Question: Suppose a computer has an atomic Compare-and-Swap instruction, which has the following effect: CSW (a, b, c): if (a-c) { c = b, return (0);
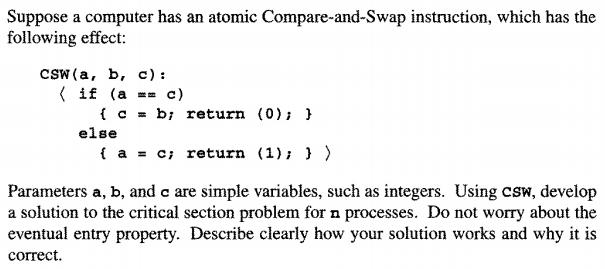
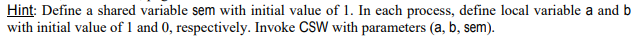
Suppose a computer has an atomic Compare-and-Swap instruction, which has the following effect: CSW (a, b, c): if (a-c) { c = b, return (0); else { a = c; return (1); } Parameters a, b, and c are simple variables, such as integers. Using csw, develop a solution to the critical section problem for n processes. Do not worry about the eventual entry property. Describe clearly how your solution works and why it is correct
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


