Question: Structuring a Make-or-Buy Problem Fresh Foods, a large restaurant chain, needs to determine if it would be cheaper to produce 5,000 units of its main
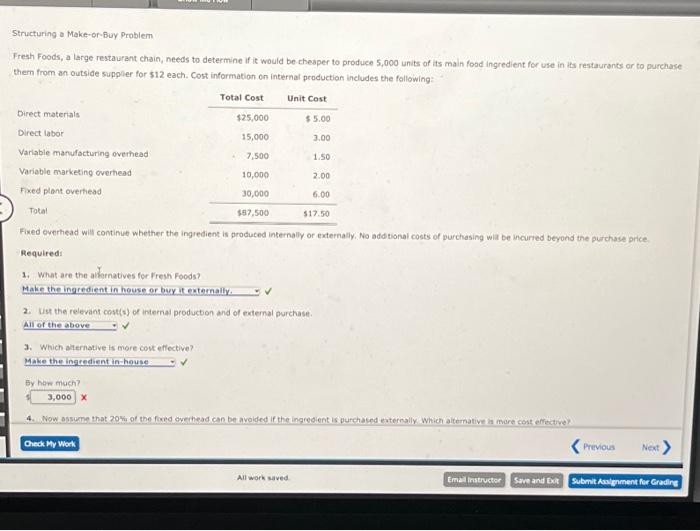
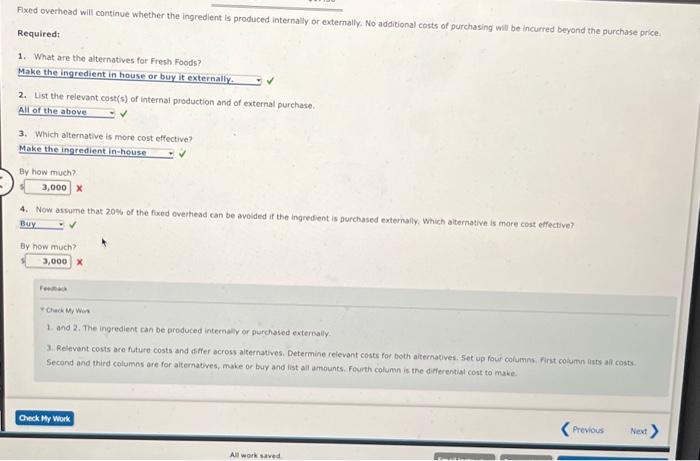
Structuring o Make-or-Buy Problem Fresh Foods, a large restaurant chain, needs to determine if it would be cheaper to produce 5,000 units of its maln foad ingredient for use in its restaurants or to purchase them from an outside suppler for $12 each. Cost information on internal production includes the following: Fixed overhead will continue whether the ingredient is produced internally or externally, No add tional costs of purchesing wia be incurred beyond the purchase price. Required: 1. What are the akharnatives for Frem Foods? Make the ingredient in house or bay it externally. 2. Iut the relevant costof of internal production and of external purchase. Fixed overhoad will continue whether the ingredient is produced internally or externally, No additional costs of purchasing will be incurred beyond the purchase price. Required: 1. What are the alternatives for Fresh Foods? 2. List the relevant cost(s) of internal production and of external purchase. 3. Which alternative is more cost effertive? By how much? 1 x 4. Now assume that 20% of the foxed overhead can be avoided if the ingredient is purchased externally. Which alternative is more cost effective? By how much? 1 x rotinus. 1. and 2. The ingredient can be produced internaly or purchased enterivily. 3. Relevant costs ace future costs and siffer across alternatives. Determine reievant costs for both aiternatives. Set up four columns, finst coiumn iuss all costs. Second and third columns are for alternatives, make or buy and list all amounts. Fourth column is the differential cost to make. Structuring o Make-or-Buy Problem Fresh Foods, a large restaurant chain, needs to determine if it would be cheaper to produce 5,000 units of its maln foad ingredient for use in its restaurants or to purchase them from an outside suppler for $12 each. Cost information on internal production includes the following: Fixed overhead will continue whether the ingredient is produced internally or externally, No add tional costs of purchesing wia be incurred beyond the purchase price. Required: 1. What are the akharnatives for Frem Foods? Make the ingredient in house or bay it externally. 2. Iut the relevant costof of internal production and of external purchase. Fixed overhoad will continue whether the ingredient is produced internally or externally, No additional costs of purchasing will be incurred beyond the purchase price. Required: 1. What are the alternatives for Fresh Foods? 2. List the relevant cost(s) of internal production and of external purchase. 3. Which alternative is more cost effertive? By how much? 1 x 4. Now assume that 20% of the foxed overhead can be avoided if the ingredient is purchased externally. Which alternative is more cost effective? By how much? 1 x rotinus. 1. and 2. The ingredient can be produced internaly or purchased enterivily. 3. Relevant costs ace future costs and siffer across alternatives. Determine reievant costs for both aiternatives. Set up four columns, finst coiumn iuss all costs. Second and third columns are for alternatives, make or buy and list all amounts. Fourth column is the differential cost to make
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


