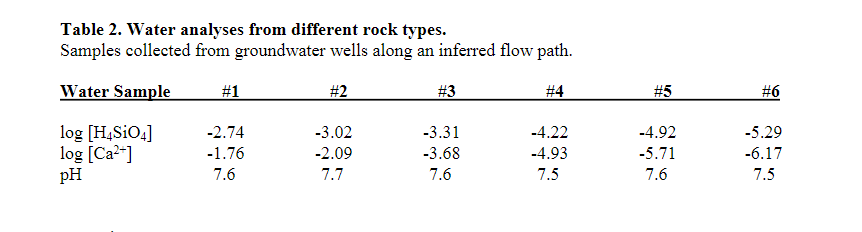
Question: Table 2. Water analyses from different rock types. Samples collected from groundwater wells along an inferred flow path. Water Sample #1 #2 #3 #4 #5
![#4 #5 #6 log [H SiO4] log (Ca2+] PH -2.74 -1.76 7.6](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f85a584c144_08766f85a57f24e7.jpg)

Table 2. Water analyses from different rock types. Samples collected from groundwater wells along an inferred flow path. Water Sample #1 #2 #3 #4 #5 #6 log [H SiO4] log (Ca2+] PH -2.74 -1.76 7.6 -3.02 -2.09 7.7 -3.31 -3.68 7.6 -4.22 -4.93 7.5 -4.92 -5.71 7.6 -5.29 -6.17 7.5 (a) A groundwater sample was collected, and a tritium (H) concentration of 3.6 TU (tritium units) was measured. What can you say about the mean residence time of this water based on the tritium concentration? (b) The helium-3 (He:) concentration was measured to be 12.3 TU in the same groundwater. Use the expression: 3He = 3H (eht - 1) to calculate the mean residence time of this water t = age in years, a = decay constant = (In2)/t12, t12 = half-life = 12.43 years for tritium. = = (c) the concentration of He gas in the atmosphere is 5.2 ppm by volume, and the "He/4He ratio in the atmosphere is 1.3 x 10-6. When the presence of He in the atmosphere is taken into account, what is the qualitative effect of atmospheric He on a calculated ?H-He mean residence time of this water - will the calculated H-He mean residence time be the same, increase, or decrease vs. the mean residence time calculated in part (b)? Explain your reasoning. Assume that the concentration of He gas in the atmosphere and the He/4He ratio in the atmosphere have remained constant vs. time. N.B. you do not need to calculate a new mean residence time. a
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


