Question: Table: S23NEWTABLE A) Code and execute a DDL statement which creates a table named S23NEWTABLE, with five attributes: Menultem, Name, Description, Price, SafeTemp, and

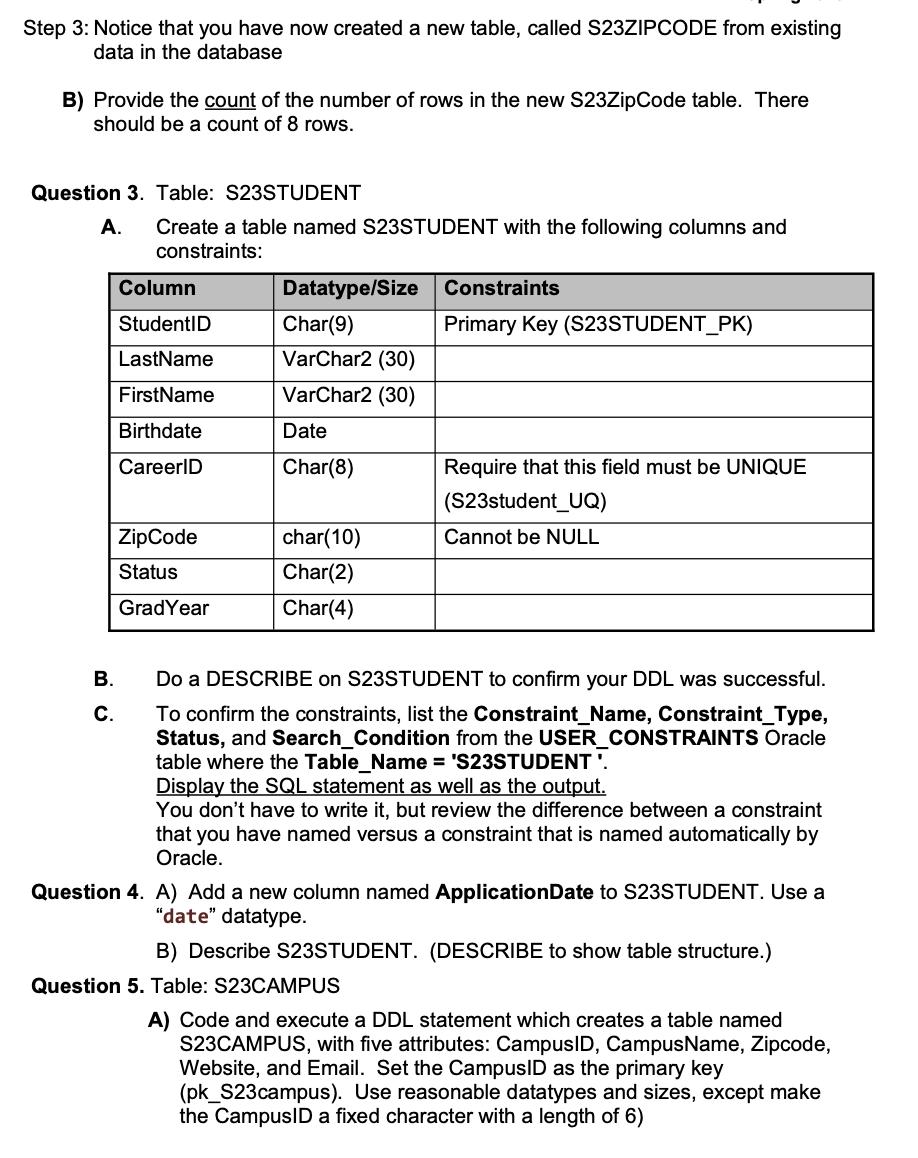

Table: S23NEWTABLE A) Code and execute a DDL statement which creates a table named S23NEWTABLE, with five attributes: Menultem, Name, Description, Price, SafeTemp, and Nutrition. a. Set the attribute Menultem as the primary key. b. Use reasonable datatypes and sizes, except make the Menultem a fixed character with a length of 8. B) Using ALTER TABLE, alter the table by adding another attribute - Vendor. Make the Vendor attribute a variable character datatype with a length of 20. C) Run a description of the S23NEWTABLE table (use the DESCRIBE command). D) Drop the table. Question 2. Table: S23ZIPCODE A) Using one SQL statement, create AND POPULATE a table called S23ZIPCODE containing columns ZipCode, and City. ZipCode should be generated. Follow these steps to walk through this SQL statement: 1 CREATE TABLE S23ZIPCODE AS ( 2 8 9 10 ); SELECT ROW_NUMBER() OVER(ORDER BY city) AS zipcode, FROM city (SELECT city FROM worker UNION SELECT supplier_city FROM food supplier) WHERE city IS NOT NULL Step 1: Use the "CREATE TABLE" format to create the table directly from the existing structure and data (see lecture slides on DDL). Step 2: Let us deconstruct the above SQL statement to understand what's happening: 2.1. ROW_NUMBER() is a function that assigns a unique number to each row to which it is applied (usually each row returned by the query). 2.2. We use the row numbers from the above discussed function to assign a unique zip code to each city. 2.3. The union of city from worker and supplier_city from food supplier should return all the cities used in our tables as depicted from line #4 to line # 8. But this UNION will also include NULL values. 2.4. The WHERE clause in line # 9 will remove all the NULL values. Step 3: Notice that you have now created a new table, called S23ZIPCODE from existing data in the database B) Provide the count of the number of rows in the new S23ZipCode table. There should be a count of 8 rows. Question 3. Table: S23STUDENT A. Create a table named S23STUDENT with the following columns and constraints: B. C. Column StudentID LastName FirstName Birthdate CareerID ZipCode Status GradYear Datatype/Size Char(9) VarChar2 (30) VarChar2 (30) Date Char(8) char(10) Char(2) Char(4) Constraints Primary Key (S23STUDENT_PK) Require that this field must be UNIQUE (S23student_UQ) Cannot be NULL Do a DESCRIBE on S23STUDENT to confirm your DDL was successful. To confirm the constraints, list