Question: Specification: The GCDRM circuit is specified below using its: 1 . Pseudocode of the functions gcd ( a , b ) and replace _ matrix
Specification: The GCDRM circuit is specified below using its: Pseudocode of the functions gcdab and replacematrixint mat expressed using CC notation. Description of the operation of the main circuit. Table of inputoutput ports.
Pseudocode of the functions gcdab and replacematrixint mat expressed using CC notation unsigned int gcdunsigned int a unsigned int b Function calculating greatest common divisor of a and b eg gcd Returning the result for the following special cases: gcd b b; gcda a gcd if a return b; if b return a; Finding k such that k is the greatest power of that divides both a and b unsigned int k; for k ; a b & ; k a ; b ; Dividing a by until a becomes odd while a & a ; From here on a is always odd do If b is even, remove all factors of in b while b & b ; Now a and b are both odd. Swap if necessary so a b then set b b a which is even if a b swapa b; b b a; while b ; restore common factors of return a k; void replacematrixunsigned int mat unsigned int rgcd; unsigned int cgcd; Initialize arrays of row and column gcds to zeros for int i ; i ; i rgcdi; for int i ; i ; i cgcdi; Calculate gcd of each row and each column in the array mat for int i ; i ; i for int j ; j ; j rgcdi gcdrgcdi matij; cgcdj gcdcgcdj matij; Replace matrix element matij by the product of the gcds for the row i and column j for int i ; i ; i for int j ; j ; j matij rgcdi cgcdj;
Description of the operation of the main circuit The GCDRM main circuit contains RAM capable of storing the array mat including bit unsigned integers. When input s the GCDRM unit is fully controlled by an external circuit. When input s the GCDRM unit is controlled by its internal controller. As soon as s becomes the GCDRM circuit executes the function replacematrixint mat and then asserts done The external circuit performs the following sequence of operations in an infinite loop: Setting input s to Initializing mat using inputs din, x y we clk Setting s to and waiting for output done Setting input s to Reading mat using inputs x y rd clk and output dout. Go to step
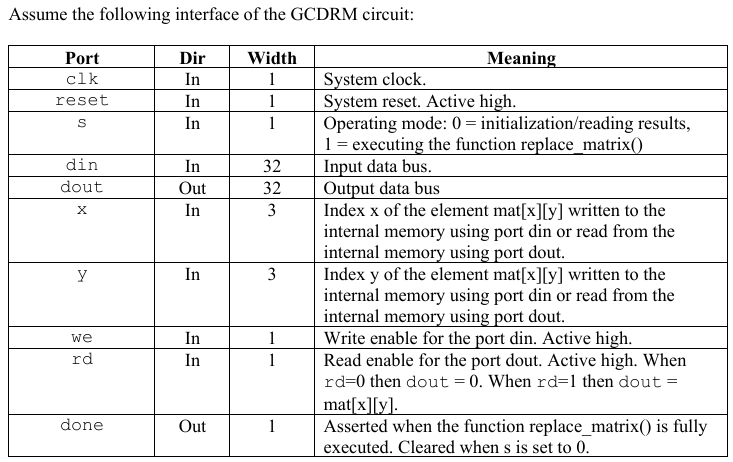
Assume the following interface of the GCDRM circuit: Attached image
Task Draw a hierarchical block diagram of the Datapath of the GCDRM circuit. Assume Primary performance target: Minimum execution time. Secondary performance target: Minimum resource utilization. Minimize the number of control signals to be generated by the Control Unit. Please clearly mark the widths of all buses in your circuit. Use only wellknown medium complexity combinational and sequential circuit building blocks. Clearly specify names, widths and directions of all buses names, widths and directions of all inputs and outputs of the logic components.
Task Draw an interface of the GCDRM circuit with the division into the Datapath and Controller.
Task Identify the most likely critical path in your circuit and mark it in your block diagram.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


