Question: SUBJECT: PHYSICS FOR ENGINEERS TOPIC: FRICTION NOTE: I NEED FULL COMPLETE SOLUTION AND CLEAR, READABLE. INCLUDE YOUR FORMULA USE! THANK YOU! COMPLETE THE TABLE BELOW
SUBJECT: PHYSICS FOR ENGINEERS
TOPIC: FRICTION
NOTE: I NEED FULL COMPLETE SOLUTION AND CLEAR, READABLE. INCLUDE YOUR FORMULA USE! THANK YOU! COMPLETE THE TABLE BELOW
write (handwritten OR TYPEWRITTEN) your complete solutions in clean bond paper . Write legibly using engineering lettering.


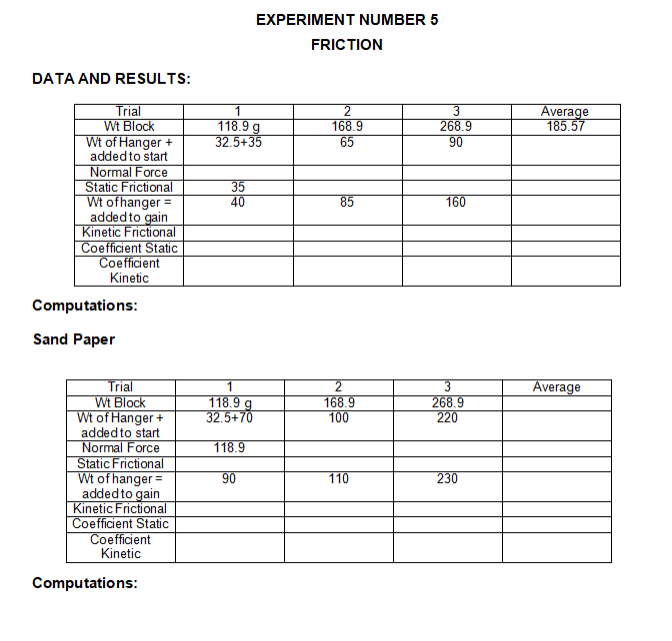
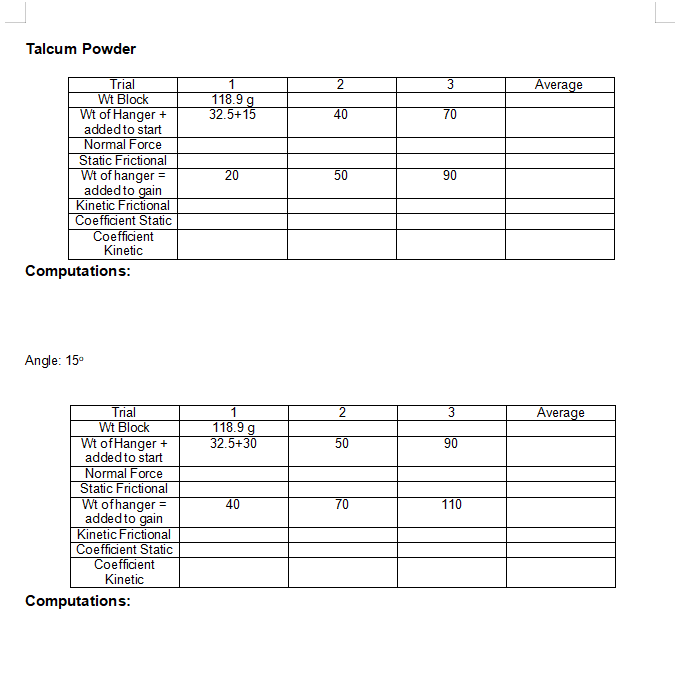
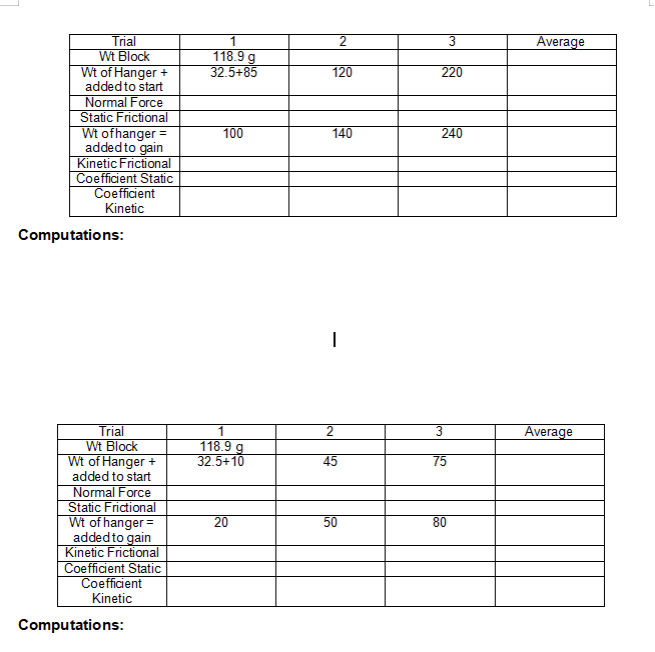

EXPERIMENT NUMBER 5 FRICTION INTRODUCTION: Friction is the resistance to motion offered by rubbing surfaces in contact. The resistance is in the form of frictional force, (f), and acting parallel to the surface of contact and against impending motion is referred to as static force of friction while the force present while there is motion is known as kinetic force of friction. Friction is likewise affected by the component of the force along the normal plane of contact. OBJECTIVES: At the end of the experiment, the students must be able to: Define Frictional Force. Resolve the coefficient of static and kinetic friction. Compare the frictional force experienced by moving the object out of different surfaces of contact. MATERIALS: 1 Wooden block 100 cm String 1 set of masses . . . 1 Plastic or metal buckets 1 paste or glue 1 sand paper 1 kg dry sand . 1 Plane with pulley 10 grams talcum powder . 1 protractor PROCEDURE: FRICTION ON A HORIZONTAL PLANE 1. Place the wooden block on a level plane and attach it to a string with hanger on the other end. Pass the string over the pulley at the edge of the plane. 2. Put small weights or sand on the hanger until the block slightly moves when the plane is highly tapped. Record the block weight and the weights of the hanger.3. Continue adding weights to the hanger to gain uniform motion. Record the block weight and the weights with the hanger. 4. Repeat step 1-3 but add 50-g to block then 100 g to the block. In step 1-4 the system illustrates a normal surface. 5. Repeat steps 1-5 but line the plane with a sand paper. The system illustrates roughened surface. 