Question: (SQL Programming) (a). Create the tables in Figure 5.7. Specify all primary keys, all foreign keys, and the domain constraints listed below in your CREATE
(SQL Programming)
(a). Create the tables in Figure 5.7. Specify all primary keys, all foreign keys, and the domain constraints listed below in your CREATE TABLE statements.
EMPLOYEE.Sex in {'F', 'M'}
EMPLOYEE.Salary > 20000
5
DEPARTMENT.Dlocation in {'Bellaire', 'Sugarland', 'Houston', 'Stafford'}
PROJECT.Plocation in {'Bellaire', 'Sugarland', 'Houston', 'Stafford'}
DEPENDENT.Relationship in {Spouse, Son, Daughter}
DEPENDENT.Sex in {'F', 'M'}
Specify foreign keys within the CREATE TABLE statement whenever possible. (An exception is when there is a cycle of foreign key references; then one of them should be suspended to break the cycle and added later using ALTER TABLE statement. Hint: name the referential integrity constraint of the foreign key in your ALTER TABLE statement so you can identify it by name later on if needed.) Specify all constraints at the column-level (i.e., as constraints on a column) whenever possible.
(b). Drop all tables created in the exercise a above. Hint: we need to break a cycle of foreign keys if there is any.
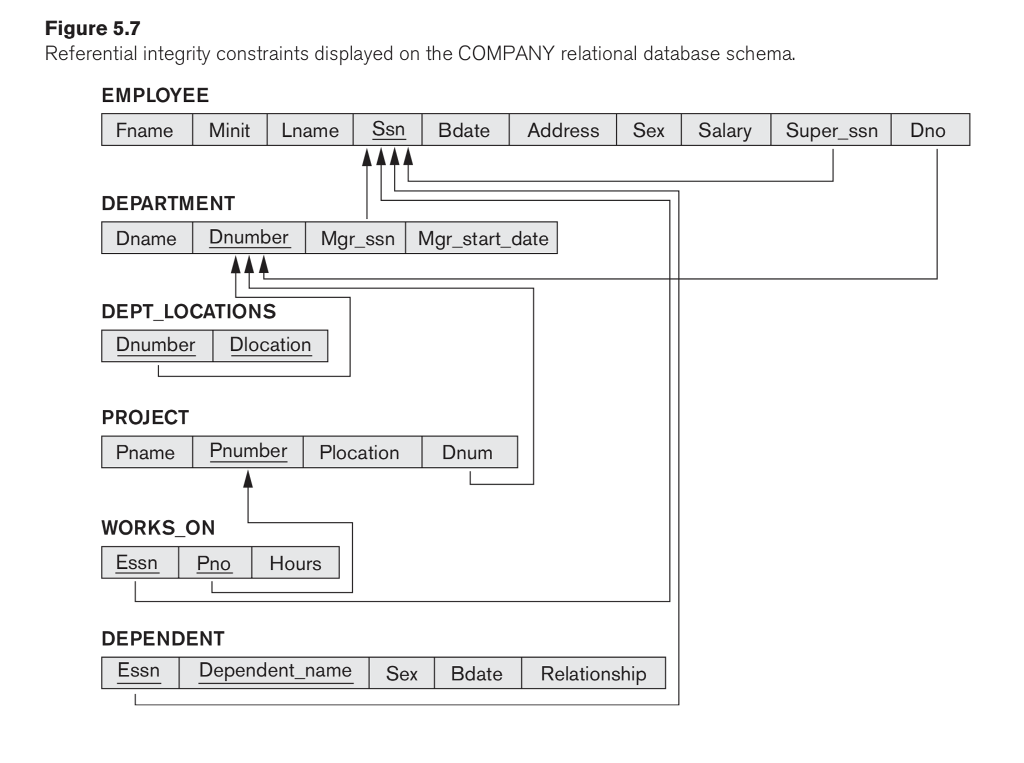
Figure 5.7 Referential integrity constraints displayed on the COMPANY relational database schema. EMPLOYEE Fname Minit Lname Ssn Bdate Address Sex Salary Super_ssnDno DEPARTMENT Dname Dnumber Mgr ssn Mgr_start_date DEPT LOCATIONS Dnumber Dlocation PROJECT Pname Pnumber Plocation Dnum WORKS_ON Essn Pno Hours DEPENDENT Essn Depnenname Sex Bdate Relationship
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


