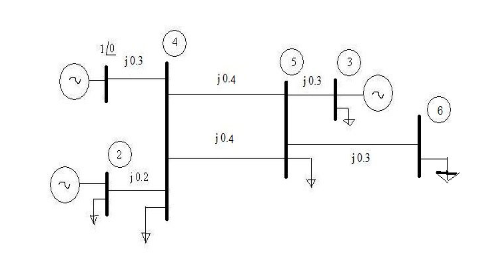
Question: Suppose the following are specified: PG 2 = 0 . 5 , V 2 = 1 . 0 5 , PG 3 = 1 .
Suppose the following are specified:
PG V PG V
PL PL PL PL PL
QL QL QL QL QL
a Classify the bus types and write out the powerflow equations.
b Compute the DC powerflow solution.
c Starting from the DC powerflow solution, implement the NewtonAlgorithm till all the power mismatch errors are smaller than pu How many iterations does it take to reach convergence?
d Starting from the DC powerflow solution, implement the fast decoupled powerflow algorithm until all the power mismatches are smaller than pu How many iterations does it take to reach the convergence?
e Repeat parts b c and d when each of the loads PLi and QLi and generations PGi specified become twice the previous values. Comment on your result.
My current code: function ybus Peq Qeq theta powerflowanalysis
Form Ybus matrix and return power flow equations, including DC power flow solution
Line data: frombus, tobus, R X B
linedata ;
;
;
;
;
;
fb linedata:; From bus
tb linedata:; To bus
r linedata:; Resistance
x linedata:; Reactance
b linedata:; Line charging
z r i x; Impedance
y z; Admittance
b i b; Ground admittance
nbus maxmaxfb maxtb; Number of buses
nbranch lengthfb; Number of branches
ybus zerosnbus nbus; Initialize Ybus matrix
Offdiagonal elements
for k :nbranch
ybusfbk tbk ybusfbk tbk yk;
ybustbk fbk ybusfbk tbk; Symmetric entry
end
Diagonal elements
for m :nbus
for n :nbranch
if fbn m tbn m
ybusm m ybusm m yn bn;
end
end
end
Display the Ybus matrix
dispYbus Matrix:;
dispybus;
Form the power flow equations for real P and reactive Q power
Peq Qeq formpowerflowequationsybus;
dispReal Power Equations P:;
dispPeq;
dispReactive Power Equations Q:;
dispQeq;
DC Power Flow Solution with specified power and voltage values
theta dcpowerflowybus;
dispDC Power Flow Voltage Angles theta in radians:;
disptheta;
end
function Peq Qeq formpowerflowequationsybus
Retrieve power flow equations real and reactive
n sizeybus; Number of buses
V symVn 'real'; Voltage magnitudes
theta symthetan 'real'; Voltage angles
Initialize symbolic power equations
Peq symzerosn;
Qeq symzerosn;
for i :n
for j :n
if i ~ j
Contributions to Pi and Qi from bus j
Peqi Peqi Vi Vj
realybusi j costhetai thetaj
imagybusi j sinthetai thetaj;
Qeqi Qeqi Vi Vj
realybusi j sinthetai thetaj
imagybusi j costhetai thetaj;
else
Diagonal selfcontribution
Peqi Peqi Vi realybusi i;
Qeqi Qeqi Vi imagybusi i;
end
end
end
Simplify equations for better readability
Peq simplifyPeq;
Qeq simplifyQeq;
end
function theta dcpowerflowybus
Compute DC power flow solution angles only
Known values for power generation and loads
PG ; ; ; ; ; ; Real power generation at buses to
PL ; ; ; ; ; ; Real power load at buses to
Net power injections P PG PL
P PG PL;
P; Slack bus power set to for DC power flow
Convert Ybus to susceptance matrix B ignore resistance
B imagybus;
Remove the slack bus assume bus as the slack bus
Breduced B:end, :end;
Preduced P:end;
Solve for voltage angles theta excluding the slack bus
thetareduced Breduced Preduced;
Append the slack bus angle theta
theta ; thetareduced;
end
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


