Question: STAT310 Fall 2020 Power and Sample Size 1.Based on today's lecture, what is a type I error? 2.What is a type II error? 3.How would
STAT310
Fall 2020
Power and Sample Size
1.Based on today's lecture, what is a type I error?
2.What is a type II error?
3.How would you define the power of a test?
4.If ? = .25, what is the power of the test? What does this mean?
5.If the power of the test is .85, what is ?? What does this mean?
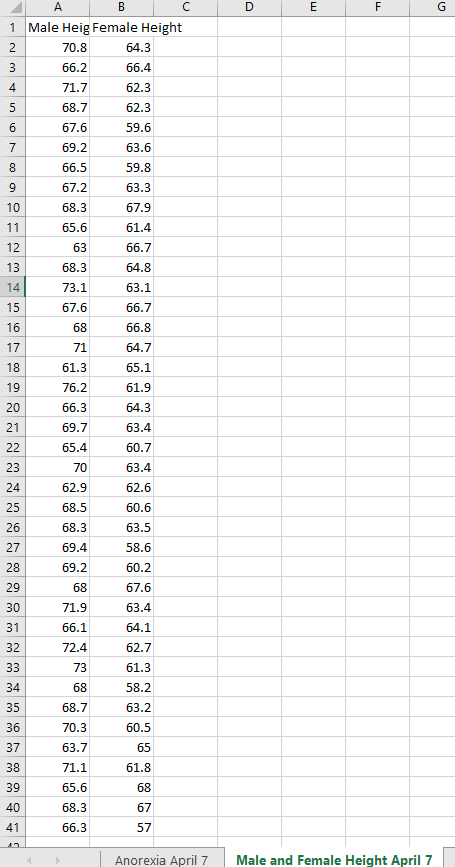
6.Using the data in the Male and Female Height file, test whether the average height of a female is different than 65.3 inches. Use inch (.5) for your difference.
a.Run the hypothesis test
b.Determine the power of the test, and what that means in terms of your findings
c.Determine the sample size necessary to have minimum 80% power.
7.A healthcare consultant wants to compare the patient satisfaction ratings of two hospitals.Before collecting the data for a 2-sample t-test, the consultant uses a power and sample size calculation to determine the sample size required to detect a difference of 5 points with a probability as high as 90% (power of 0.9). Previous studies indicate the ratings have a standard deviation of 10.
ChooseStat>Power and Sample Size>2-Sample t.
InSample Sizes, leave blank to estimate sample sizes
In Differences, enter5.
InPower values, enter0.9.
InStandard deviation, enter10.
ClickOK.
i.Determine the sample size required to detect a difference of 5 with a probability as high as 90% (power of 0.9).
ii.Determine the sample size required to detect a difference of 3 with a power of .8.
iii.Determine the sample size required to detect a difference of 3 with a power of .9.
iv.Determine the power for a sample size of 20 with a difference of 5 and a standard deviation of 10. For this, enter 20 as your sample size and leave the power box blank.
v.Determine the power for a sample size of 90 with a difference of 3.
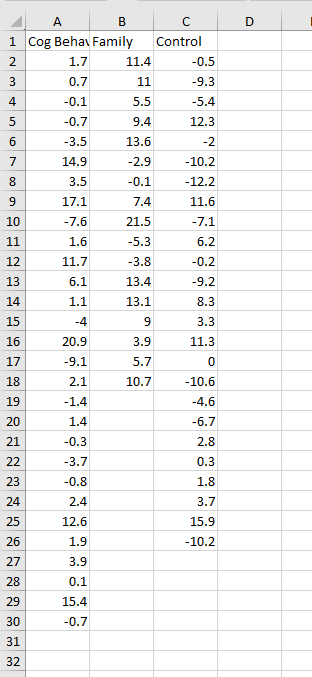
8.Using the Anorexia data on Blackboard, conduct a two-sample t-test for a difference of the two means Cognitive and Family Therapy. Under options check the box for assume equal variances.
ChooseStat>Power and Sample Size>2-Sample t.
InSample Sizes enter the sample sizes used for the test, in this case, use 29 and 17. Enter the sample sizes in the box, separated by a space: 29 17
In Differences, enterthe difference you found in your test.
InPower values, leave this blank to determine the power of the test.
InStandard deviation, enterthe value from the test you just performed.
ClickOK.
i.Using the results from your test, determine the power of the test you just performed - follow the instructions above.
ii.Determine the sample sizes needed for 80% power, using the difference you found on your test, and the pooled standard deviation.
iii.Determine the sample sizes needed for 90% power, using the difference you found on your test, and the pooled standard deviation.
iv.Determine the sample sizes needed for 80% power, with a difference of 2 pounds, and the pooled standard deviation.
v.Determine the sample sizes needed for 90% power with a difference of 2 pounds, and the pooled standard deviation.
\f\f
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


