Question: Task one.. You have been assigned to construct a portfolio comprising two risky assets (Portfolios A & B) while considering your client's risk tolerance. The
Task one..
You have been assigned to construct a portfolio comprising two risky assets (Portfolios A & B) while considering your client's risk tolerance. The attached spread sheet shows historical monthly returns of the two portfolios; the market portfolio as represented by the S&P 500 index; and the risk free rate as represented by 90-day Treasury Bills. Also shown are the annualized returns for each investment during the period. The first risky asset (Portfolio A) is a US equity strategy that uses publically available valuation, technical and sentiment factors to assess which stocks are over-priced and which are under-priced. Fundamental factors indicate the magnitude and quality of a company's earnings and the strength of its balance sheet. Examples of such factors include: cash flow growth, cash flow return on invested capital, price to cash flow, and accruals which assess earnings quality (low quality earnings indicate that management may be manipulating earnings by adjusting accruals). Companies with favorable fundamental factors tend to outperform those with less favorable factors. Technical and sentiment factors seek to identify mis-pricings resulting from investor behavior. Examples include: momentum and price reversals where investors tend to over-react to good news by bidding up prices ABOVE fair value and bad news by bidding down prices BELOW fair value; short interest on a stock which can indicate the investor sentiment about the company's prospects; share buybacks which can indicate a positive signal from management's optimism regarding a firm's future prospects; and earnings / revenue surprise. Firms with favorable technical and sentiment factors also tend to outperform. For example, firms whose earnings and revenue exceed analysts' expectations tend to continue to outperform vs. those firms that experience earnings surprise due to cost cutting. Starting with the market portfolio, the US equity strategy over-weights those stocks with more favorable fundamental, technical and sentiment factors and under-weights or avoids those stocks with less-favorable or un-favorable factors. The strategy seeks to out-perform the market portfolio as represented by the S&P 500. The monthly returns of the US equity strategy are shown in the attached spreadsheet (Portfolio A). The second risky asset (Portfolio B) is a global macro hedge fund. This strategy seeks to benefit from mis-pricings within and across broad asset classes by taking long and short positions in equity markets, bond markets and currencies. For example, if the manager believes that US equities will out-perform Japanese equities, the portfolio will go long S&P 500 futures and short TOPIX futures (TOPIX is an index that serves as a proxy for Japanese equities). This long/short trade is not impacted by the overall direction of global equities, but rather the relative movement between US and Japanese equities. Similarly for bonds, if the manager believes that interest rates in the United Kingdom (UK) will decline more so than interest rates in Australia, then the manager will buy UK gilt futures (gilt is the 10-year UK bond) and short Australian 10-year bond futures. Again, this trade is not impacted by the overall direction of global interest rates, but rather the relative movement between UK and Australian rates. Recall that bond prices rise as interest rates decline. The global macro hedge fund is mostly market neutral meaning that long positions equal short positions thereby dramatically reducing systematic exposures (low beta). Portfolios A & B are much more volatile than the risk free rate. You will find that their correlation is small indicating that there is a diversification benefit to be had from holding both in a portfolio (you will need to calculate this using the excel function "=correl(range 1, range2)". You will be meeting with a client that is looking for investment advice from you based on the two strategies A & B. In preparation for your upcoming meeting with the client, your boss asks that you respond to the questions below and be ready to discuss. Hint: You will need to determine the correlations and volatilities for each risk premium.
Your client believes in the weak form of market efficiency as it relates to security selection. Is Portfolio A's performance sufficient justification to prove this belief? Why or why not.
Task 2.
For each of the following situations, select the best answer that applies to consolidating financial information subsequent to the acquisition date:
(A) Initial value method.
(B) Partial equity method.
(C) Equity method.
(D) Initial value method and partial equity method but not equity method.
(E) Partial equity method and equity method but not initial value method.
(F) Initial value method, partial equity method, and equity method.
____1. Method(s) available to the parent for internal record-keeping.
____2. Easiest internal record-keeping method to apply.
____3. Income of the subsidiary is recorded by the parent when earned.
____4. Designed to create parallel between the parent's investment accounts and changes in the underlying equity of the acquired company.
____5. For years subsequent to acquisition, requires the *C entry.
____6. Uses the cash basis for income recognition.
____7. Investment account remains at initially recorded amount.
____8. Dividends received by the parent from the subsidiary reduce the parent's investment account.
____9. Often referred to in accounting as a single-line consolidation.
____10. Increases the investment account for subsidiary earnings, but does not decrease the subsidiary account for equity adjustments such as amortizations.
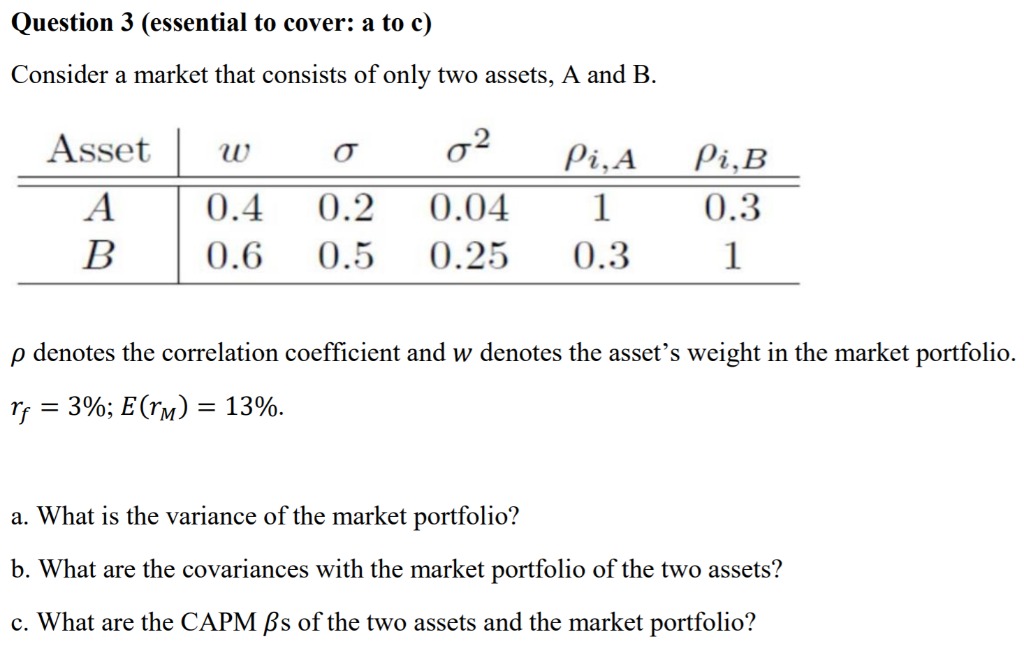
Part c.


Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


