Question: Submit the following two files to the relevant dropbox on course website. 1. One single pdf file of your report. This file should be



![[17]](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2023/09/64f2a04980835_1693622346361.jpg)
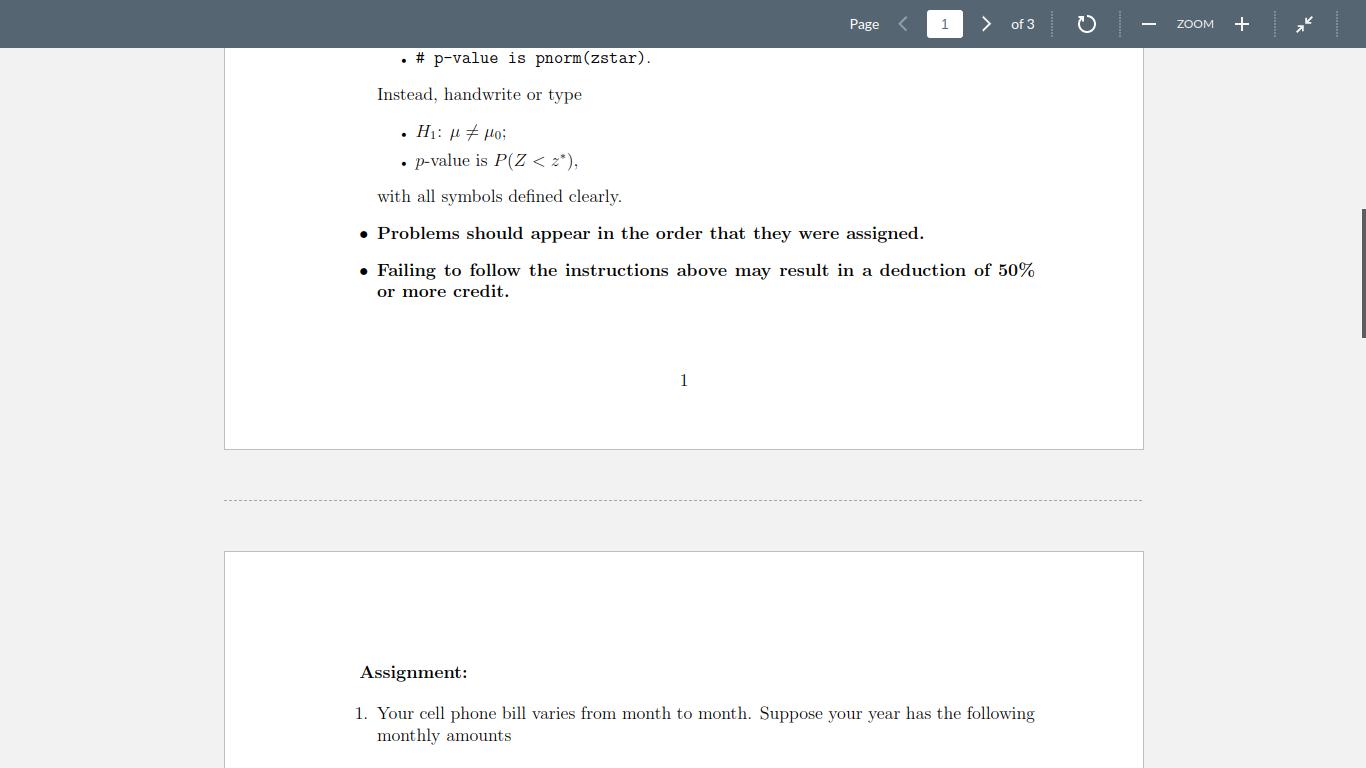
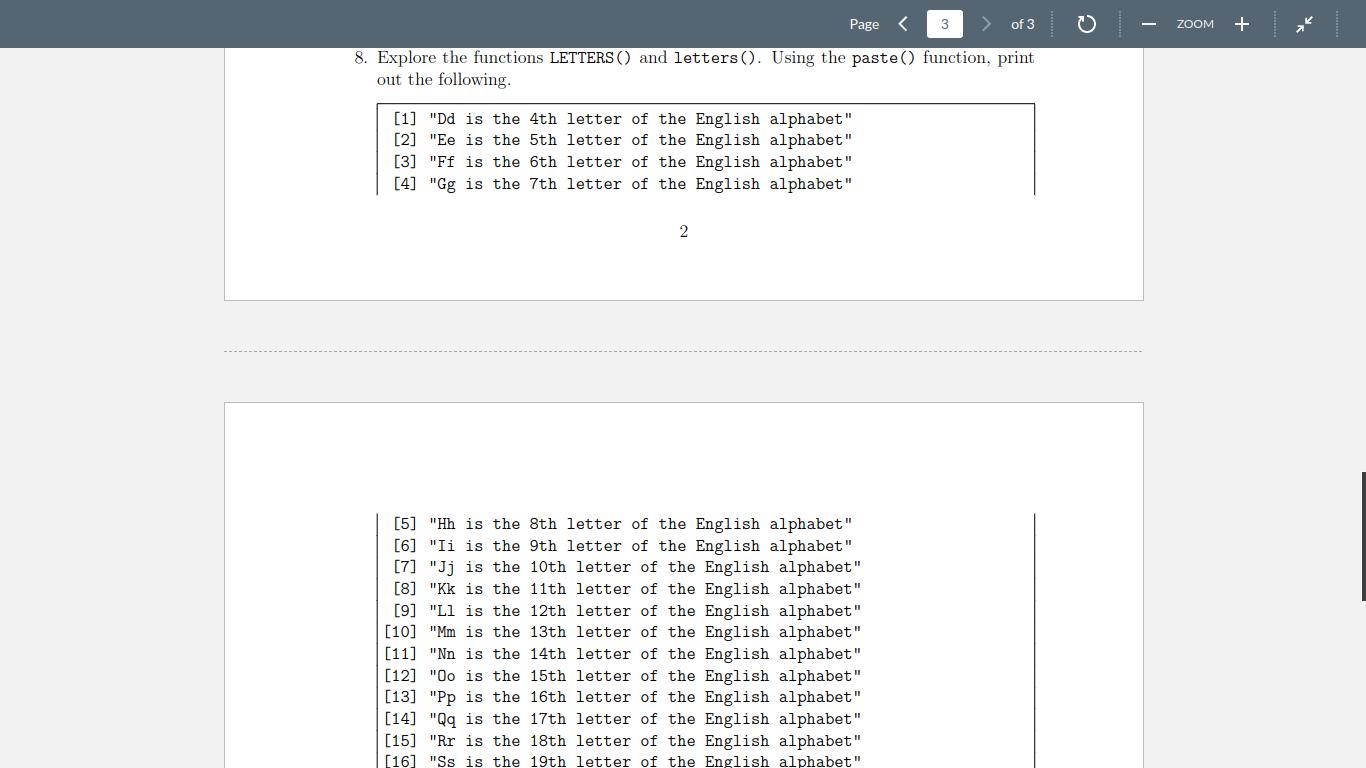
Submit the following two files to the relevant dropbox on course website. 1. One single pdf file of your report. This file should be named HWx_Last.pdf, where x is the homework number and Last is your last name (e.g., HW1_Lee.pdf). Show your steps, code, and output in your report so that the grader can see your work without actually running your code. You do not need to explain your code line by line, but you should provide enough details so that the grader can understand the flow of your code. 2. One single R file of your code. This file should be named HWx_Last.R, where x and Last are the same as before. This file is to allow the grader to verify your work if necessary. The grader should be able to run your code without modification except (possibly) changing the paths that you use for filenames, etc. In summary, your report should stand alone! You are not allowed to use any non-Base R package unless otherwise spec- ified. Do not use R comments to answer a theoretical question. Handwrite or type your answer clearly with appropriate statistical notations. For example, do not write something like . # H1: mu != mu0; # p-value is pnorm (zstar). Instead, handwrite or type H: o; . p-value is P(Z < z*), with all symbols defined clearly. Problems should appear in the order that they were assigned. . # p-value is pnorm (zstar). Instead, handwrite or type Page 1 1 of 3 : # ; p-value is P(Z < z*), with all symbols defined clearly. Problems should appear in the order that they were assigned. Failing to follow the instructions above may result in a deduction of 50% or more credit. Assignment: 1. Your cell phone bill varies from month to month. Suppose your year has the following monthly amounts ZOOM + 46 33 39 37 46 30 48 32 49 35 30 48 Page 2 of 3 Explore the function scan () and use it to read the data. How much did you spend this year on the cell phone? What is the smallest amount you spent in a month? What is the largest? How many months was the amount greater than 40? What percentage was this? Answer all questions using R. 2. Using the rep() function once, create a vector of four 2s, then three 3s, then two 5s. Next, using the rep() and seq() functions, create a vector where each of (1,3,5,7,9) is replaced by two repeats of itself. First do this with the argument each, then with the argument times. 