Question: // // stack.h // // Specification file for Stack class, a stack of integers implemented // using doubly-linked nodes. // // // #include using namespace
// // stack.h // // Specification file for Stack class, a stack of integers implemented // using doubly-linked nodes. // // // #include
#ifndef STACK_H #define STACK_H
class StackEmpty { /* No Code */ }; // StackEmpty exception class - throw an object of this type when stack is empty // Hint: there is no code for exception classes
class StackFull { /* No Code */ }; // StackFull exception class - throw an object of this type when stack is full
class StackInvalidPeek { /* No Code */ }; // StackInvalidPeek exception class - throw an object of this type when invalid peek position is used
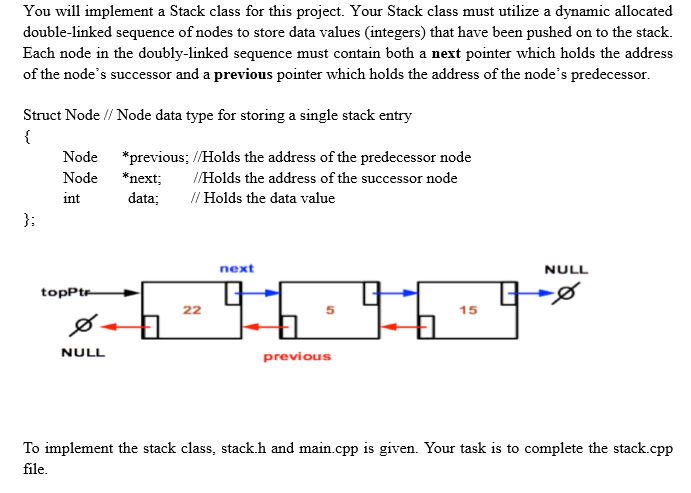
struct Node // Node data type for storing a single stack entry along with pointers to { // neighboring entries (previous and next) in the stack Node* previous; // Member variable that holds the address of the predessor node in the stack sequence Node* next; // Member variable that holds the address of the successor node in the stack sequence int data; // Member variable that holds the data value };
class Stack // Implements stack of integers ADT using doubly-linked sequence of nodes { private: Node* topPtr; // Points to the top node on the stack array public: Stack(); // Default constructor initializes empty stack
~Stack(); // Destructor deallocates all nodes from stack // Must not create a memory leak
void Push(int n); // Pushes integer n onto top of stack. // If unable to push, throws StackFull exception.
void Pop(); // Removes top integer from stack // If stack is already empty, throws StackEmpty exception
bool IsEmpty() const; // Returns true if stack is empty; false otherwise
bool IsFull() const; // Returns true if stack is full; false otherwise
void MakeEmpty(); // Removes all nodes from stack leaving an empty, but usable stack // Must not create a memory leak int Top() const; // Returns value of top integer on stack WITHOUT modifying the stack // If stack is empty, throws StackEmpty exception
int Size() const; // Returns number of items on stack WITHOUT modifying the stack
int Max() const; // Returns value of largest integer within stack WITHOUT modifying the stack // If stack is empty, throws StackEmpty
int Min() const; // Returns value of smallest integer within stack WITHOUT modifying the stack // If stack is empty, throws StackEmpty
int Peek( int n) const; // Returns stack value n levels down from top of stack. Peek(0) = Top() // If position n does not exist, throws StackInvalidPeek /******* DO NOT MODIFY ANY OF THE CODE FOR PRINT() *******/ /****** DO NOT PLACE A COPY OF PRINT() CODE IN STACK.CPP!!! *******/ void Print() const // Prints stack contents to stdout in both top-to-bottom and bottom-to-top order { Node* temp = topPtr; cout data
if (temp->next == NULL) break;
temp = temp->next; } cout
// Reverse print while (temp != NULL) { cout data previous; } cout
#endif
// // main.cpp-- Stacks // #include
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { ifstream inputs; // Input file for commands char op; // Hold operation and optional char input int value; // Value input from file string comment; // Holds comment from file Stack* sPtr = NULL; // Will point to stack object // Output usage message if one input file name is not provided if (argc != 2) { cout "; return 1; } // Attempt to open input file -- terminate if file does not open inputs.open(argv[1]); if (!inputs) { cout
// Input and echo header comment from file getline(inputs, comment); // Input and echo the comment appearing in the test file cout > op; // Attempt to input first command while (inputs) { switch (op) // Process operation input from file { case '#': // Test file comment getline(inputs, comment); // Input and echo the comment appearing in the test file cout
case '+': // Push inputs >> value; cout Push(value); cout
case '-': // Pop cout Pop(); cout IsFull()) cout IsEmpty()) cout MakeEmpty(); cout Print(); break;
case 't': // Top of Stack try { cout Top() ': // Max value within Stack try { cout Max()
case 'Min() > value; try { cout Peek(value) Size()
case 'd': // Destructor delete sPtr; sPtr = NULL; cout
default: // Error cout > op; // Attempt to input next command } return 0; } // End main()
You will implement a Stack class for this project. Your Stack class must utilize a dynamic allocated double-linked sequence of nodes to store data values (integers that have been pushed on to the stack. Each node in the doubly-linked sequence must contain both a next pointer which holds the address of the node's successor and a previous pointer which holds the address of the node's predecessor. Struct Node Node data type for storing a single stack entry Node *previous //Holds the address of the predecessor node Node next /Holds the address of the successor node data; Holds the data value int next NULL to te 15 NULL previous To implement the stack class, stack.h and main.cpp is given. Your task is to complete the stack.cpp file
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


