Question: std::chrono::high_resolution_clock is a good timer to use for C++ code performance measurement True False For a continuously running piece of code that spends most of
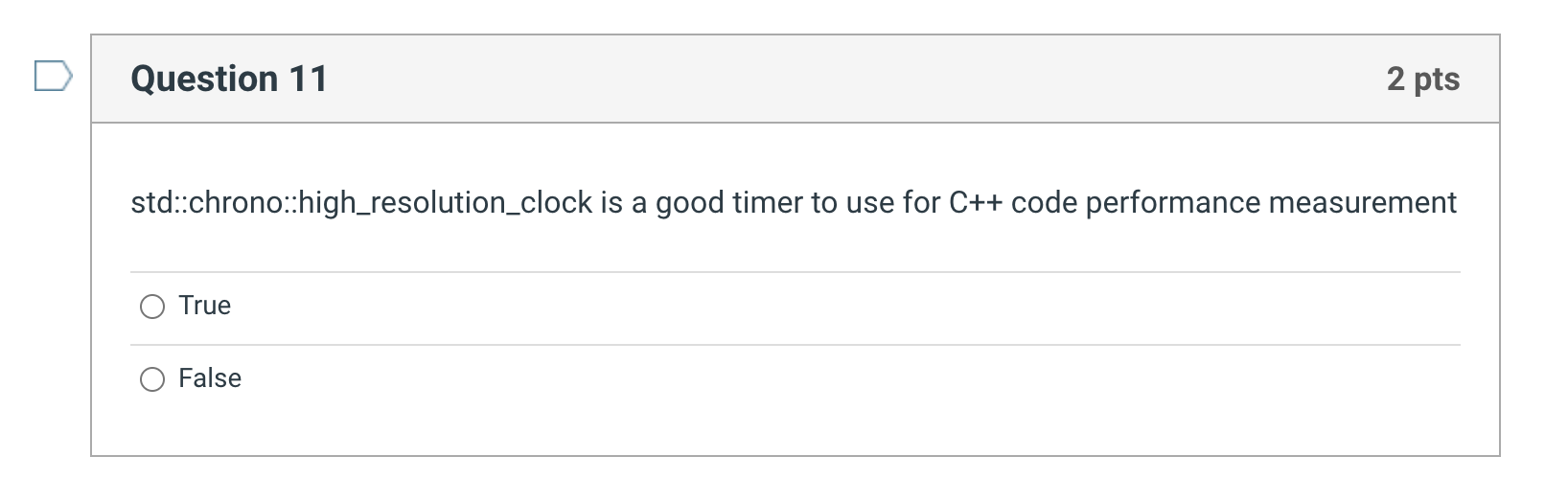
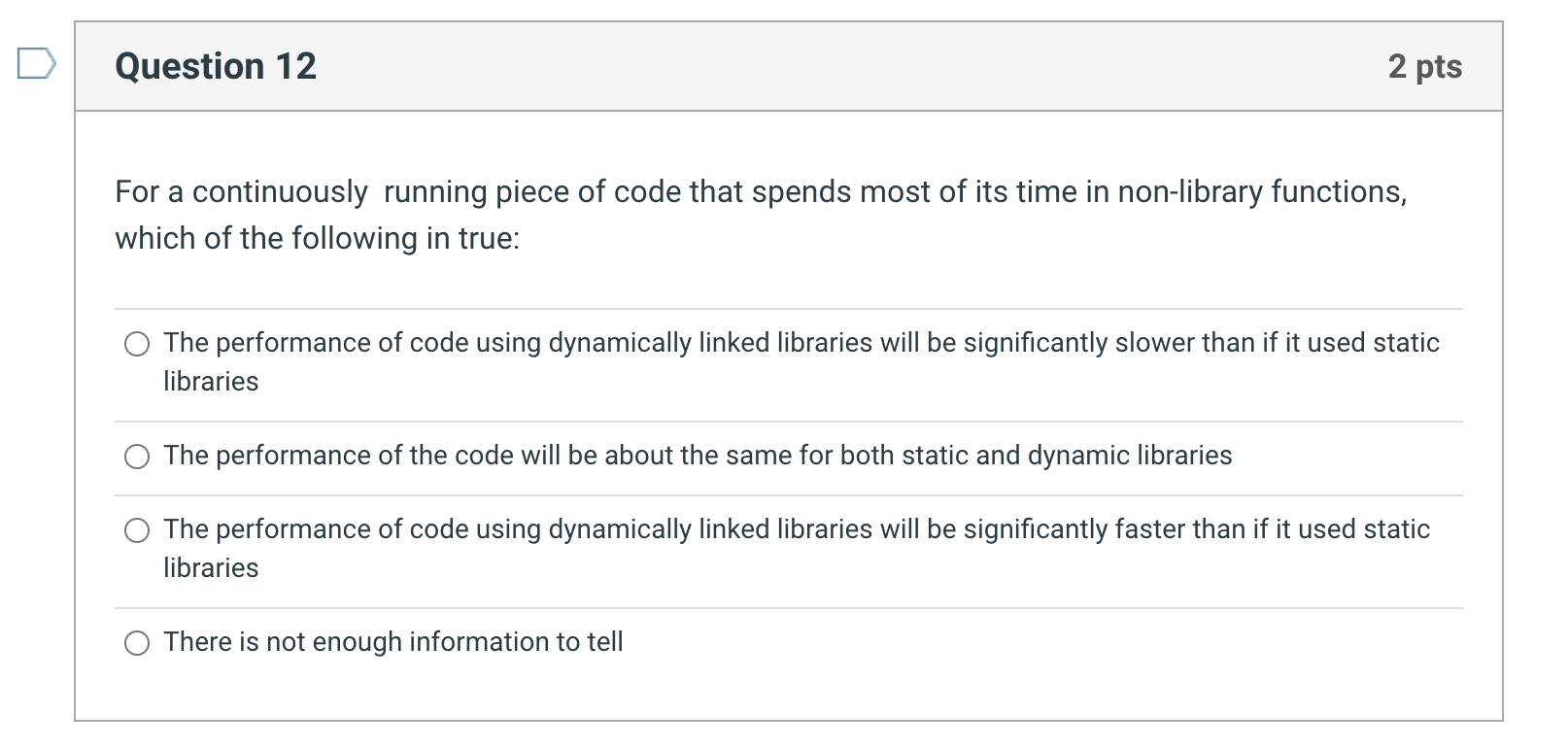

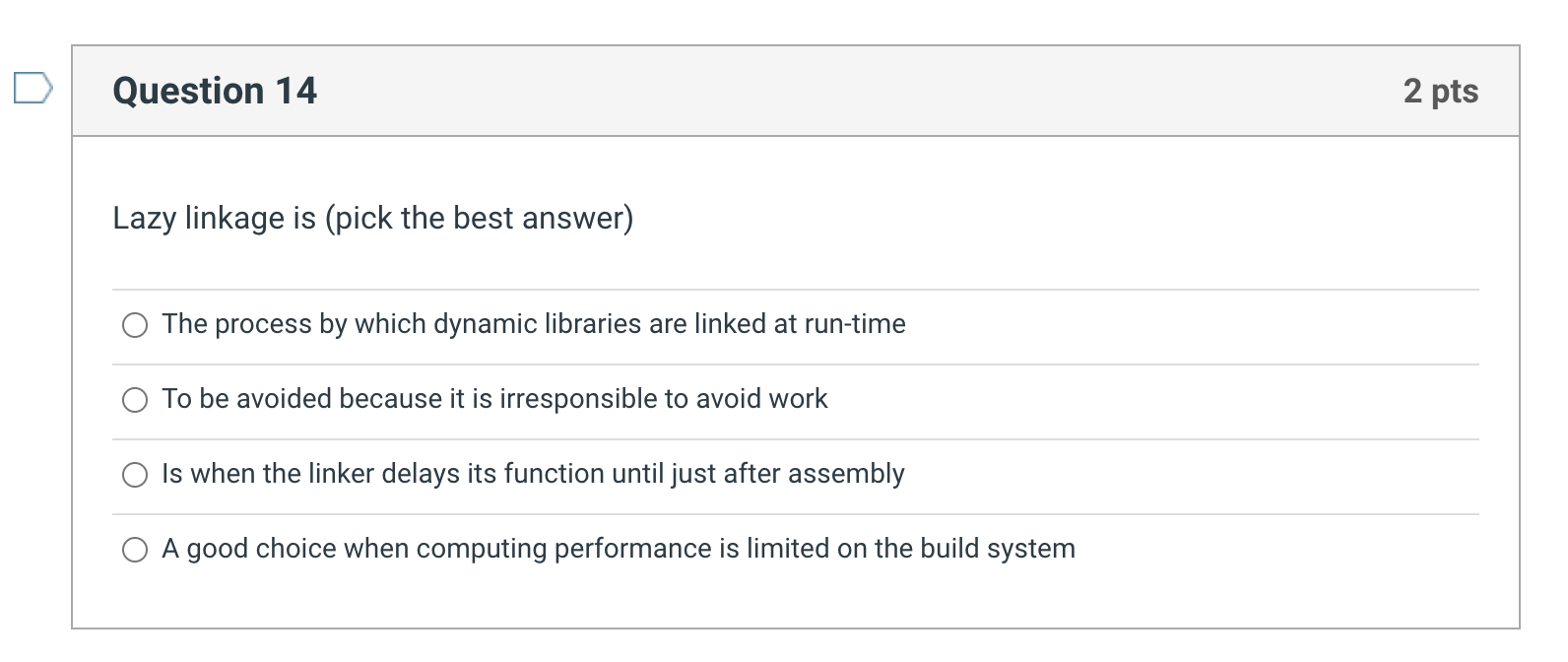

std::chrono::high_resolution_clock is a good timer to use for C++ code performance measurement True False For a continuously running piece of code that spends most of its time in non-library functions, which of the following in true: The performance of code using dynamically linked libraries will be significantly slower than if it used static libraries The performance of the code will be about the same for both static and dynamic libraries The performance of code using dynamically linked libraries will be significantly faster than if it used static libraries There is not enough information to tell For a very short piece of code that makes one short library call, the performance difference between dynamic and static linked versions of the code will be dominated by which factor The number of library calls The time spent outside the library The time to load the library The time spent inside the library Lazy linkage is (pick the best answer) The process by which dynamic libraries are linked at run-time To be avoided because it is irresponsible to avoid work Is when the linker delays its function until just after assembly A good choice when computing performance is limited on the build system From a business perspective, what is not a reason why dynamically linked libraries would be attractive Distribution code is smaller Application code will automatically benefit from new revisions of the library without recompile Distribution code is somewhat platform dependent (dynamic libraries provide hardware abstraction) Guaranteed higher performance
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