the Constraint_Name, Constraint_Type, Status, and Search_Condition from the USER_CONSTRAINTS Oracle table where the Table_Name = 'S23STUDENT'. Display the SQL statement as well as the output. You don't have to write it, but review the difference between a constraint that you have named versus a constraint that is named automatically by Oracle. Question 4. A) Add a new column named Application Date to S23STUDENT. Use a "date" datatype. Question 5. Table: S23CAMPUS B) Describe S23STUDENT. (DESCRIBE to show table structure.) A) Code and execute a DDL statement which creates a table named S23CAMPUS, with five attributes: CampusID, CampusName, Zipcode, Website, and Email. Set the CampusID as the primary key (pk_S23campus). Use reasonable datatypes and sizes, except make the CampusID a fixed character with a length of 6) B) Run a description of the table (use the DESCRIBE command). Question 6. Add CampusID as a Foreign Key to S23STUDENT. A) First using ALTER TABLE, add CampusID to S23STUDENT using the same datatype and size as in the parent table (S23CAMPUS). B) Second, add a constraint called S23Student_FK establishing referential integrity between the CampusID in the S23Student (child) table and the S23Campus (parent) table. C) Describe S23STUDENT. Question 7. Add a check constraint for the Status attribute in the S23STUDENT A) Use the CHECK clause to limit the options to FR, SO, JR, or SR. Name the constraint: S23STUDENT_STATUS_CK B) Copy and execute the following statement to check the constraint for Status: GR'); Then copy and paste the error result as well as the SQL statement that you just used. You should have an ORA-01400: cannot insert NULL into as an error INSERT INTO S23student (studentid, status) VALUES ('PU3922', Question 8. Run a SQL statement that displays your userID (USER) and the system time stamp (SYSDATE) Select the USER and SYSDATE from the DUAL table Question 9. A) Using the USER_CONSTRAINTS Oracle table, list the Constraint_Name, Table_Name and Status from the USER_CONSTRAINTS view where the Constraint_Type = 'P' (i.e., Primary Key). Copy and paste the last ten lines to your document. B) List the Constraint_Name, Table_Name, R_Constraint_Name and Status from the USER_CONSTRAINTS view where the Constraint pe = 'R' (i.e., Foreign Key). The R_Constraint_Name is the parent's constraint name. Copy and paste the last ten lines to your document. Question 10. Drop S23ZIPCODE, S23STUDENT, and S23CAMPUS. Cascade the constraints. Show the SQL statement to drop the 3 tables as well as the output. DROP TABLE tablename CASCADE CONSTRAINTS;
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


