Question: source code: In C, a main function can take no arguments (as you are accustomed to), or it can take in some special information about


source code:
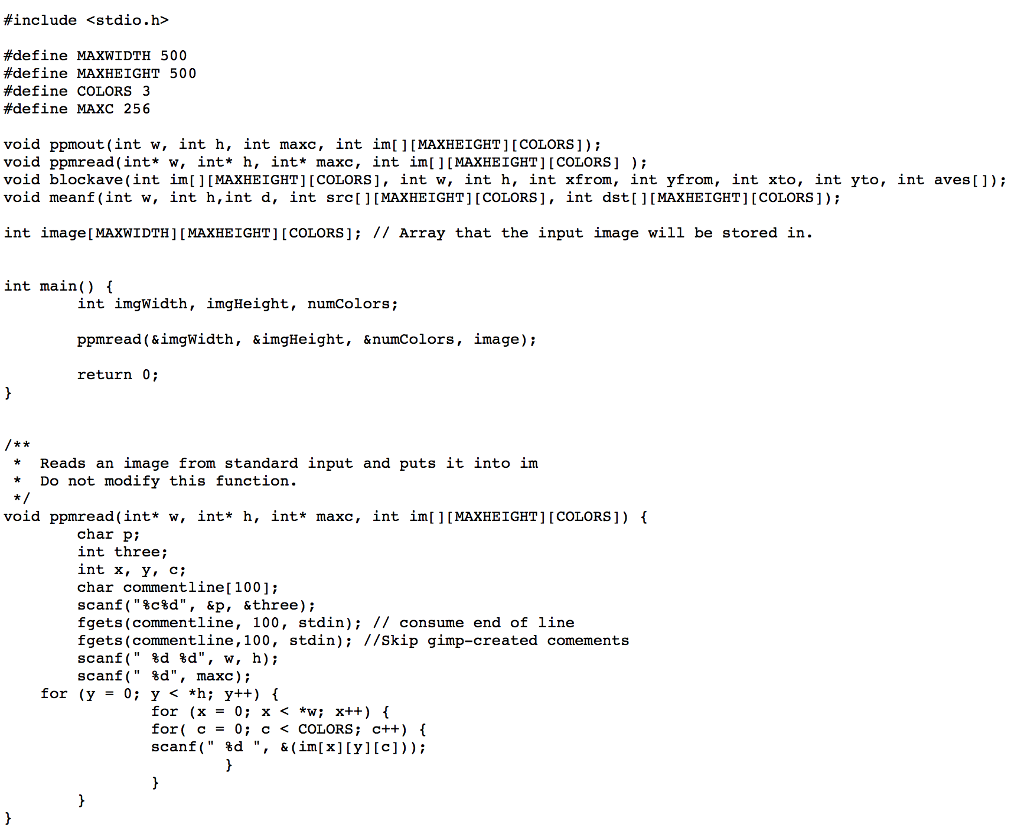


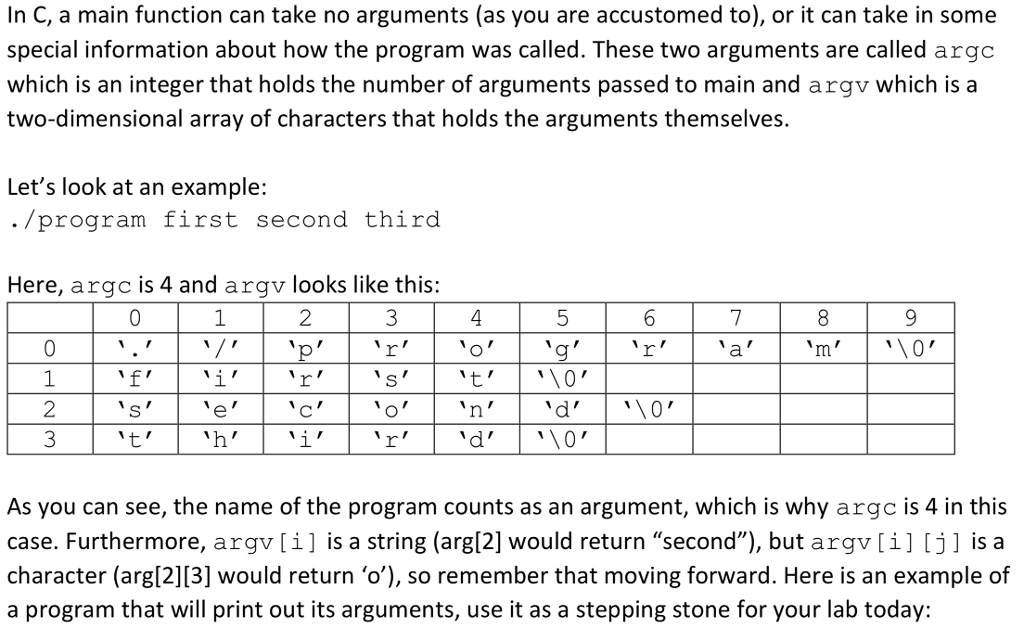
In C, a main function can take no arguments (as you are accustomed to), or it can take in some special information about how the program was called. These two arguments are called argc which is an integer that holds the number of arguments passed to main and argv which is a two-dimensional array of characters that holds the arguments themselves. Let's look at an example: /program first second third Here, argc is 4 and argv looks like this: As you can see, the name of the program counts as an argument, which is why argc is 4 in this case. Furthermore, argv[i] is a string (arg[2] would return "second"), but argv[i] [j] is a character (arg[2][3] would return o'), so remember that moving forward. Here is an example of a program that will print out its arguments, use it as a stepping stone for your lab today: In C, a main function can take no arguments (as you are accustomed to), or it can take in some special information about how the program was called. These two arguments are called argc which is an integer that holds the number of arguments passed to main and argv which is a two-dimensional array of characters that holds the arguments themselves. Let's look at an example: /program first second third Here, argc is 4 and argv looks like this: As you can see, the name of the program counts as an argument, which is why argc is 4 in this case. Furthermore, argv[i] is a string (arg[2] would return "second"), but argv[i] [j] is a character (arg[2][3] would return o'), so remember that moving forward. Here is an example of a program that will print out its arguments, use it as a stepping stone for your lab today
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