3. For a nonnegative integer k, k! can be computed using the command factorial (k). Using the function factorial () once, print out the vector (1, 2, 3, 4, 5!). Do this again using the function cumprod(). 4. Let x = (1, 2, 3, 4, 5!) from Problem B. Compute the sample mean and standard deviation of using only the sum () and length() functions. Verify your results using the built-in mean and standard deviation functions. 5. Let x, i = 1,..., 5, be the ith element of x = (1, 2, 3, 4, 5!). Compute log x; (i.e., the natural logarithm) and log3.. Also, verify the equality log (I-1) = Ei=1 log.x. 6. For observations y, i = 1,..., n, the arithmetic mean is defined as A = n= [1 Yi; the geometric mean is defined as JG = (IT-19); the harmonic mean is defined as 1/n. JH = n(1). The sample mean of x = (1!, 2!, 3!, 4!, 5!) computed in Problem is in fact the arithmetic mean of x. Here, compute the geometric and harmonic means of r. Verify your results using the functions geometric.mean() and harmonic.mean() in the package psych. Is there an equality/inequality relating the three means? 7. Assign the vector (2,8, 3, 7, 4, 1,9) to an object. Using one single command, find the elements of the vector that are even or greater than 7, multiply those elements by -1 and use them to replace the original elements. Print out the new vector. (Hint: You may find the %% operator useful. Explore it using the command ?"%%".) ZOOM + 46 33 39 37 46 30 48 32 49 35 30 48 Page 2 of 3 Explore the function scan () and use it to read the data. How much did you spend this year on the cell phone? What is the smallest amount you spent in a month? What is the largest? How many months was the amount greater than 40? What percentage was this? Answer all questions using R. 2. Using the rep() function once, create a vector of four 2s, then three 3s, then two 5s. Next, using the rep() and seq() functions, create a vector where each of (1,3,5,7,9) is replaced by two repeats of itself. First do this with the argument each, then with the argument times. 3. For a nonnegative integer k, k! can be computed using the command factorial (k). Using the function factorial () once, print out the vector (1, 2, 3, 4, 5!). Do this again using the function cumprod(). 