Question: Suppose S, T, U are physical quantities that satisfy the rule (#) a Sb Tc = U for some constants a, b, c. An
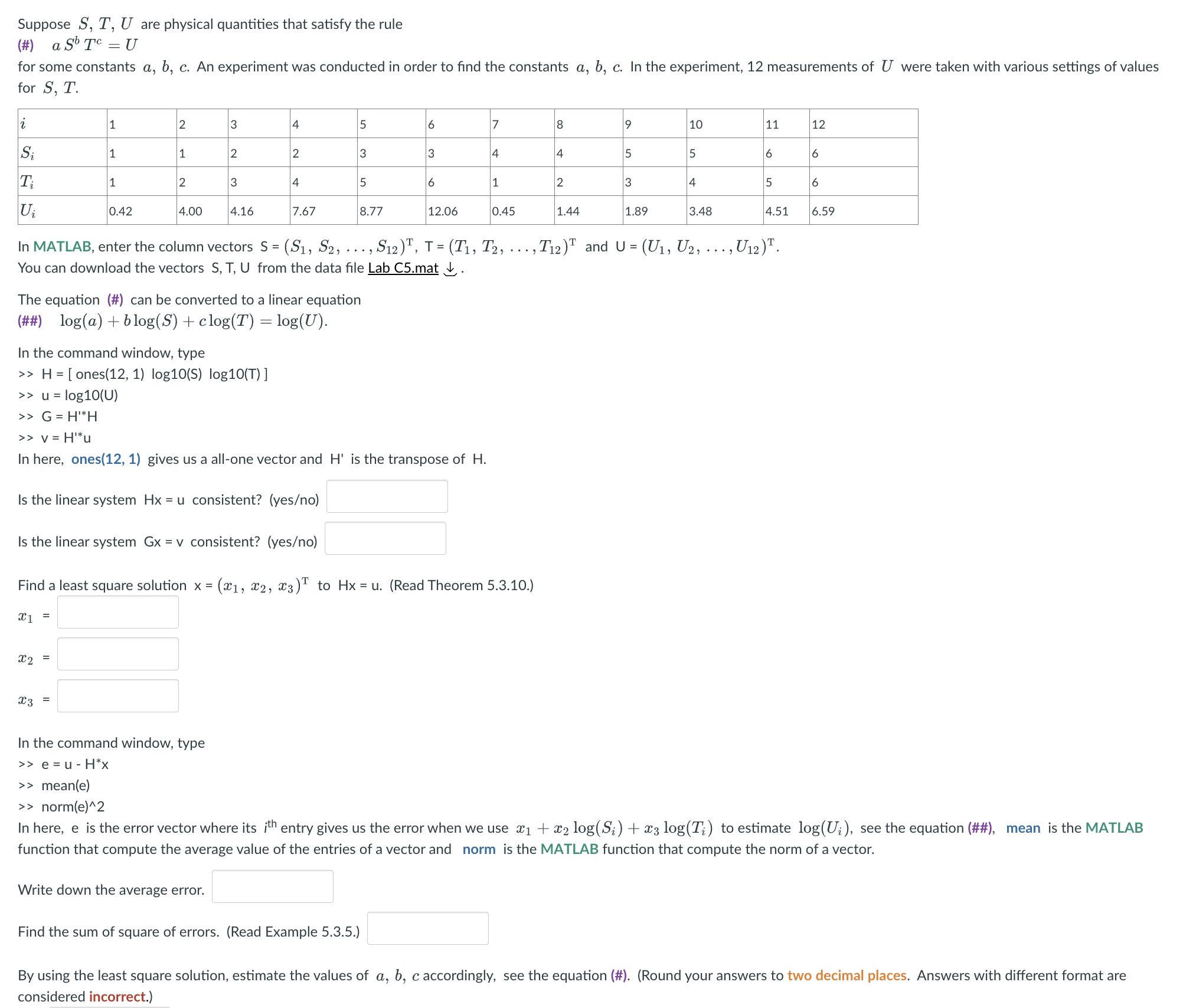
Suppose S, T, U are physical quantities that satisfy the rule (#) a Sb Tc = U for some constants a, b, c. An experiment was conducted in order to find the constants a, b, c. In the experiment, 12 measurements of U were taken with various settings of values for S, T. i Si Ti U 1 1 x1 = 1 X2 0.42 = 2 x3 = 1 2 4.00 Find a least square solution x = 3 2 3 4.16 4 Write down the average error. 2 Is the linear system Gx = v consistent? (yes/no) 4 7.67 The equation (#) can be converted to a linear equation (##) log(a) + blog(S) + clog(T) = log(U). 5 3 5 8.77 In the command window, type >> H = [ones(12, 1) log10(S) log10(T)] >> u = log10 (U) >> G = H'*H >> v = H*u In here, ones(12, 1) gives us a all-one vector and H' is the transpose of H. Is the linear system Hx = u consistent? (yes/no) In MATLAB, enter the column vectors S = (S, S2, ..., S12)T, T = (T1, T2, You can download the vectors S, T, U from the data file Lab C5.mat. 6 3 6 12.06 Find the sum of square of errors. (Read Example 5.3.5.) 7 4 1 0.45 (x, x2, x3) to Hx = u. (Read Theorem 5.3.10.) 8 4 2 1.44 9 5 3 1.89 10 5 4 3.48 ..., T12) and U = (U, U, 11 6 5 4.51 , U12)T. 12 6 6 In the command window, type >>e=u-H*x >> mean(e) >> norm(e)^2 In here, e is the error vector where its ith entry gives us the error when we use x + x log(S;) + x3 log(T;) to estimate log(U;), see the equation (##), mean is the MATLAB function that compute the average value of the entries of a vector and norm is the MATLAB function that compute the norm of a vector. 6.59 By using the least square solution, estimate the values of a, b, c accordingly, see the equation (#). (Round your answers to two decimal places. Answers with different format are considered incorrect.) In MATLAB, enter the column vectors S = (S, S2, ..., S12)T, T = (T1, T2, You can download the vectors S, T, U from the data file Lab C5.mat. The equation (#) can be converted to a linear equation (##) log(a) + blog(S) + clog(T) = log(U). In the command window, type >> H = [ones(12, 1) log10(S) log10(T)] >> u log10(U) >> G = H'*H >> v = H**u In here, ones(12, 1) gives us a all-one vector and H' is the transpose of H. Is the linear system Hx = u consistent? (yes/no) Is the linear system Gx = v consistent? (yes/no) Find a least square solution x = = (x1, x2, x3)T to Hx = u. (Read Theorem 5.3.10.) x1 = x2 x3 = In the command window, type >>e=u-H*x >> mean(e) >> norm(e)^2 In here, e is the error vector where its ith entry gives us the error when we use x + x log(S;) + x3 log(T;) to estimate log(U;), see the equation (##), mean is the MATLAB function that compute the average value of the entries of a vector and norm is the MATLAB function that compute the norm of a vector. Write down the average error. = Find the sum of square of errors. (Read Example 5.3.5.) a = b = , T2) and U = (U, U2, ..., U12). By using the least square solution, estimate the values of a, b, c accordingly, see the equation (#). (Round your answers to two decimal places. Answers with different format are considered incorrect.) C =
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


