Question: Table 1: Historical Demand Week 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Atlanta 120 110 100 90 80 130110 90 100 100
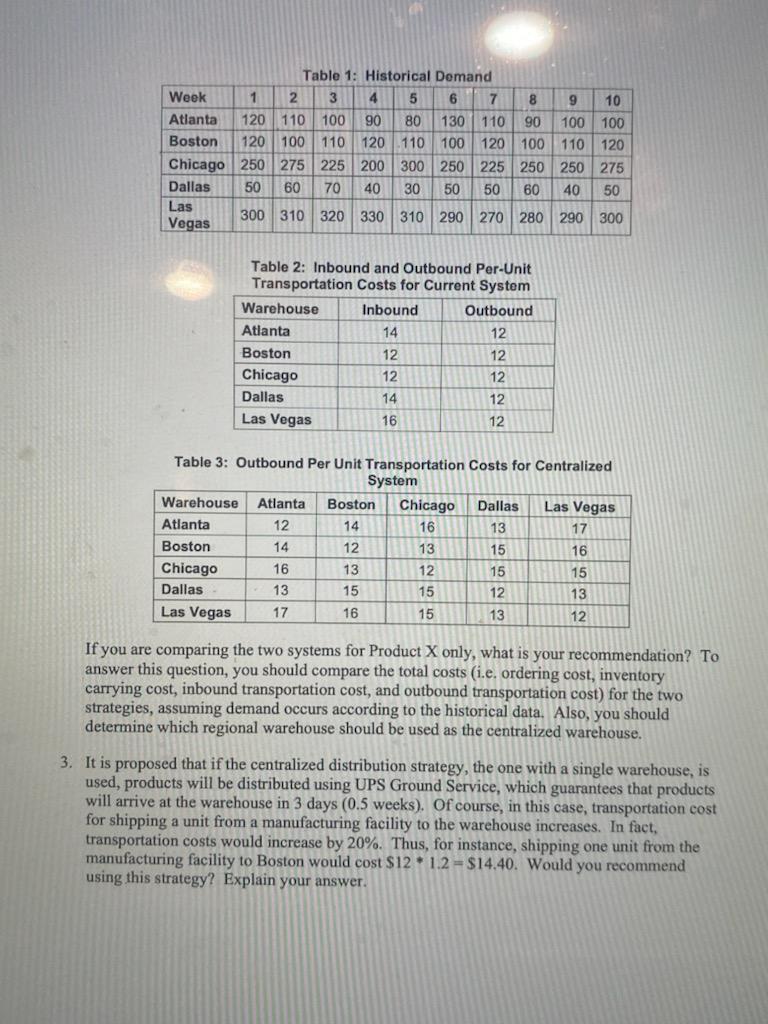

Table 1: Historical Demand Week 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Atlanta 120 110 100 90 80 130110 90 100 100 Boston 120 100 110 120 110 100 120 100 | 110 120 Chicago 250 275 225 200 300 250 225 250 250 275 Dallas 50 60 70 40 30 50 50 60 40 50 Las 300 310 320 330 | 310 290 270 280 290 300 Vegas Table 2: Inbound and Outbound Per-Unit Transportation Costs for Current System Warehouse Inbound Outbound Atlanta 14 12 Boston 12 12 Chicago 12 12 Dallas 14 12 Las Vegas 16 12 Table Warehouse Atlanta Boston Chicago Dallas Las Vegas Per Unit Transportation Costs for Centralized System Atlanta Boston Chicago Dallas Las Vegas 12 14 16 13 17 14 12 13 15 16 16 13 12 15 15 13 15 15 12 13 17 16 15 13 12 If you are comparing the two systems for Product X only, what is your recommendation? To answer this question, you should compare the total costs (i.e. ordering cost, inventory carrying cost, inbound transportation cost, and outbound transportation cost) for the two strategies, assuming demand occurs according to the historical data. Also, you should determine which regional warehouse should be used as the centralized warehouse. 3. It is proposed that if the centralized distribution strategy, the one with a single warehouse, is used, products will be distributed using UPS Ground Service, which guarantees that products will arrive at the warehouse in 3 days (0.5 weeks). Of course, in this case, transportation cost for shipping a unit from a manufacturing facility to the warehouse increases. In fact, transportation costs would increase by 20%. Thus, for instance, shipping one unit from the manufacturing facility to Boston would cost $12.1.2 = $14.40. Would you recommend using this strategy? Explain your answer. Adapted from D. Simchi-Levi, P. Kaminsky, and E. Simchi-Levi, "Designing& Managing the Supply Chain," 3nd edition. McGraw-Hill/Irwin: New York, NY. ABC Company is a manufacturer of plastics. The company has a single manufacturing facility in Utica, New York and distributes its products through five regional warehouses located in Atlanta, Boston, Chicago, Dallas, and Las Vegas. Under the current distribution system, the United States is partitioned into five major markets, each of which is served by a single regional warehouse in the market. That is, each customer is assigned to one market and receives deliveries from a single regional warehouse. The warehouse receive items from the manufacturing facility. It typically takes 4 weeks to satisfy an order placed by any of the regional warehouses. Currently, ABC provides regional warehouses with a service level of 95%. In recent years, ABC has seen a significant increase in competition and intense pressure from its customers to reduce costs. To do so, it would like to consider an alternative distribution strategy in which the five regional warehouses are replaced with a single, central warehouse that would process all customer orders. This warehouse will be one of the five existing warehouses. The company's CEO insists that whatever distribution strategy is used, ABC should maintain a service level of 95%. I Please address the following three questions: 1. A detailed analysis of customer demand in the five market areas reveals that the demand in the five regions is very similar; that is, it is common that if weekly demand in one region is above average, so is the weekly demand in other regions. How does this observation affect the attractiveness of the new system? Please explain (no calculations are needed). 2. To perform a rigorous analysis, you have identified a typical product, X. Table 1 provides historical data that includes weekly demand for this product for the last 10 weeks in each of the market areas. An order placed by a warehouse to the factory costs $2,000 per order and inventory carrying costs are $1.50 per unit per week. The costs of inbound and outbound transportation costs under the current distribution system are given in Table 2. Finally, Table 3 provides information about inbound and outbound transportation costs between the existing regional warehouses and the other market areas if a particular regional warehouse were to become the centralized warehouse






