Question: Suppose X1, . . . , Xn is a random sample from the Normal(0, 2) distribution and consider three situations: 1. TestH0: ??0versusH1: ?>0withtest: RejectH0
Suppose X1, . . . , Xn is a random sample from the Normal(0, 2) distribution and consider three situations:
1. TestH0: ??0versusH1: ?>0withtest: RejectH0 iff?nX ?n/2>C1
2. Test H0: ? = 0 versus H1: ? ?= 0 with test: Reject H0 iff |?nX ?n/2| > C2
3. TestH0: ??0versusH1: ?
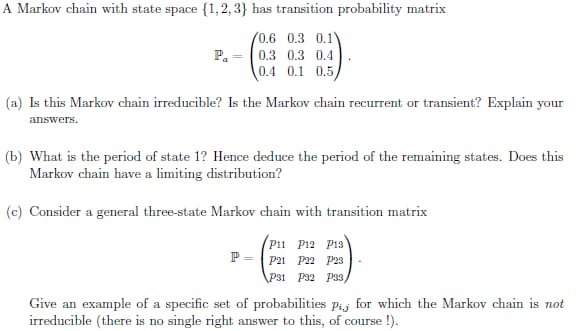
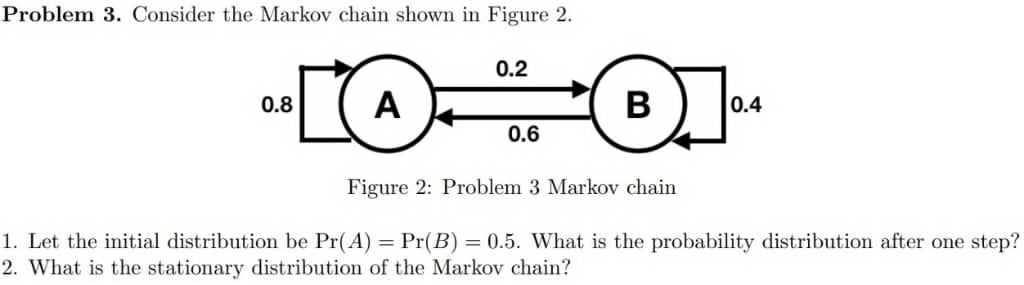

A Markov chain with state space {1, 2, 3) has transition probability matrix 0.6 0.3 0.1\\ P. = 0.3 0.3 0.4 0.4 0.1 0.5 (a) Is this Markov chain irreducible? Is the Markov chain recurrent or transient? Explain your answers. (b) What is the period of state 1? Hence deduce the period of the remaining states. Does this Markov chain have a limiting distribution? (c) Consider a general three-state Markov chain with transition matrix Pit P12 P13 P = P21 P22 P23 P31 P32 P33 Give an example of a specific set of probabilities paj for which the Markov chain is not irreducible (there is no single right answer to this, of course !).Problem 3. Consider the Markov chain shown in Figure 2. Figure 2: Problem 3 Markov chain 1' Let the initial distribution be Pr(A) = Pr(B) = 0.5. What is the probability distribution after one step? 2. What is the stationary distribution of the Markov chain? State-space equation of a linear autonomous system are given below -5/3 4/3 a x ( t ) = - 1/ 3 0 7/3 O - 2 a ) find the eat state transition matrix of system by the Lapalace transform b ) find the At state transition matrix of system with the Cayley - Hamilton Theorem ( ) find the efit state transition matrix of system using eigenvectors
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


