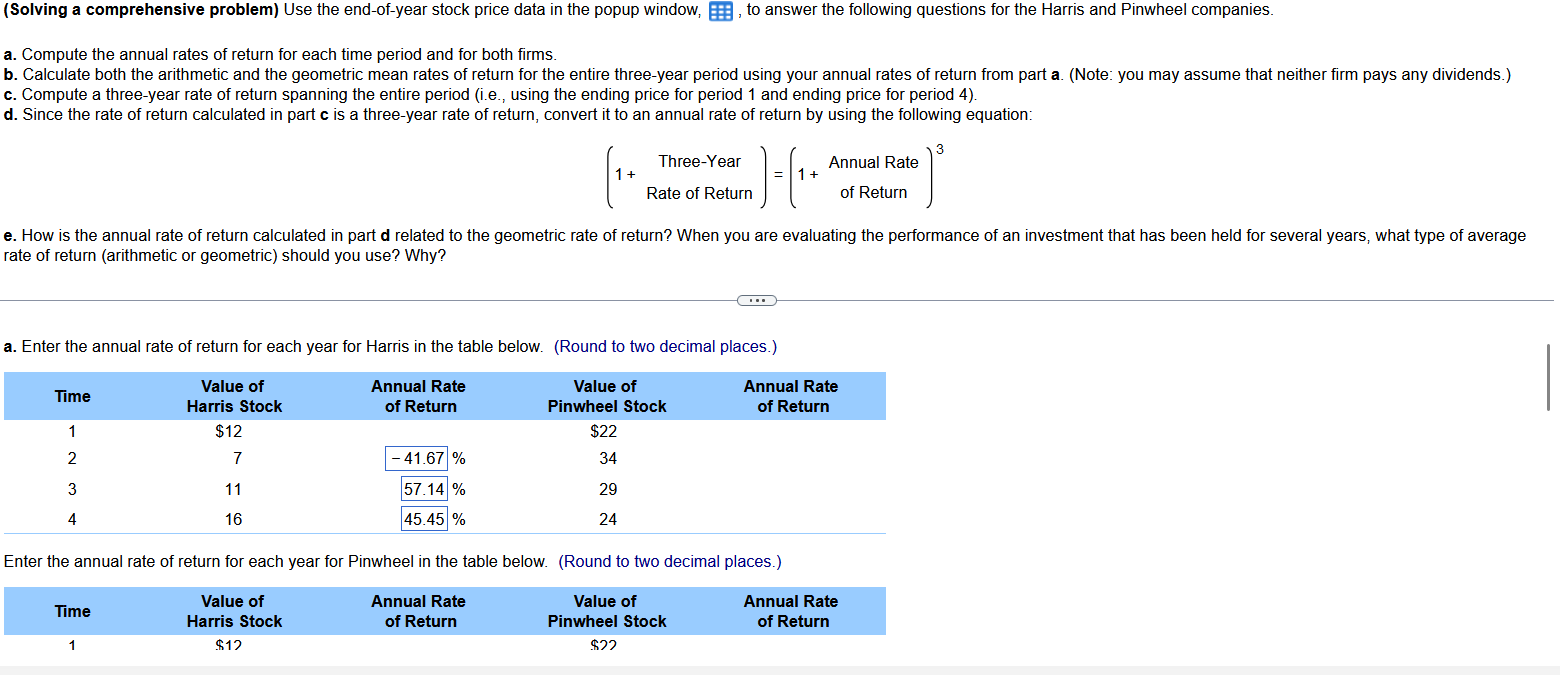
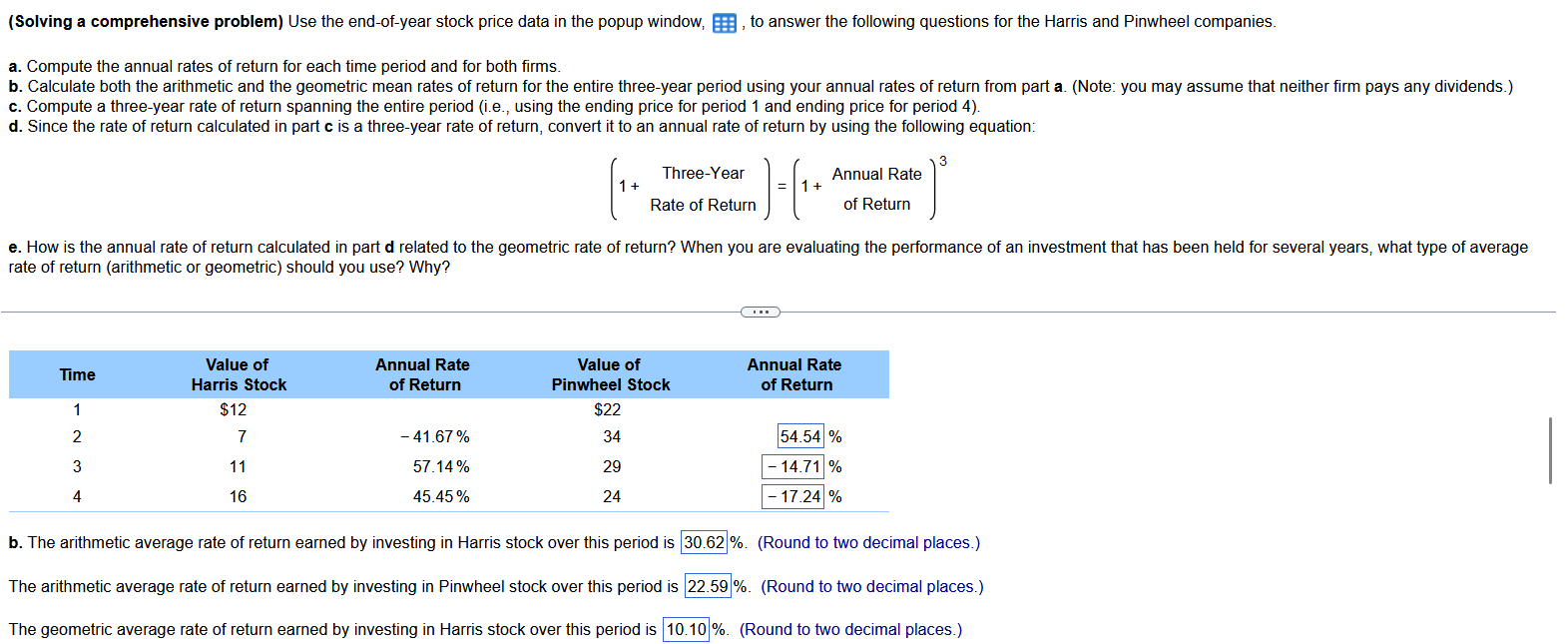
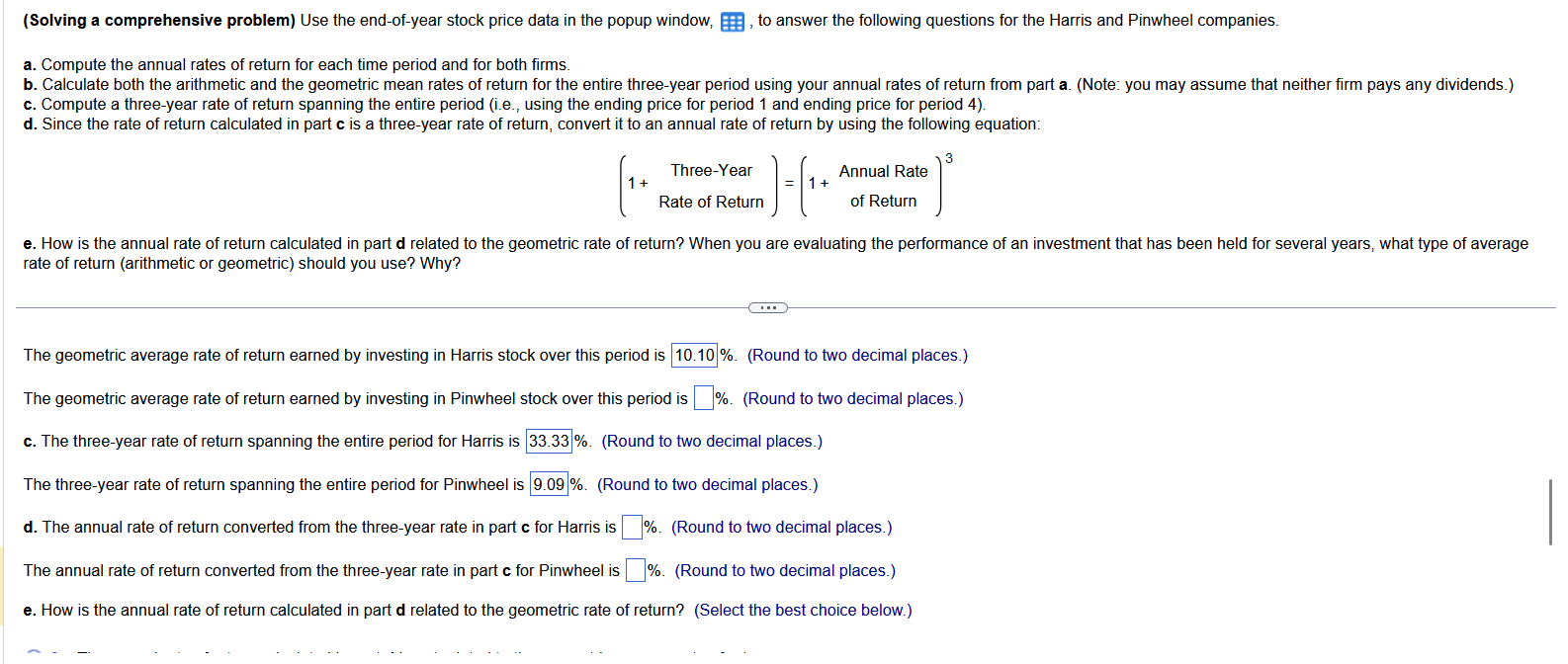
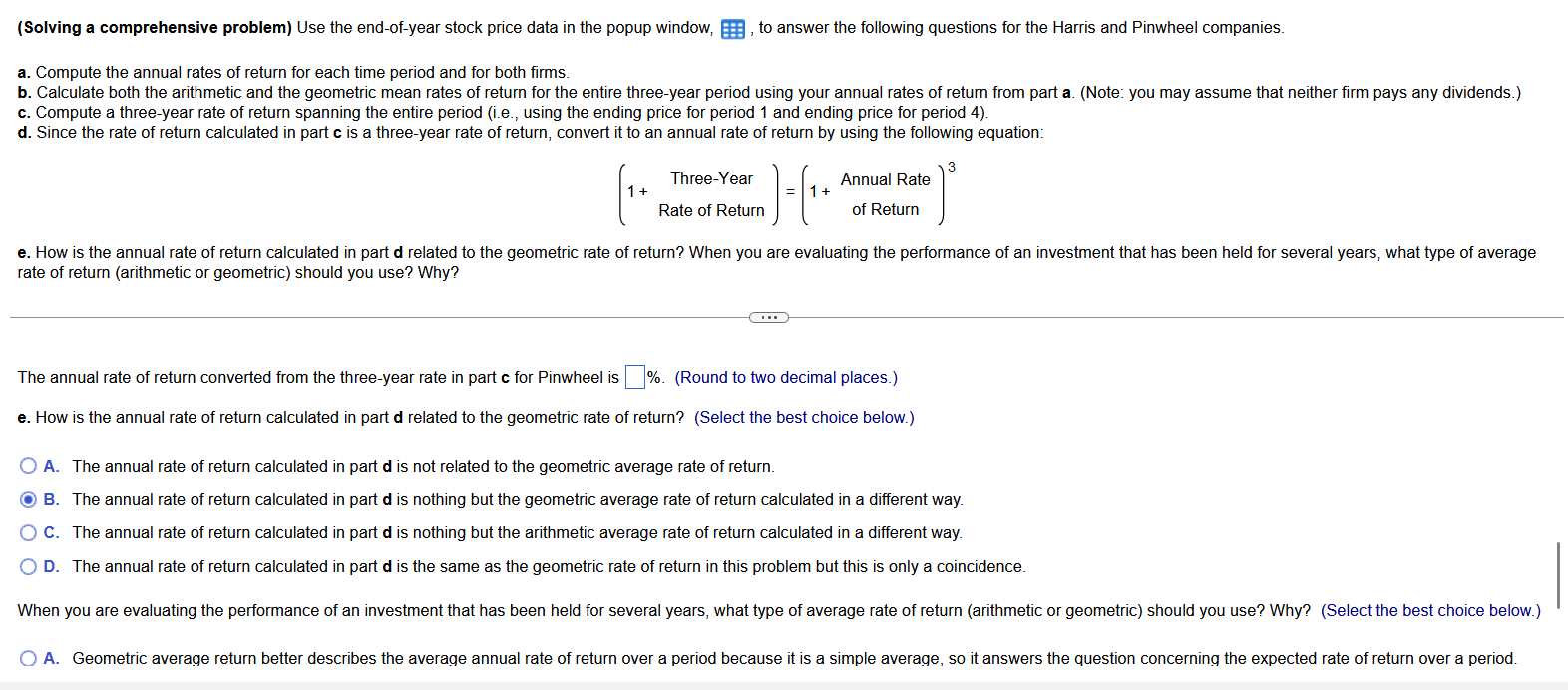

(Solving a comprehensive problem) Use the end-of-year stock price data in the popup window, , to answer the following questions for the Harris and Pinwheel companies. a. Compute the annual rates of return for each time period and for both firms. c. Compute a three-year rate of return spanning the entire period (i.e., using the ending price for period 1 and ending price for period 4 ). d. Since the rate of return calculated in part c is a three-year rate of return, convert it to an annual rate of return by using the following equation: (1+Three-YearRateofReturn)=(1+AnnualRateofReturn)3 rate of return (arithmetic or geometric) should you use? Why? a. Enter the annual rate of return for each year for Harris in the table below. (Round to two decimal places.) (Solving a comprehensive problem) Use the end-of-year stock price data in the popup window, , to answer the following questions for the Harris and Pinwheel companies. a. Compute the annual rates of return for each time period and for both firms. c. Compute a three-year rate of return spanning the entire period (i.e., using the ending price for period 1 and ending price for period 4 ). d. Since the rate of return calculated in part c is a three-year rate of return, convert it to an annual rate of return by using the following equation: (1+Three-YearRateofReturn)=(1+AnnualRateofReturn)3 rate of return (arithmetic or geometric) should you use? Why? b. The arithmetic average rate of return earned by investing in Harris stock over this period is 30.62%. (Round to two decimal places.) The arithmetic average rate of return earned by investing in Pinwheel stock over this period is 6. (Round to two decimal places.) The geometric average rate of return earned by investing in Harris stock over this period is 10.10%. (Round to two decimal places.) (Solving a comprehensive problem) Use the end-of-year stock price data in the popup window, , to answer the following questions for the Harris and Pinwheel companies. a. Compute the annual rates of return for each time period and for both firms. c. Compute a three-year rate of return spanning the entire period (i.e., using the ending price for period 1 and ending price for period 4 ). d. Since the rate of return calculated in part c is a three-year rate of return, convert it to an annual rate of return by using the following equation: (1+Three-YearRateofReturn)=(1+AnnualRateofReturn)3 rate of return (arithmetic or geometric) should you use? Why? The geometric average rate of return earned by investing in Harris stock over this period is 1. (Round to two decimal places.) The geometric average rate of return earned by investing in Pinwheel stock over this period is %. (Round to two decimal places.) c. The three-year rate of return spanning the entire period for Harris is \%. (Round to two decimal places.) The three-year rate of return spanning the entire period for Pinwheel is %. (Round to two decimal places.) d. The annual rate of return converted from the three-year rate in part c for Harris is (Round to two decimal places.) The annual rate of return converted from the three-year rate in part c for Pinwheel is 6. (Round to two decimal places.) e. How is the annual rate of return calculated in part d related to the geometric rate of return? (Select the best choice below.) (Solving a comprehensive problem) Use the end-of-year stock price data in the popup window, , to answer the following questions for the Harris and Pinwheel companies. a. Compute the annual rates of return for each time period and for both firms. c. Compute a three-year rate of return spanning the entire period (i.e., using the ending price for period 1 and ending price for period 4 ). d. Since the rate of return calculated in part c is a three-year rate of return, convert it to an annual rate of return by using the following equation: (1+Three-YearRateofReturn)=(1+AnnualRateofReturn)3 rate of return (arithmetic or geometric) should you use? Why? The annual rate of return converted from the three-year rate in part c for Pinwheel is \%. (Round to two decimal places.) e. How is the annual rate of return calculated in part d related to the geometric rate of return? (Select the best choice below.) A. The annual rate of return calculated in part d is not related to the geometric average rate of return. B. The annual rate of return calculated in part d is nothing but the geometric average rate of return calculated in a different way. C. The annual rate of return calculated in part d is nothing but the arithmetic average rate of return calculated in a different way. D. The annual rate of return calculated in part d is the same as the geometric rate of return in this problem but this is only a coincidence. (Solving a comprehensive problem) Use the end-of-year stock price data in the popup window, , to answer the following questions for the Harris and Pinwheel companies. a. Compute the annual rates of return for each time period and for both firms. c. Compute a three-year rate of return spanning the entire period (i.e., using the ending price for period 1 and ending price for period 4 ). d. Since the rate of return calculated in part c is a three-year rate of return, convert it to an annual rate of return by using the following equation: (1+Three-YearRateofReturn)=(1+AnnualRateofReturn)3 rate of return (arithmetic or geometric) should you use? Why? C. The annual rate of return calculated in part d is nothing but the arithmetic average rate of return calculated in a different way. D. The annual rate of return calculated in part d is the same as the geometric rate of return in this problem but this is only a coincidence. single period. single period
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


