Question: TCP estimates its timeout value based on measurements of packets round trip time ( RT ) . As RTT increases, the timeout value increases as
TCP estimates its timeout value based on measurements of packets round trip time RT As RTT increases, the timeout value increases as well. The variability in RTT is also factored into the calculation. If RTT is a consistent value, the timeout will be closer to the measured RTT If there is a lot of variability in RTT then then timeout will increase. TCP only tracks the RTT of a single packet at a time. When one ongoing RTT measurement finishes, a new measurement will be started when the next packet is sent. This means that RTT is not measured for every packet sent. These measurements are then combined together using a moving average, so as not to give too much weight to any one reading which may not be representative of the current state of the network The below equations are used by TCP to compute its timeout value.
EstimatedRTTn EstimatedRTTn SampleRTTn
DevRTTn beta DevRTTnbeta SampleRTTn EstimatedRTTn
Timeoutn EstimatedRTTn DevRTTn
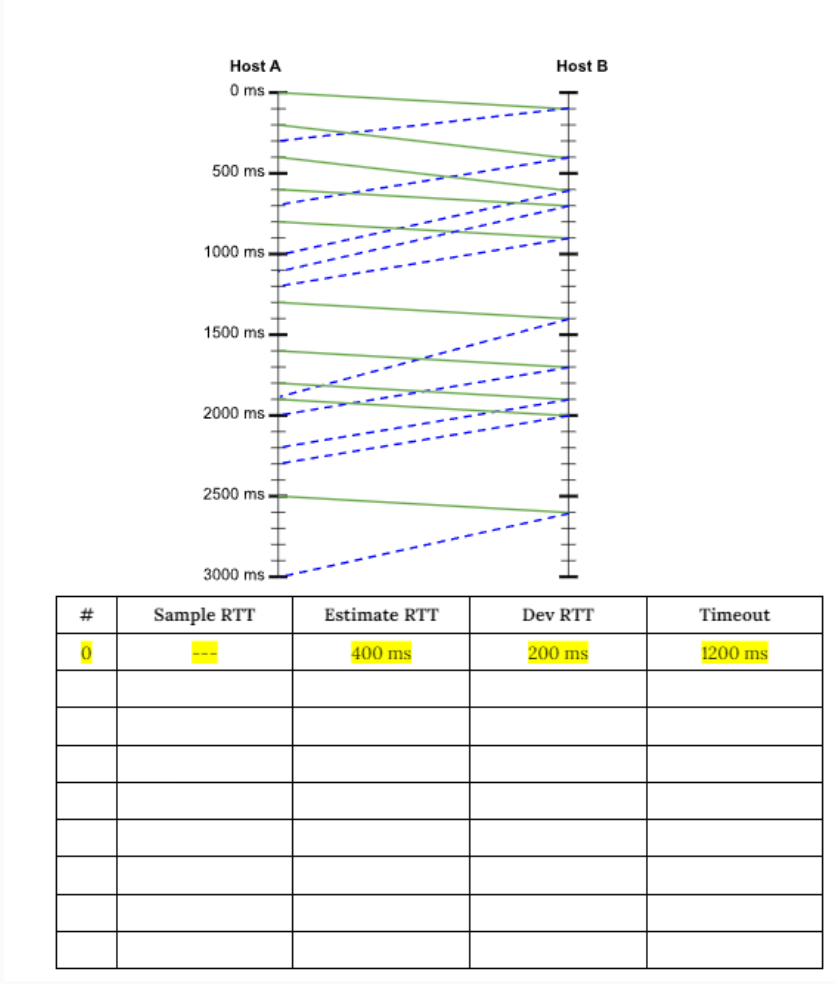
SampleRTT is the most recently measured RTT value. The timeout is updated every time a new SampleRTT is measured. and beta are constants that are used to tune the moving average. Use values and beta for this problem. The below ladder diagram shows several packets traveling back and forth between two TCP endpoints. Your task is to collect each SampleRTT value TCP would measure and then update the timeout value accordingly. Report each value you calculate in the table on the next page.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


