Question: Testing Implement and test the following functions in MiniMac: Tri ( n ) = 1 + 2 + . . . + n / /
Testing
Implement and test the following functions in MiniMac:
Trin n stored in a file called tri
Fibn nth Fibonacci number stored in a file called fib
Lessn mn m: true and false
Logn m where m n and n m
In each case the output, fn should be stored in memory and the inputs should be stored beginning in memory
Hints
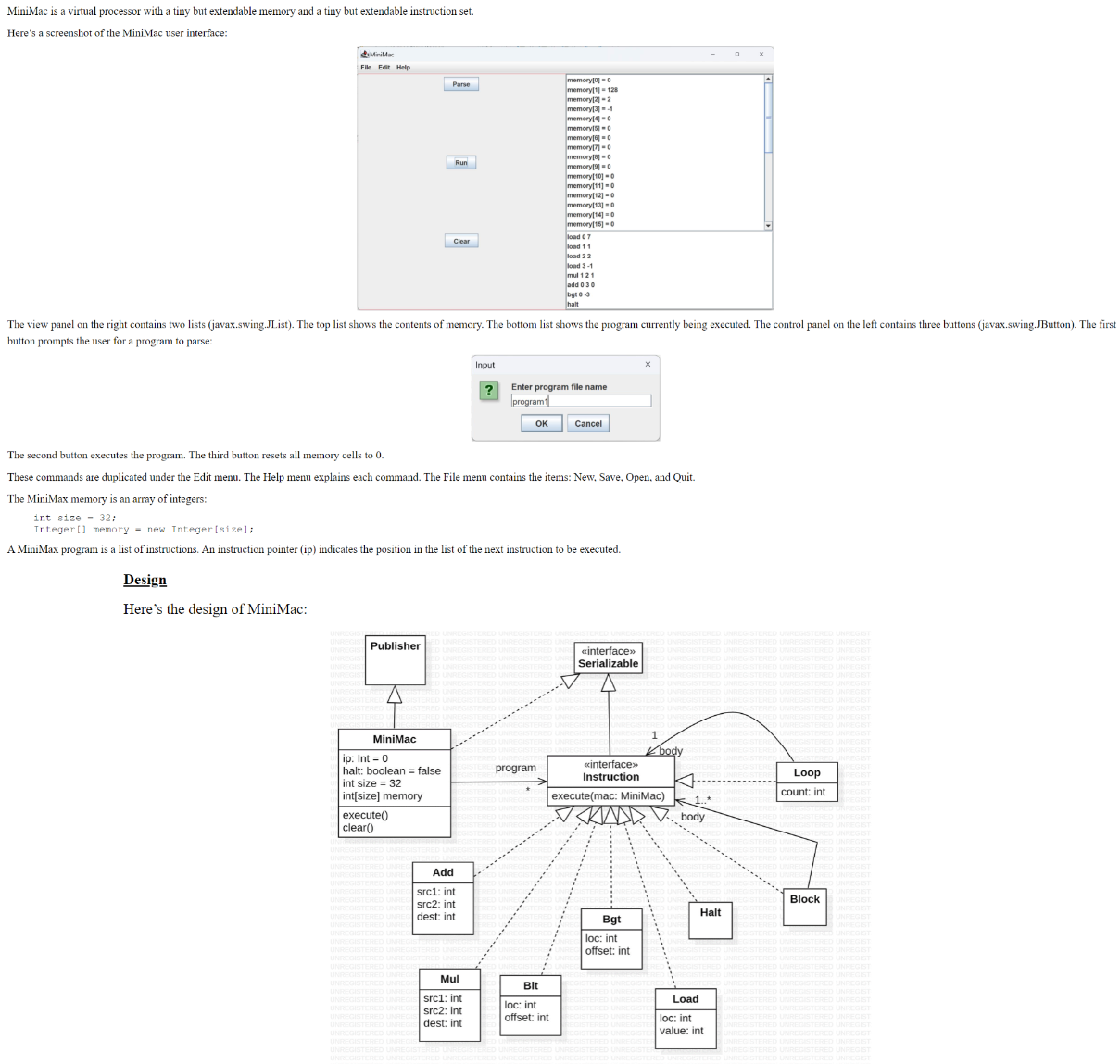
The MiniMac is a publisher and the view panel is its subscriber. Each time memory is updated or a new program is set, MiniMac notifies its subscribers.
The control panel is the action listener for its buttons. It navigates to the MiniMac and calls the appropriate procedure execute and clear
Parsing is more complicated. The control panel must prompt the user for a file name, read the file as a string then pass the string to MiniMaxParser.parseprogram It then sets the MiniMac program to the parsers output, which causes a subscriber notification. Suggestion: ask ChatGPT how to read a text file in Java.
Ask ChatGPT for a simple example of how to use a JList.
MiniMacParser.java:
package minimac;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
class ParserUtils
protected static Integer parseIntegerIterator it throws Exception
if ithasNext
return Integer.parseIntitnext;
else
throw new ExceptionParsing error, integer expected";
public class MiniMacParser extends ParserUtils
static public List parseString program throws Exception
List result new ArrayList;
split program into a list of tokens ie numbers and operations:
List tokens Arrays.asListprogramsplits;ss;
Iterator it tokens.iterator;
while ithasNext
result.addparseNextit;
return result;
dispatcher method:
static public Instruction parseNextIterator it throws Exception
String opcode itnext;
if opcodeequalsIgnoreCasehalt return new Halt;
if opcodeequalsIgnoreCaseadd return parseAddit;
if opcodeequalsIgnoreCasemul return parseMulit;
if opcodeequalsIgnoreCaseload return parseLoadit;
if opcodeequalsIgnoreCaseloop return parseLoopit;
if opcodeequalsIgnoreCaseBgt return parseBgtit;
if opcodeequalsIgnoreCaseBlt return parseBltit;
if opcodeequalsIgnoreCase return parseBlockit;
if opcodeequalsIgnoreCase return null; used to indicate the end of a block
throw new ExceptionParsing error, unrecognized operator: opcode;
static protected Add parseAddIterator it throws Exception
int src parseIntegerit;
int src parseIntegerit;
int dest parseIntegerit;
return new Addsrc src dest;
static protected Mul parseMulIterator it throws Exception
int src parseIntegerit;
int src parseIntegerit;
int dest parseIntegerit;
return new Mulsrc src dest;
static protected Load parseLoadIterator it throws Exception
int loc parseIntegerit;
int value parseIntegerit;
return new Loadloc value;
static protected Loop parseLoopIterator it throws Exception
int count parseIntegerit;
List blockInstructions new ArrayList;
if itnextequals
throw new ExceptionLoop must be followed by ;
Instruction instruction;
while instruction parseNextitequals
blockInstructions.addinstruction;
return new Loopcondition blockInstructions;
static protected Bgt parseBgtIterator it throws Exception
int loc parseIntegerit;
int offset parseIntegerit;
return new Bgtloc offset;
static protected Blt parseBltIterator it throws Exception
int loc parseIntegerit;
int offset parseIntegerit;
return new Bltloc offset;
static protected Block parseBlockIterator it throws Exception
List blockInstructions new ArrayList;
while ithasNext
Instruction nextInstruction parseNextit;
if nextInstruction null
break;
blockInstructions.addnextInstruction;
return new BlockblockInstructions;
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


