Question: Step 1 : Inspect Vertex.java, Edge.java, and DirectedGraph.java Inspect the Vertex class declaration in the Vertex.java file. The Vertex class represents a graph vertex and
Step : Inspect Vertex.java, Edge.java, and DirectedGraph.java
Inspect the Vertex class declaration in the Vertex.java file. The Vertex class represents a graph vertex and has a string for the vertex label.
Inspect the Edge class declaration in the Edge.java file. The edge class represents a directed graph edge and has fields for a fromvertex and a tovertex.
Inspect the DirectedGraph class declaration in the DirectedGraph.java file. DirectedGraph is an abstract base class for a directed, unweighted graph.
Step : Inspect AdjacencyListGraph.java and AdjacencyListVertex.java
The AdjacencyListGraph class inherits from DirectedGraph and is declared in AdjacencyListGraph.java. The vertices field is an ArrayList of AdjacencyListVertex references The vector contains all the graph's vertices.
The AdjacencyListVertex class inherits from Vertex and is declared in the readonly AdjacencyListVertex.java file. The adjacent field is a vector of adjacent vertices.
Step : Inspect AdjacencyMatrixGraph.java
The AdjacencyMatrixGraph class inherits from DirectedGraph and is declared in AdjacencyMatrixGraph.java. The vertices field is a vector of Vertex references. The vector contains all the graph's vertices. The matrixRows field is a vector of matrix rows. Each row itself is a vector of Boolean values. If matrixRowsXY is true, then an edge exists from verticesX to verticesY
Indices in vertices correspond to indices in matrixRows. So if vertex C exists at index in vertices, then row and column in the matrix correspond to vertex C
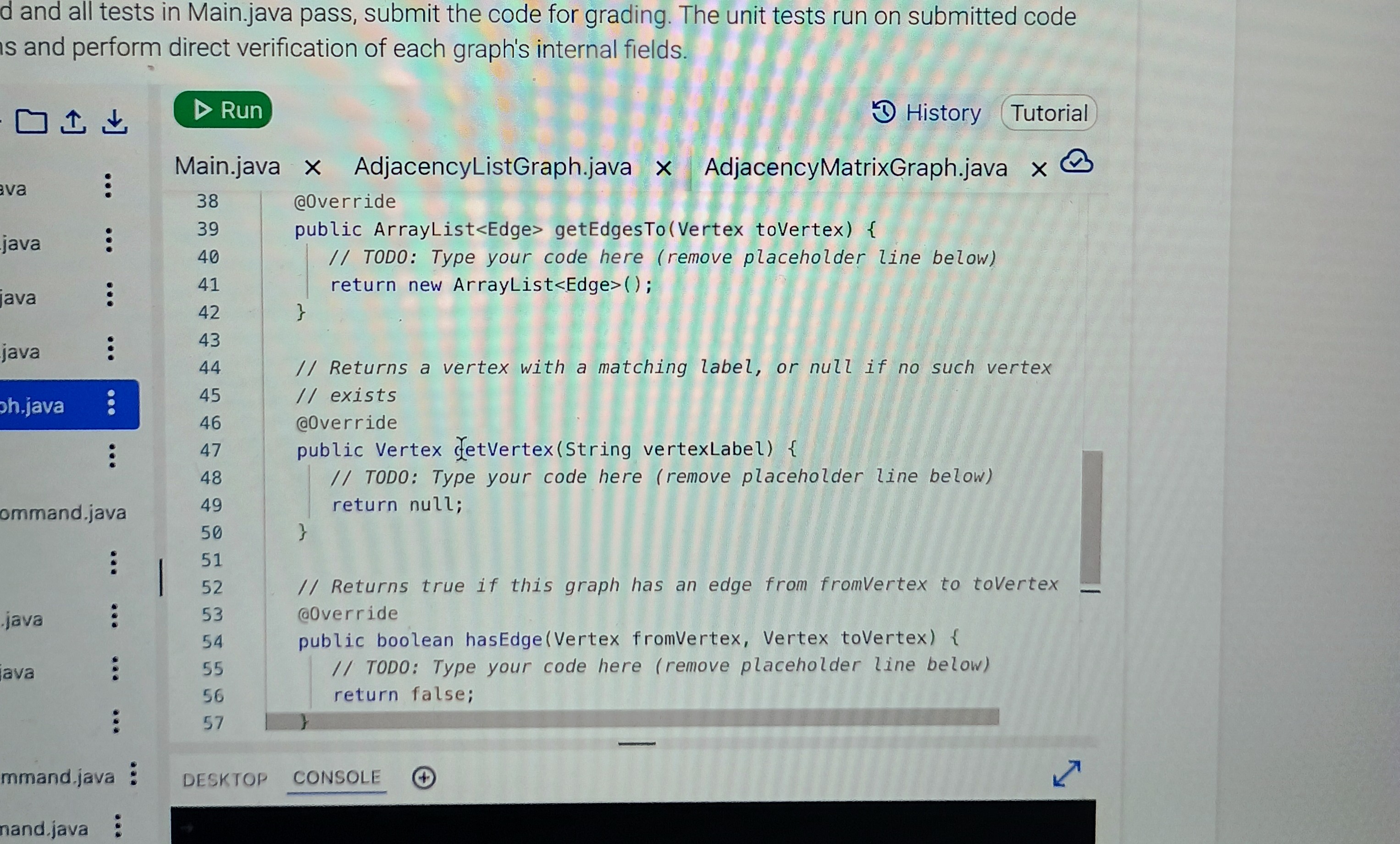
Step : Implement the AdjacencyListGraph class
Implement the required methods in AdjacencyListGraph. Each method has a comment indicating the required functionality. The vertices vector must be used to store the graph's vertices and must not be removed. New methods can be added, if needed, but existing method signatures must not change.
Step : Implement the AdjacencyMatrixGraph class
Implement the required methods in AdjacencyMatrixGraph. Each method has a comment indicating the required functionality. The vertices and matrixRows vectors must be used to store the graph's vertices and adjacency matrix, respectively. Both must not be removed. New methods can be added, if needed, but existing method signatures must not change.
Step : Test code, then submit
File Main.java contains test cases for each graph operation. The test operations are first run on an AdjacencyListGraph. Then the same test operations are run on an AdjacencyMatrixGraph. Results of each test are displayed.
After each method is implemented and all tests in Main.java pass, submit the code for grading. The unit tests run on submitted code are similar but use different graphs and perform direct verification of each graph's internal fields. is and perform direct verification of each graph's internal fields. are similar but use different graphs and perform direct verification of each g
Files
AddEdgeCommand.java
AddVertexCommand.java
AdjacencyListVertex.java
AdjacencyMatrixGraph.java
DirectedGraph.java
DirectedGraphTestCommand.java
Edgeringa
GetVertexCommand.java
HasEdgeCommand.java
Main.java
VerifyEdgesFromCommand.java
VerifyEdgesToCommand.java
Vertex.java
Run
Main.java
times Adjacency
import java.io;
public class Edge
public Vertex fr
public Vertex to
public EdgeVerte
fromVertex f
toVertex to;
@Override
public boolean eq
if this
return true;
if o instanc return false b
DESKTOP
CONSOLE
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


