Question: TACTICS BOX 1 8 . 5 Ray tracing for a convex mirror Draw an optical axis. Use graph paper or a ruler. Establish an appropriate
TACTICS BOX Ray tracing for a convex mirror
Draw an optical axis. Use graph paper or a ruler. Establish an appropriate scale.
Center the mirror on the axis. Mark and label the focal point at distance from the mirror's surface. Draw the mirror plane through the mirror's center, perpendicular to the axis.
Represent the object with an upright arrow at distance It is usually best to place the base of the arrow on the axis and to draw the arrow about half the radius of the mirror.
Draw the three "special rays" from the tip of the arrow. Use a straightedge or a ruler. The rays should reflect off the mirror plane.
a A ray parallel to the axis Ray reflects as though it came from the focal point.
b A ray initially directed toward the focal point Ray reflects parallel to the axis.
c A ray that strikes the center of the mirror Ray reflects at an equal angle on the opposite side of the optical axis.
Extend the emerging rays behind the mirror until they converge. The point of convergence is the image point. Draw the rest of the image in the image plane. If the base of the object is on the axis, then the base of the image will also be on the axis.
Measure the image distance Also, if needed, measure the image height relative to the object height. The magnification can be found from
Follow the steps above to solve the following problem: An object is cm from a convex mirror with a focal length of cm Use ray tracing to determine the location of the image.
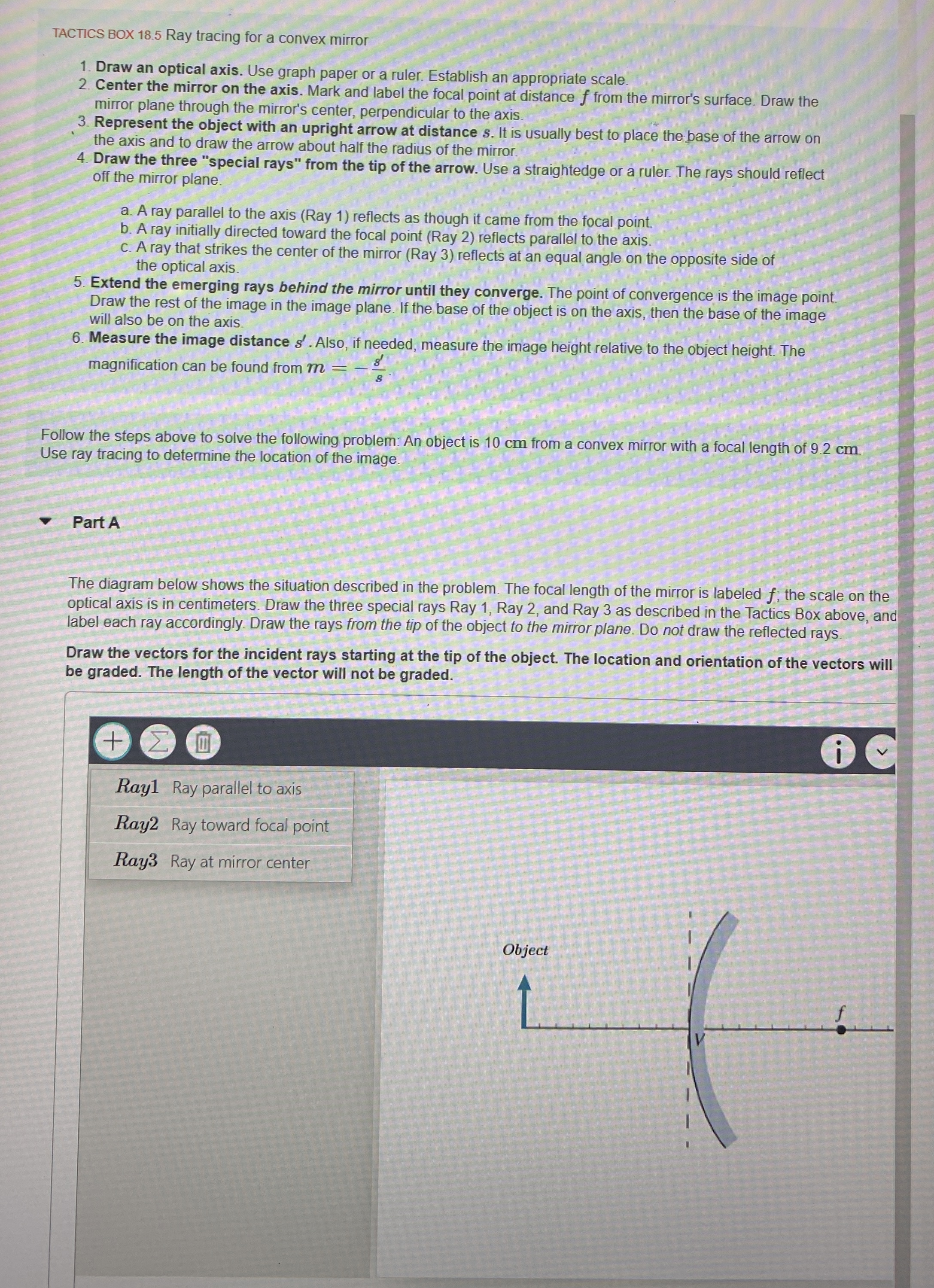
Part A
The diagram below shows the situation described in the problem. The focal length of the mirror is labeled ; the scale on the optical axis is in centimeters. Draw the three special rays Ray Ray and Ray as described in the Tactics Box above, and label each ray accordingly. Draw the rays from the tip of the object to the mirror plane. Do not draw the reflected rays.
Draw the vectors for the incident rays starting at the tip of the object. The location and orientation of the vectors will be graded. The length of the vector will not be graded.
Ray Ray parallel to axis
Ray Ray toward focal point
Ray Ray at mirror center
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


