Question: . Swaps Carter Enterprises can issue floating-rate debt at LIBOR + 1% or fixed-rate debt at 10%. Brence Manufacturing can issue floating-rate debt at LIBOR
.

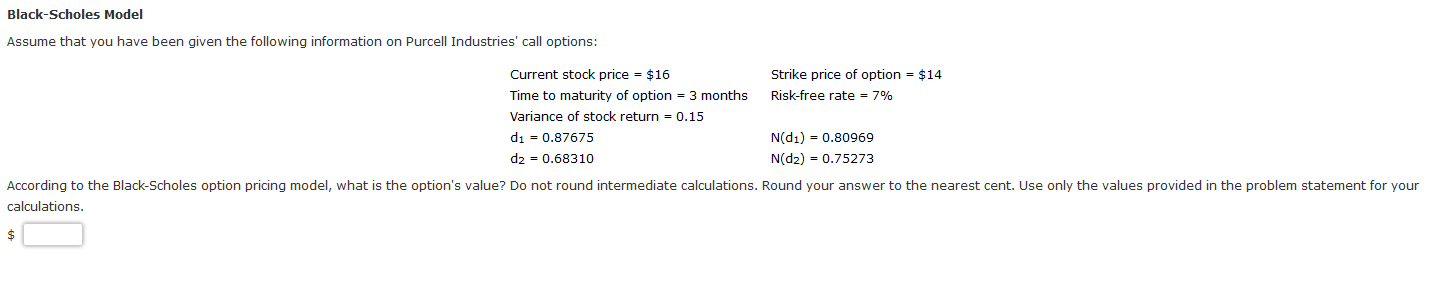
Swaps Carter Enterprises can issue floating-rate debt at LIBOR + 1% or fixed-rate debt at 10%. Brence Manufacturing can issue floating-rate debt at LIBOR + 2.9% or fixed-rate debt at 12%. Suppose Carter issues floating-rate debt and Brence issues fixed-rate debt. They are considering a swap in which Carter makes a fixed-rate payment of 7.85% to Brence and Brence makes a payment of LIBOR to Carter. What are the net payments of Carter and Brence if they engage in the swap? Round your answers to two decimal places. Use a minus sign to enter negative values, if any. Net payment of Carter: % Net payment of Brence: -(LIBOR + %) Put-Call Parity The current price of a stock is $33, and the annual risk-free rate is 3%. A call option with a strike price of $32 and with 1 year until expiration has a current value of $6.92. What is the value of a put option written on the stock with the same exercise price and expiration date as the call option? Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to the nearest cent. $ Black-Scholes Model Assume that you have been given the following information on Purcell Industries' call options: Current stock price = $16 Strike price of option = $14 Time to maturity of option = 3 months Risk-free rate = 7% Variance of stock return = 0.15 di = 0.87675 N(di) = 0.80969 dz = 0.68310 N(D2) = 0.75273 According to the Black-Scholes option pricing model, what is the option's value? Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to the nearest cent. Use only the values provided in the problem statement for your calculations. $
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


