Question: TAULE Write a Python script for each that will apply the algorithm to any given zero-one matrix. Algorithm 0.1 (A Procedure for Computing the


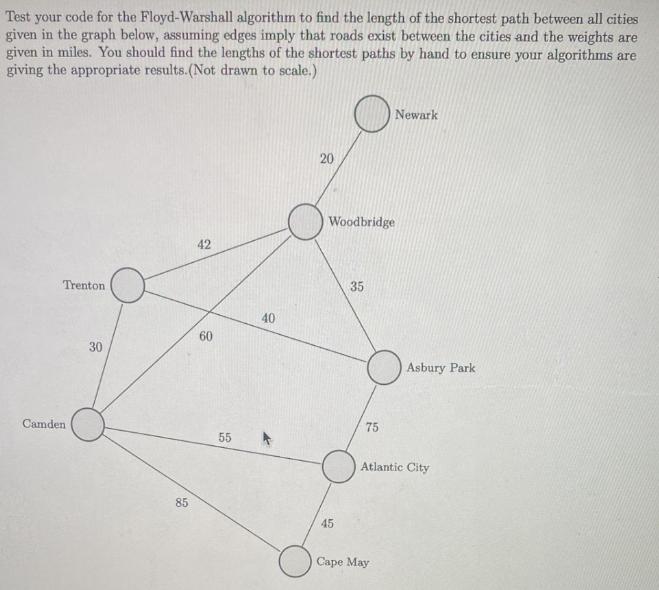
TAULE Write a Python script for each that will apply the algorithm to any given zero-one matrix. Algorithm 0.1 (A Procedure for Computing the Transitive Closure). procedure transitive closure (Ma: zero-one nx n matrix) A: MR BA for i:=2 to n A:AO MR BBVA return B (the zero-one matrix for R.) Algorithm 0.2 (Warshall Algorithm). procedure Warshall (Mn: nxn zero-one ma- trix) W : MR for k:=1 to n for i:=1 to n for i:=1 to n W = WV (wie wks) return W (W = [w] is the zero-one matrix for R".) 2. It is known that Warshall's algorithm is more efficient, when compared to Algorithm 0.1, at computing the transitive closure. Verify this claim by doing the following. I (a) Using the scripts you wrote from question 1, run a sequence of tests utilizing random zero-one matrices with n 10, 20, 30,.,100 where you record completion time, taking a 10 run average for each n-value. Plot your results of your experiments on an appropriate chart. (b) What conclusions can you claim based on your results from part (b)? 3. Both algorithms given above can be adapted to find the reflexive closure of the transitive closure for a given relation. Adapt your scripts from 1.(a) so that you have the option to find either the transitive closure, or the reflexive transitive closure, for a given relation. Test your scripts, for each of the four cases, on a random 20 x 20 zero-one matrix and return the matrices resulting from these tests. 4. The Floyd-Warshall Aglorithm can be used to find the length of a shortest path between all pairs of vertices in a weighted connected simple graph. However, this algorithm cannot be used to construct shortest paths. Use the psuedocode below to write a script that applies the Floyd-Warshall algorithm to a weighted connected simple graph. Algorithm (Floyd-Warshall Algorithm). procedure FW(G: weighted connected simple graph, with all weights positive.) {G has vertices vo, U1,..., Un and weights w (v, v.) where w (v., v.) = oo if (vi, u,) is not an edge in G} for i:=1 to n for j:=1 to n d (v, vs) := w (v, vj) for i:=1 to n for j:=1 to n for k:=1 to n if d (v,vi) + d(vi, Uk) < d (vj, vk) then d(u, v):= d (vj, v) + d(vi, vk) return d (v,v;) {d (v, v;) is the length of the shortest path between us and u; for 1 i n, 1jn.} Test your code for the Floyd-Warshall algorithm to find the length of the shortest path between all cities given in the graph below, assuming edges imply that roads exist between the cities and the weights are given in miles. You should find the lengths of the shortest paths by hand to ensure your algorithms are giving the appropriate results. (Not drawn to scale.) Trenton. Camden 30 85 42 60 55 40 K 20 O 45 Woodbridge 35 75 Newark Cape May Asbury Park Atlantic City 35 36 transitive_closure (MR) 37 38 39 40 41 42 tc_time_list.append(total_time/10) 43 44 # Plot 45 46 plt.plot(n_list, w_time_list, label="Warshall Algorithm) 47 48 plt.plot(n_list, tc_time_list, label="Transitive Closure Algorithm) 49 50 pttxlabel(n) 51 52 pltylabel(average time (seconds)') 53 plt.title(Computation Time Comparison Between Algorithms) 54 55 plt.legend end = time.time( total time + end-start Trace IDE Learn Python Programs ... More
Step by Step Solution
3.40 Rating (163 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Algorithm Start Define functions for algorithm01 warshallalgorithm reflexiveclosure reflexivetransitiveclosure and generaterandommatrix Implement the algorithm01 function that computes the transitive ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


