Question: Table IV - Airborne Launch using Ramp - Single Bounce Complete the table below using data from Table I, data from your Energy Plots (see
Table IV - Airborne Launch using Ramp - Single Bounce
Complete the table below using data from Table I, data from your Energy Plots (see the Energy Plots tab), and information found under the Background tab.
Note: Be very careful with units to get correct answers! 1.00 cm = 0.0100 m, 100 mJ = 0.100 J
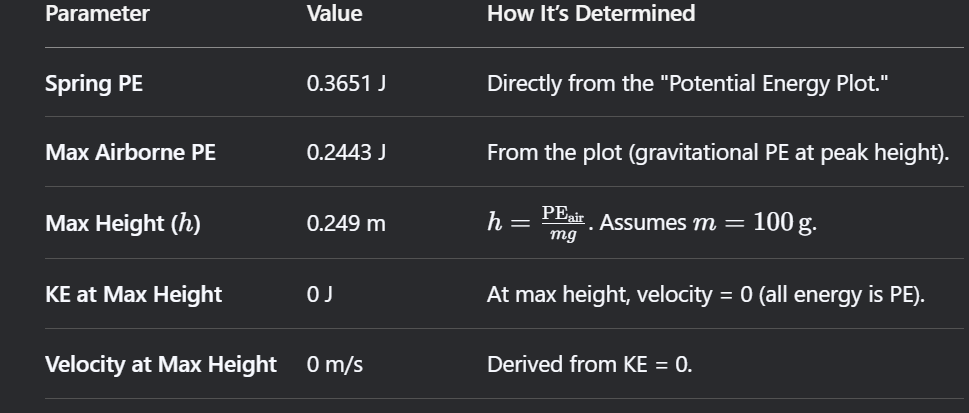
Spring | Ball | Compression Distance (m) | Spring PE (J) | Max Airborne PE (J) | Max Height (m) | KE at Max Height (J) | Max Height Velocity (m/s) |
1 | 1 | ||||||
2 |
Sample Calculation: Show your maximum height calculation for ball 1.
Sample Calculation: For ball 1, show your calculations for kinetic energy and velocity at maximum height. Hint: use Max Airborne PE and conservation of energy to determine KE at Max Height.
Observations and Questions
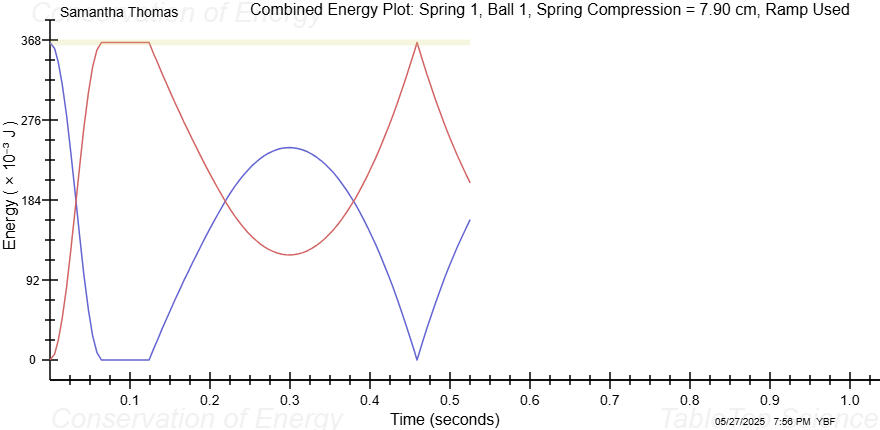
[1] The spring potential energy and maximum airborne potential energy are not equal in table IV. Provide an explanation for the difference.
[2] Based on your Combined Energy Plots for ball 1 and ball 2, is mechanical energy conserved for both balls? Use details from these plots to support your answers. Give specific locations on the plot (times, etc.) to back up your arguments.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