6. Repeat steps 1-5 but sprinkle talcum powder over the inclined plane. The system illustrates lubricated surface. 7. From the data obtained, solve the coefficients of static ad kinetic friction. FRICTION ON AN INCLINED PLANE 1. Place the block on the horizontal plane. Slowly tilt one end of the plane until the block slides down with uniform velocity. 2. Measure the angle of repose. 3. Repeat steps 1-2 with the sand paper-lined plane; then with talcum powder.EXPERIMENT NUMBER 5 FRICTION DATA AND RESULTS: Trial 2 3 Average Wt Block 118.9g 168.9 268.9 185.57 Wt of Hanger + 32.5+35 65 90 added to start Normal Force Static Frictional 35 Wt ofhanger = 40 85 160 added to gain Kinetic Frictional Coefficient Static Coefficient Kinetic Computations: Sand Paper Trial 2 3 Average Wt Block 118.9 g 168.9 268.9 Wt of Hanger + 32.5+70 100 220 added to start Normal Force 118.9 Static Frictional Wt of hanger = 90 110 230 added to gain Kinetic Frictional Coefficient Static Coefficient Kinetic Computations:Talcum Powder Trial 2 Average Wt Block 118.9g Wt of Hanger + 32.5+15 40 70 added to start Normal Force Static Frictional Wt of hanger = 20 50 90 added to gain Kinetic Frictional Coefficient Static Coefficient Kinetic Computations: Angle: 15 Trial 1 2 3 Average Wt Block 118.9 g Wt ofHanger + 32.5+30 50 90 added to start Normal Force Static Frictional Wt ofhanger = 40 70 110 added to gain Kinetic Frictional Coefficient Static Coefficient Kinetic Computations:Trial 2 3 Average Wt Block 118.9g Wt of Hanger + 32.5+85 120 220 added to start Normal Force Static Frictional Wt ofhanger = 100 140 240 added to gain Kinetic Frictional Coefficient Static Coefficient Kinetic Computations: = Trial 2 3 Average Wt Block 118.9 g Wt of Hanger + 32.5+10 45 75 added to start Normal Force Static Frictional Wt of hanger = 20 50 80 added to gain Kinetic Frictional Coefficient Static Coefficient Kinetic Computations:L QUESTIONS: 1. Differentiate coefficient of static friction from coefficient of kinetic friction. 2. Which has a greater coefficient value? The coefficient of static friction or the coefficient of kinetic friction? Explain. CONCLUSION
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


