Question: TABLE 2 Present value of $1 PV=$1/(1+i)n Table 6 Present Value of an Annuity Due of $1 PVAD =((1(1/(1+i)n))/i)(1+i) Table 3 Future Value of an
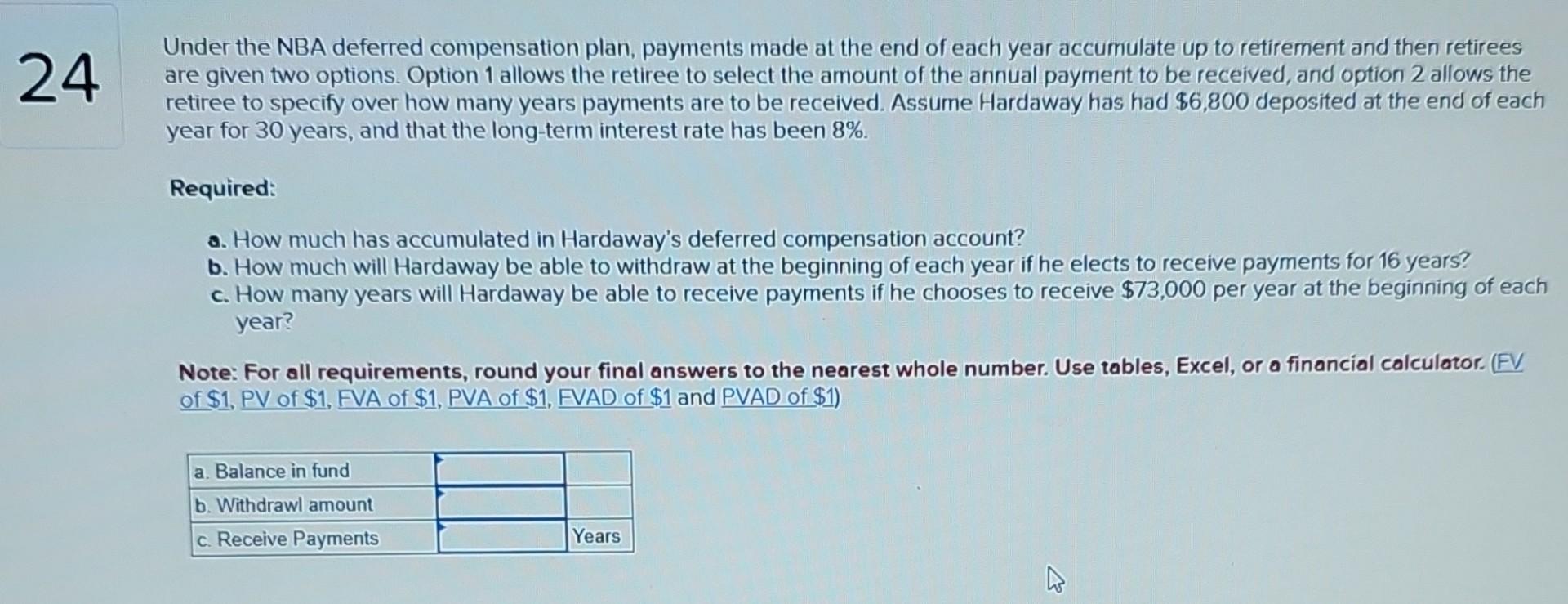
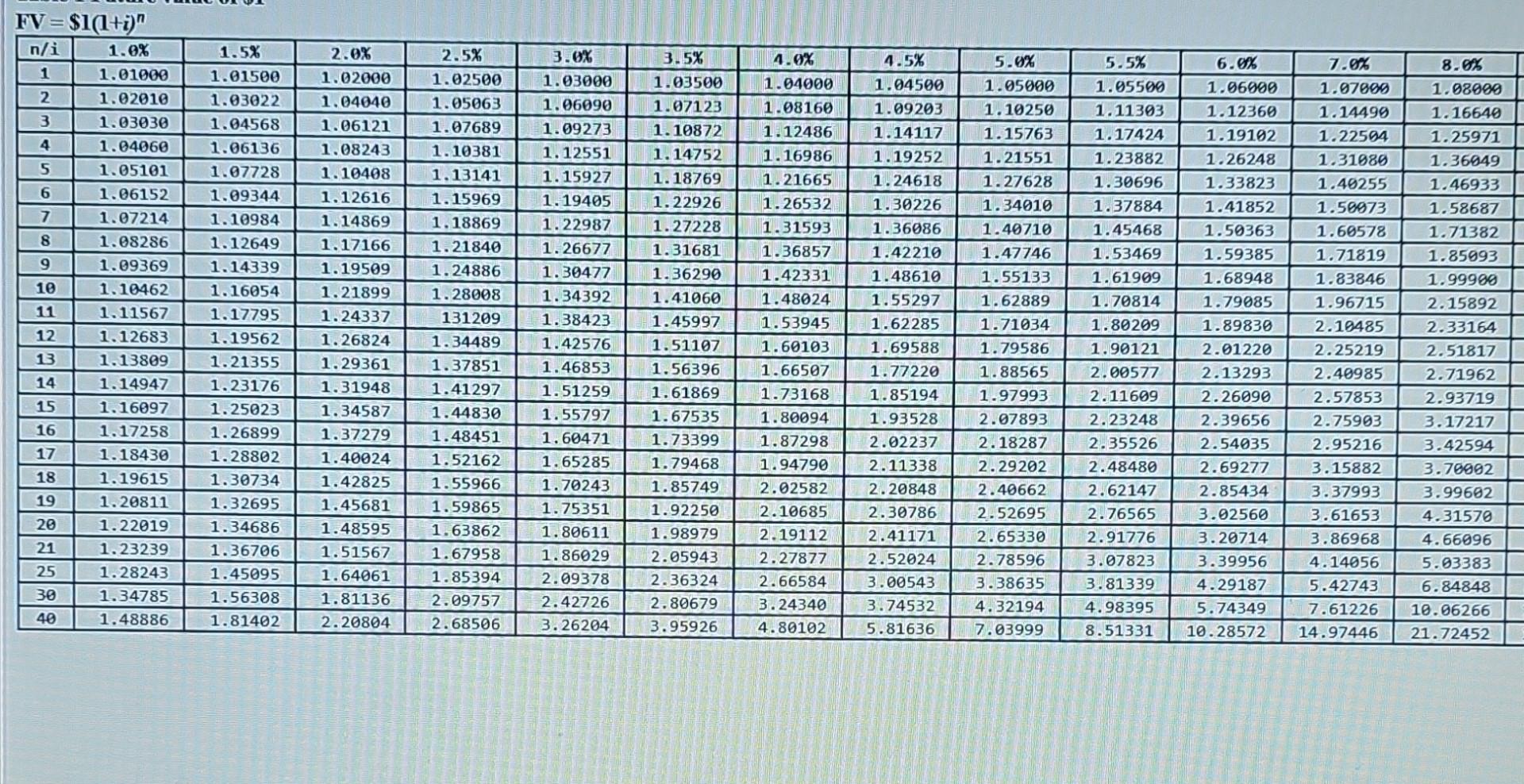
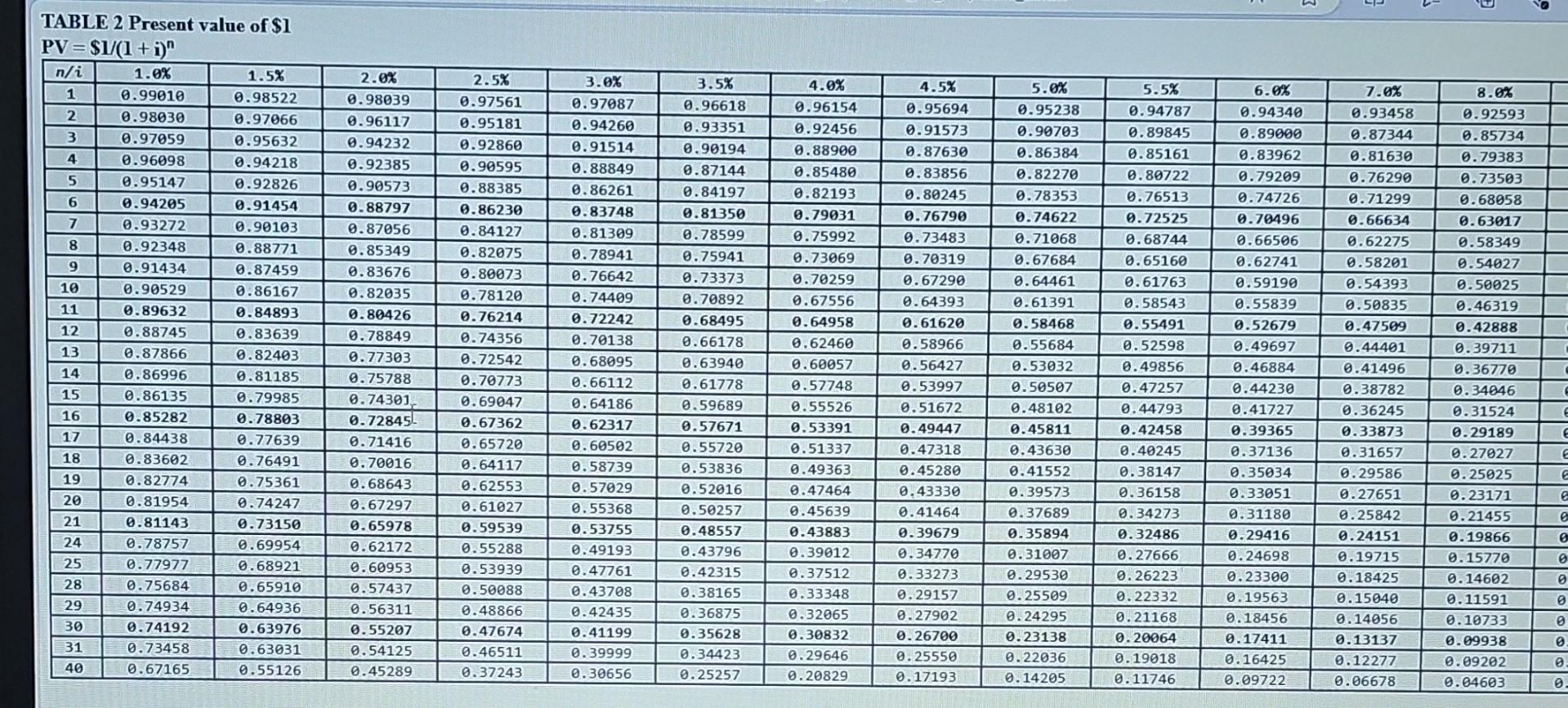
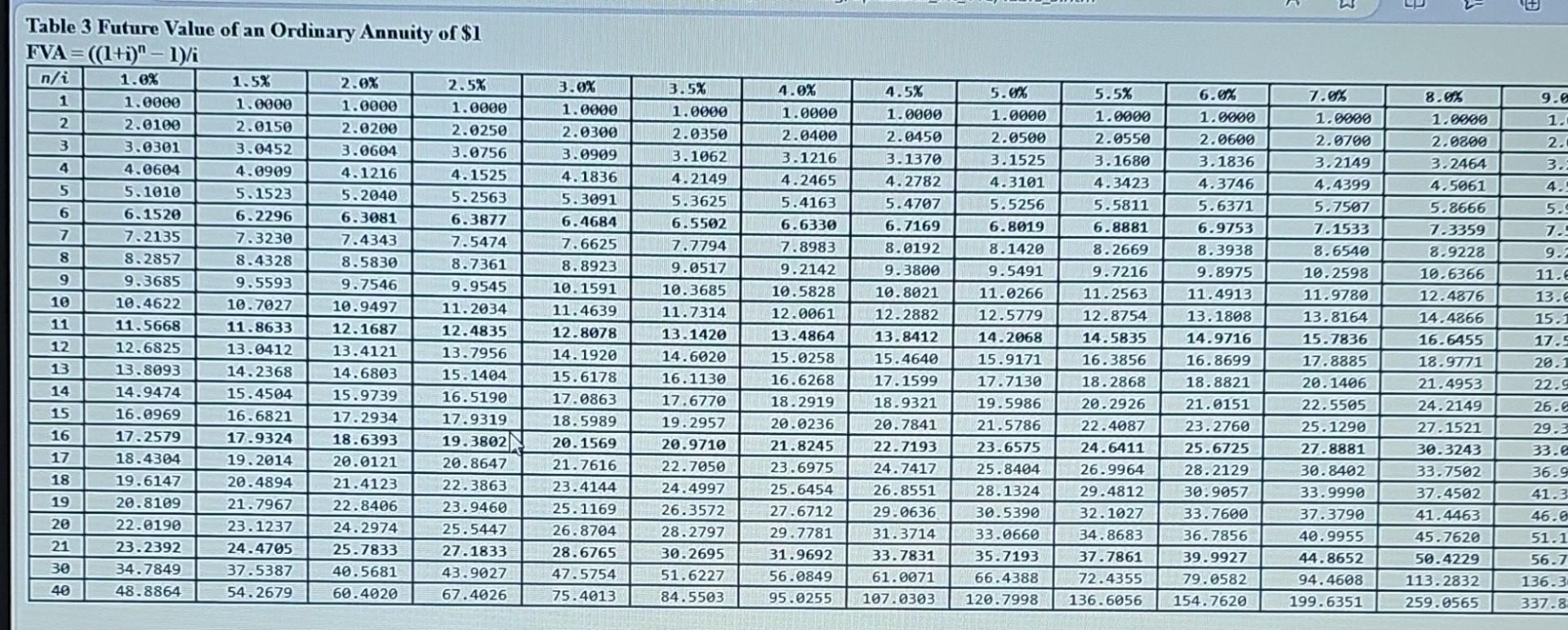