4. Let x = (1, 2, 3, 4, 5!) from Problem B. Compute the sample mean and standard deviation of using only the sum () and length() functions. Verify your results using the built-in mean and standard deviation functions. 5. Let x, i = 1,..., 5, be the ith element of x = (1, 2, 3, 4, 5!). Compute log x; (i.e., the natural logarithm) and logg i. Also, verify the equality log (1) = Ei log.x. 6. For observations y, i = 1,..., n, the arithmetic mean is defined as A = n= [1 Yi; the geometric mean is defined as JG = (IT-19); the harmonic mean is defined as 1/n. JH = n(1). The sample mean of x = (1!, 2!, 3!, 4!, 5!) computed in Problem is in fact the arithmetic mean of x. Here, compute the geometric and harmonic means of r. Verify your results using the functions geometric.mean() and harmonic.mean() in the package psych. Is there an equality/inequality relating the three means? 7. Assign the vector (2,8, 3, 7, 4, 1,9) to an object. Using one single command, find the elements of the vector that are even or greater than 7, multiply those elements by -1 and use them to replace the original elements. Print out the new vector. (Hint: You may find the %% operator useful. Explore it using the command ?"%%".) ZOOM + Page < of 3 8. Explore the functions LETTERS () and letters (). Using the paste() function, print out the following. [1] "Dd is the 4th letter of the English alphabet" [2] "Ee is the 5th letter of the English alphabet" [3] "Ff is the 6th letter of the English alphabet" [4] "Gg is the 7th letter of the English alphabet" 2 3 [5] "Hh is the 8th letter of the English alphabet" [6] "Ii is the 9th letter of the English alphabet" [7] "Jj is the 10th letter of the English alphabet" [8] "Kk is the 11th letter of the English alphabet" [9] "L1 is the 12th letter of the English alphabet" [10] "Mm is the 13th letter of the English alphabet" [11] "Nn is the 14th letter of the English alphabet" [12] "Oo is the 15th letter of the English alphabet" [13] "Pp is the 16th letter of the English alphabet" [14] "Qq is the 17th letter of the English alphabet" [15] "Rr is the 18th letter of the English alphabet" [16] "Ss is the 19th letter of the English alphabet" ZOOM + [17] "Tt is the 20th letter of the English alphabet [18] "xx in the 24th letter of the English alphabet [19] "Yy is the 25th letter of the English alphabet (20) "2z in the 26th letter of the English alphabet
Step by Step Solution
3.57 Rating (154 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Let 1 true average wear of brandA 2 true average wear of brandB null hy... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


