Question: Strategic Management mgt401 Learning Outcomes : Recognize the basic concepts and terminology used in Strategic Management. ClO-1 Describe the different issues related to environmental scanning,
Strategic Management mgt401
Learning Outcomes:
- Recognize the basic concepts and terminology used in Strategic Management. ClO-1
- Describe the different issues related to environmental scanning, strategy formulation, and strategy implementation in diversified organizations. ClO-2
- Demonstrate how executive leadership is an important part of strategic management. ClO-5
Assignment Question(s):
- Discussion questions
- How can a decision maker identify strategic factors in a corporations external international environment? (2 marks)
- Discuss the relationship between corporate governance and social responsibility? Give examples. (2 marks)
- Critical thinking
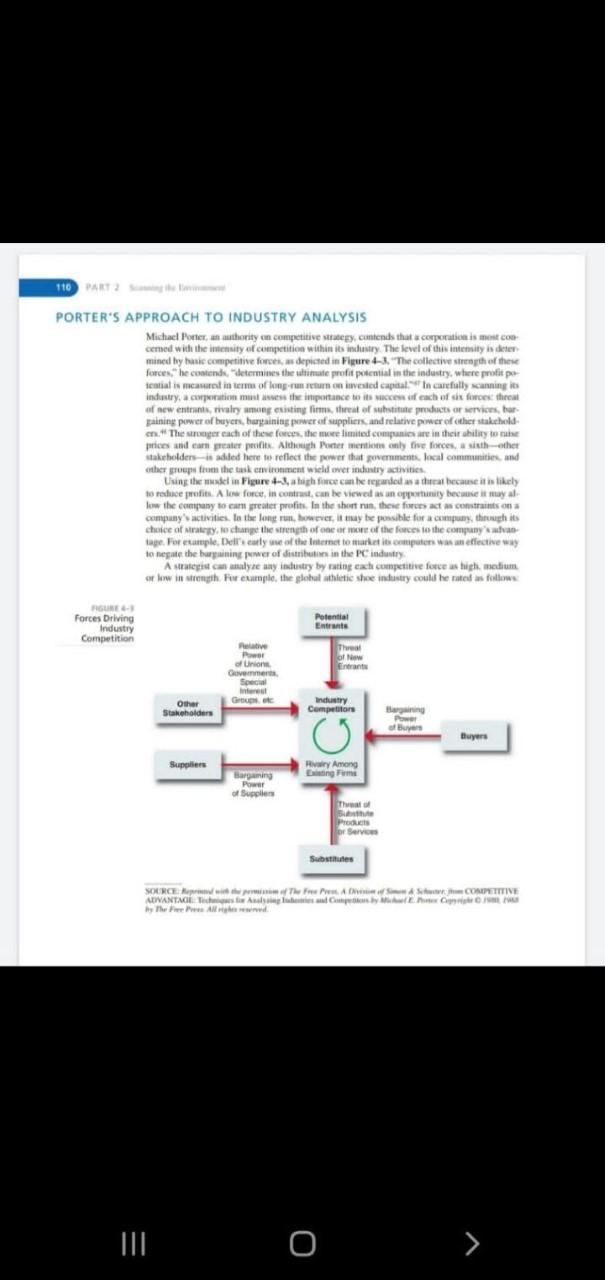
Review the figure 4-3, p.110 from your textbook and answer the following questions:
- Choose any example of industry from the real national or international market, and detail Porters five forces framework with a graphic representation. (2.5 marks)
- According to Porters framework, what determines the level of competitive intensity in your chosen industry? (1.5 marks)
- Assess the threat of new entrants, and substitute products/ services for your chosen industry. (1 mark)
- Is your chosen industry attractive for investment? Why or why not? (1 mark)
Answers
- Discussion questions
- Answer Q1-
- Answer Q2-
- Critical thinking
- Answer Q1-
- Answer Q2-
- Answer Q3-
- Answer Q4-
110 PART 2 PORTER'S APPROACH TO INDUSTRY ANALYSIS Michael Porter, an authority on competitive strategy, contends that corporation is mes con cemed with the intensity of competition within its incestry. The level of this intensity is deter mined by basic competitive forces, as depicted in Figure 1-1. The collective strength of these forces he contends, determines the ultimate profit potential in the industry, where profit per tential is measure in terms of long-run on invested capital carefully scanning is industry, a corporation must use the importance to its access of each of six faces that of new entrant, rivalry among existing firm, threat of substitute products or services, har paining power of buyers, burgaining power of suppliers and relative power of other stakehold n. The stronger each of these forces, the more limited companies are in their ability to use prices and earn greater polits. Although Pontet mention only five forces a sithther stakeholders-sadited here to reflect the power that government local communities and other groups from the task environment wield over industry activities Using the model in Figure 4-1, aigh fonce can be regarded as that because it is likely to reduce it. A low force, in contrast, can be viewed as an opportunity because it may al How the company to carreater profits. In the short run, there forest constraints on a company activities to the long rum, however, it may be possible for a company, through its choice of Mrategy to change the strength of one or more of the free to the company's tape. For example Dell's early one of the Internet to market in computer was an effective way to negate the bargaining power of distribution in the PC industry A strategist can asulye any industry by eating each competitive force as high medium of low in trength. For example, the global thetic shoe industry could he rate as follow ROURE Forces Driving Industry Competition Potential Entrants The of w eve Power of Union Gemers Spew interest Groot Other Stakeholders Industry Competitors Bar Power of buyers thuyers Supplier Rewry Among Bargaining Power of Supplies That Products or Service Subtites SOURCE: The COMPETITIVE AVANTAGL la Competente Cris There w III O >