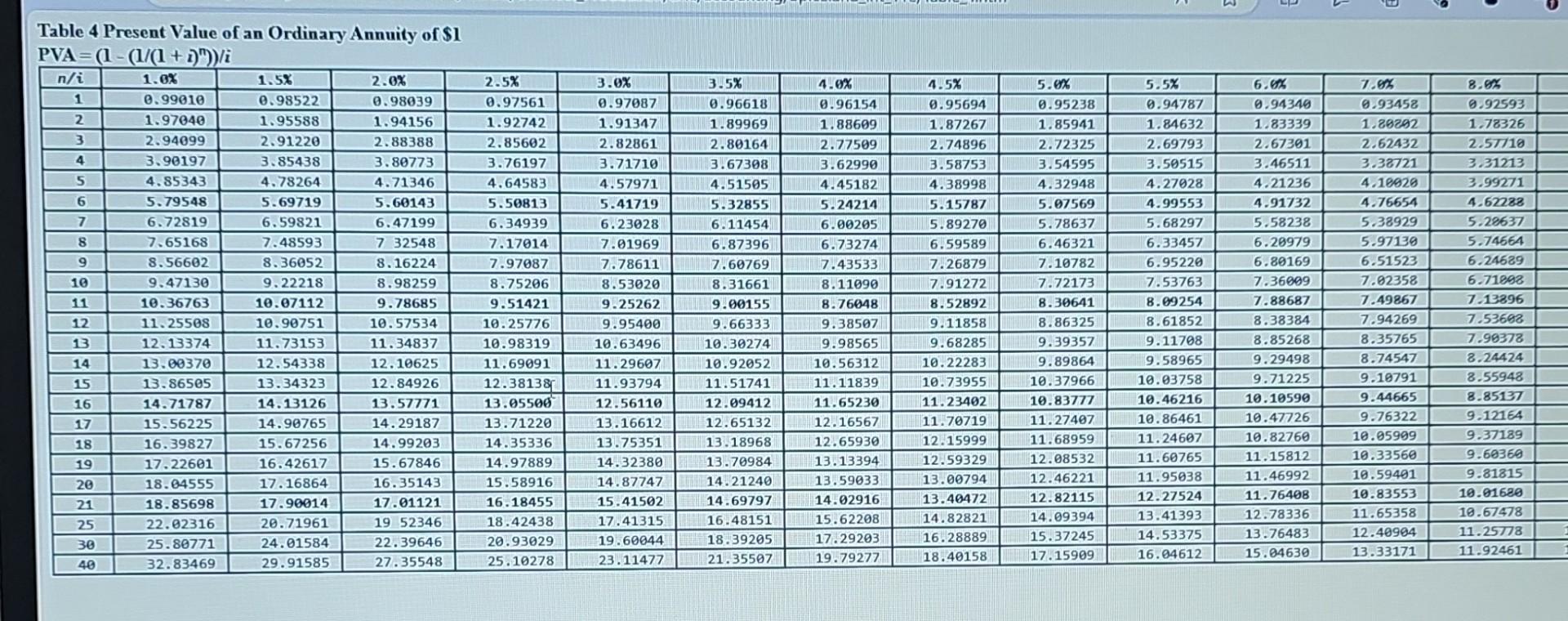
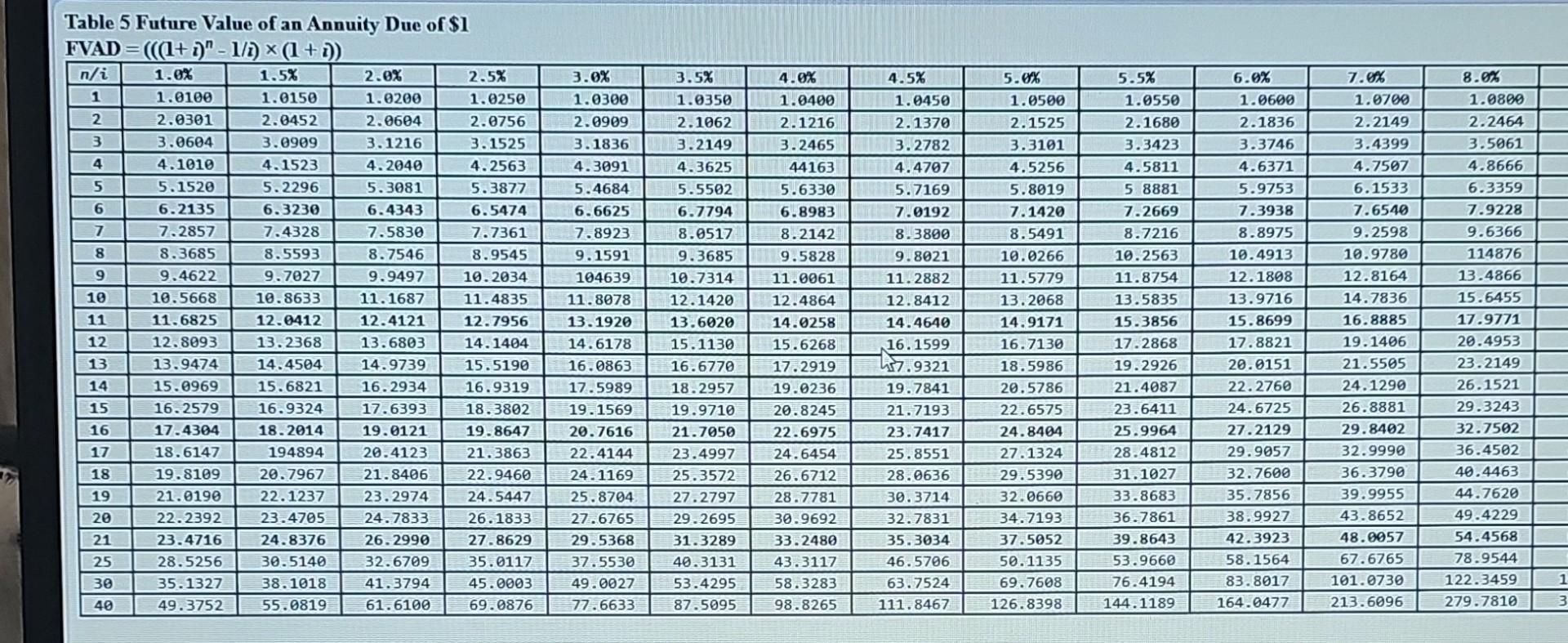
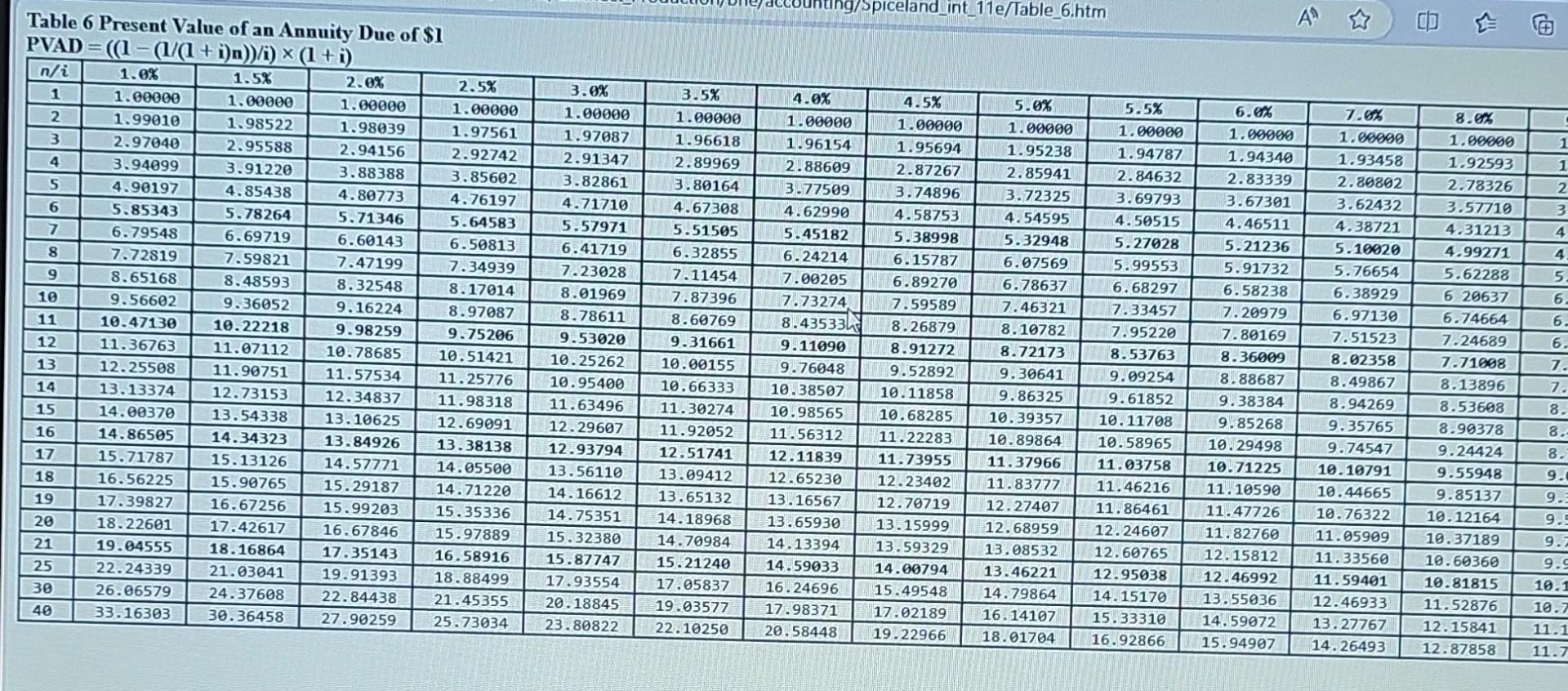
TABLE 2 Present value of $1 PV=$1/(1+i)n Table 6 Present Value of an Annuity Due of \$1 PVAD =((1(1/(1+i)n))/i)(1+i) Table 3 Future Value of an Ordinary Annuity of \$1 FVA=((1+i)n1)/i Table 5 Future Value of an Annuity Due of \$1 FVA n=((n+n1(n+) Table 4 Present Value of an Ordinary Annuity of \$1 PVA =(1(1)/(1+m)/i FV=sin(i)n Under the NBA deferred compensation plan, payments made at the end of each year accumulate up to retirement and then retirees are given two options. Option 1 allows the retiree to select the amount of the annual payment to be received, and option 2 allows the retiree to specify over how many years payments are to be received. Assume Hardaway has had \$6,800 deposited at the end of each year for 30 years, and that the long-term interest rate has been 8%. Required: a. How much has accumulated in Hardaway's deferred compensation account? b. How much will Hardaway be able to withdraw at the beginning of each year if he elects to receive payments for 16 years? c. How many years will Hardaway be able to receive payments if he chooses to receive $73,000 per year at the beginning of each year? Note: For all requirements, round your final answers to the nearest whole number. Use tables, Excel, or a financial calculator. (FV of $1,PV of $1, FVA of $1, PVA of $1, FVAD of $1 and PVAD of $1 )
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


