Question: Standard Direct Materials Cost per Unit from Variance Data The following data relating to direct materials cost for October of the current year are taken
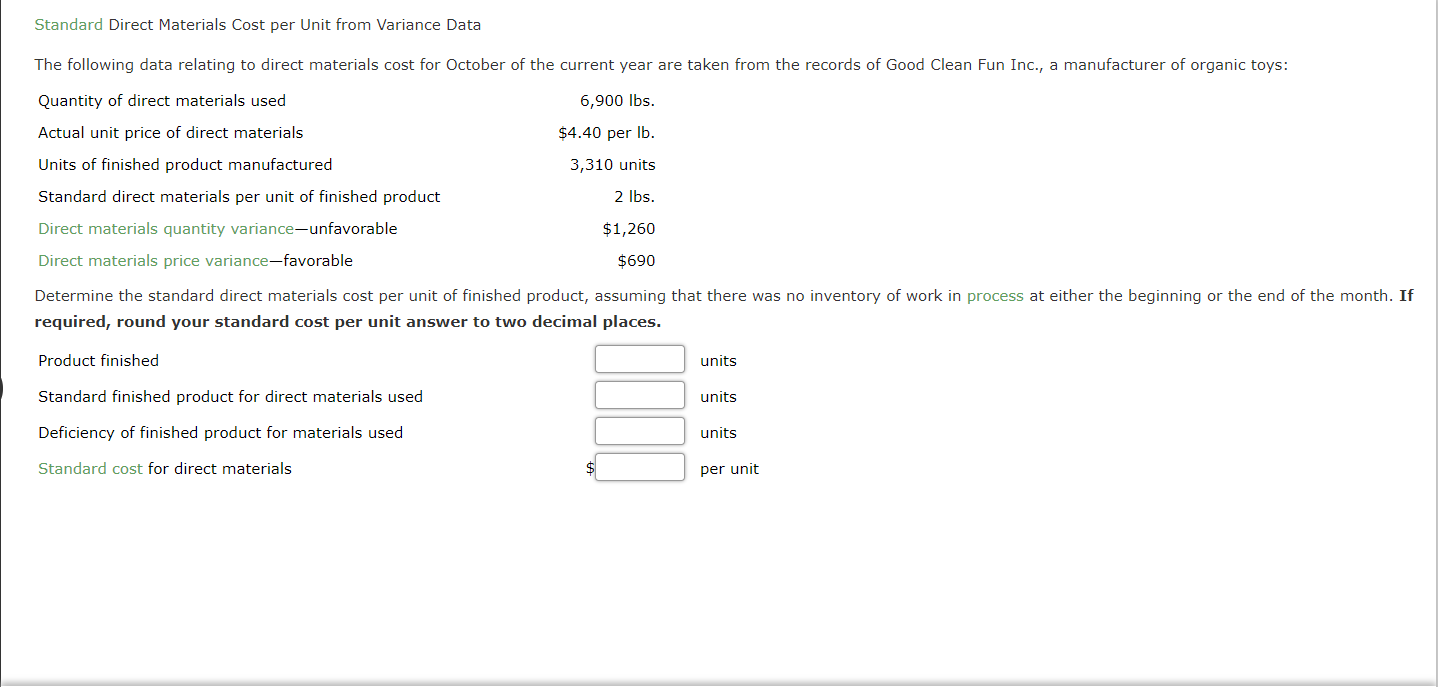
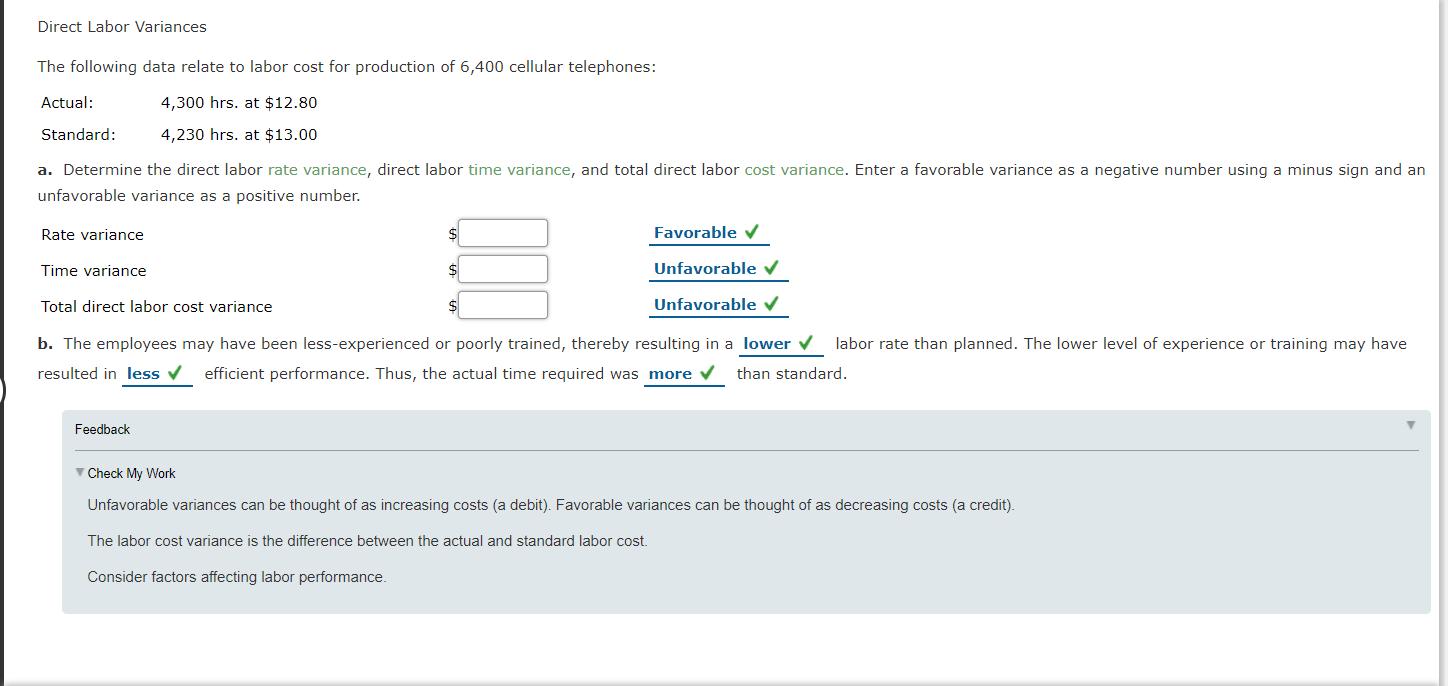
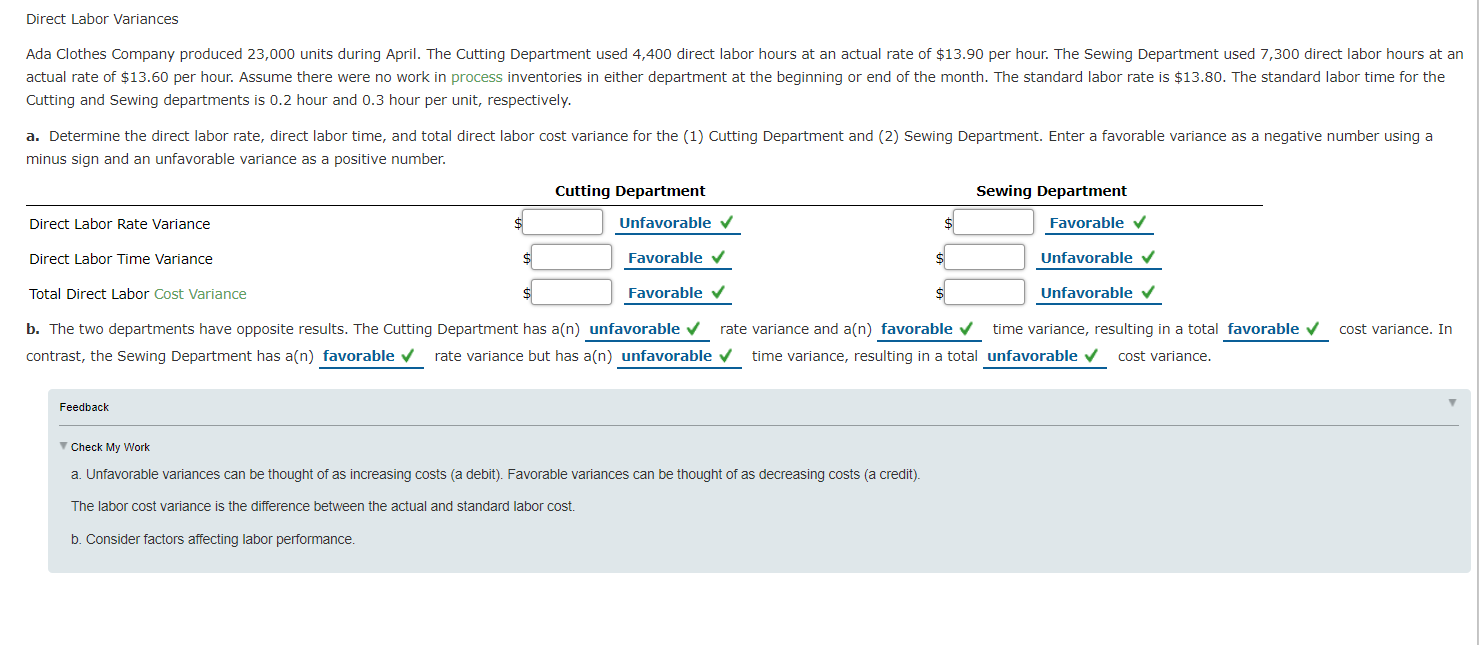
Standard Direct Materials Cost per Unit from Variance Data The following data relating to direct materials cost for October of the current year are taken from the records of Good Clean Fun Inc., a manufacturer of organic toys: Quantity of direct materials used 6,900 lbs. Actual unit price of direct materials $4.40 per Ib. 3,310 units 2 lbs. Units of finished product manufactured Standard direct materials per unit of finished product Direct materials quantity variance-unfavorable Direct materials price variance-favorable $1,260 $690 Determine the standard direct materials cost per unit of finished product, assuming that there was no inventory of work in process at either the beginning or the end of the month. If required, round your standard cost per unit answer to two decimal places. Product finished units Standard finished product for direct materials used units Deficiency of finished product for materials used units Standard cost for direct materials per unit Direct Labor Variances The following data relate to labor cost for