Question: State the rules of probabilities How do you define a probability model? How do you compute probabilities using the empirical method? How do you compute

State the rules of probabilities
How do you define a probability model?
How do you compute probabilities using the empirical method?
How do you compute probabilities using the classical method?
State the generalized addition rule
State the complement rule
When are events independent?
State the multiplication rule for independent events
State the multiplication rule of counting
Give the definition of permutation
Give the definition of combination
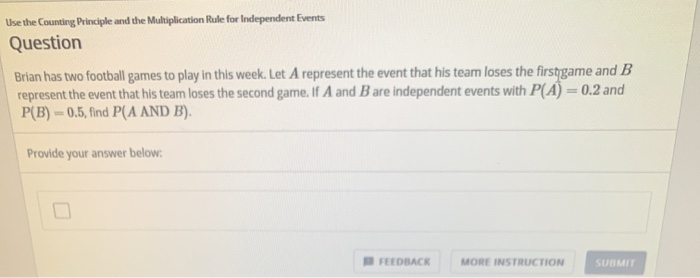
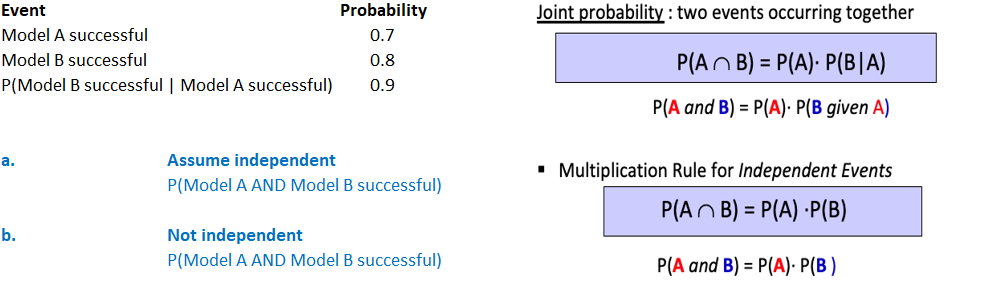

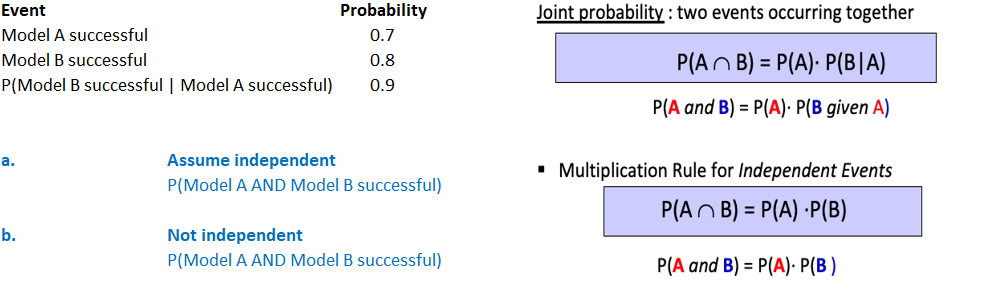
Use the Counting Principle and the Multiplication Rule for Independent Events Question Brian has two football games to play in this week. Let A represent the event that his team loses the firstgame and B represent the event that his team loses the second game. If A and B are independent events with P(A) = 0.2 and P(B) = 0.5, find P( A AND B). Provide your answer below: FEEDBACK MORE INSTRUCTION SUBMITEvent Probability Joint probability : two events occurring together Model A successful 0.7 Model B successful 0.8 P(An B) = P(A) . P(B| A) P(Model B successful | Model A successful) 0.9 P(A and B) = P(A). P(B given A) a. Assume independent * Multiplication Rule for Independent Events P(Model A AND Model B successful) P(An B) = P(A) .P(B) b. Not independent P(Model A AND Model B successful) P(A and B) = P(A) . P(B )7. (2) Suppose that 50% of students carry a Visa credit card, 40% of students carry a MasterCard credit card, and 10% of students carry both Visa and MasterCard. We choose a student at random. Show that the events {selected student carries a Visa} and {selected student carries a MasterCard} are not independent by (a) using the definition of independent events (P(A| B)=P(A)) and by (b) showing that the multiplication rule for independent events does not hold
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