production of 6,400 cellular telephones: Actual: 4,300 hrs. at $12.80 Standard: 4,230 hrs. at $13.00 a. Determine the direct labor rate variance, direct labor time variance, and total direct labor cost variance. Enter a favorable variance as a negative number using a minus sign and an unfavorable variance as a positive number. Rate variance $ Favorable Time variance Unfavorable Total direct labor cost variance Unfavorable b. The employees may have been less-experienced or poorly trained, thereby resulting in a lower labor rate than planned. The lower level of experience or training may have resulted in less efficient performance. Thus, the actual time required was more than standard. Feedback Check My Work Unfavorable variances can be thought of as increasing costs (a debit). Favorable variances can be thought of as decreasing costs (a credit). The labor cost variance is the difference between the actual and standard labor cost. Consider factors affecting labor performance. Direct Labor Variances Ada Clothes Company produced 23,000 units during April. The Cutting Department used 4,400 direct labor hours at an actual rate of $13.90 per hour. The Sewing Department used 7,300 direct labor hours at an actual rate of $13.60 per hour. Assume there were no work in process inventories in either department at the beginning or end of the month. The standard labor rate is $13.80. The standard labor time for the Cutting and Sewing departments is 0.2 hour and 0.3 hour per unit, respectively. a. Determine the direct labor rate, direct labor time, and total direct labor cost variance for the (1) Cutting Department and (2) Sewing Department. Enter a favorable variance as a negative number using a minus sign and an unfavorable variance as a positive number. Cutting Department Sewing Department Direct Labor Rate Variance Unfavorable $ Favorable Direct Labor Time Variance Favorable Unfavorable Total Direct Labor Cost Variance Favorable Unfavorable cost variance. In b. The two departments have opposite results. The Cutting Department has a(n) unfavorable contrast, the Sewing Department has a(n) favorable rate variance but has an unfavorable rate variance and a(n) favorable time variance, resulting in a total favorable time variance, resulting in a total unfavorable cost variance. Feedback Check My Work a. Unfavorable variances can be thought of as increasing costs (a debit). Favorable variances can be thought of as decreasing costs (a credit). The labor cost variance is the difference between the actual and standard labor cost. b. Consider factors affecting labor performance
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


