Question: //TestingAssignment3 public class TestingAssignment3 { // creating the tree // 5 // / // 2 6 // / // 1 4 // /


//TestingAssignment3
public class TestingAssignment3
// creating the tree // 5 // / \ // 2 6 // / \ // 1 4 // / \ // 8 -2 public static BinaryTree
BTNode
BTNode
return new BinaryTree
public static void testNumberOfLeaves() { BinaryTree
public static void testCountDepthK() { BinaryTree
public static void testMap() { BinaryTree
if (root.getData() == 10 && ll.getData() == 2 && lr.getData() == 8 && r.getData() == 12) System.out.println("map OK"); else System.out.println("map ERROR"); }
public static void testPathFromRoot() { BinaryTree
public static void testDistance() { BinaryTree
BTNode
try { tree.distance(five, eleven); } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) { } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("distance: wrong exception"); return; }
if (tree.distance(five, six) == 1 && tree.distance(negativeTwo, five) == 3 && tree.distance(negativeTwo, six) == 4) System.out.println("distance OK"); else System.out.println("distance ERROR"); }
public static void testPreOrderIterator() { BinaryTree
// it has [8,-2,6,100,-50] left int last5[] = {8,-2,6,100,-50}; for (int i = 0; i
if (flag) System.out.println("preOrderIterator OK"); else System.out.println("preOrderIterator ERROR"); }
public static void main(String[] args) { testNumberOfLeaves(); testCountDepthK(); testMap(); testPathFromRoot(); testDistance(); testPreOrderIterator(); }
}
//BINARY TREE

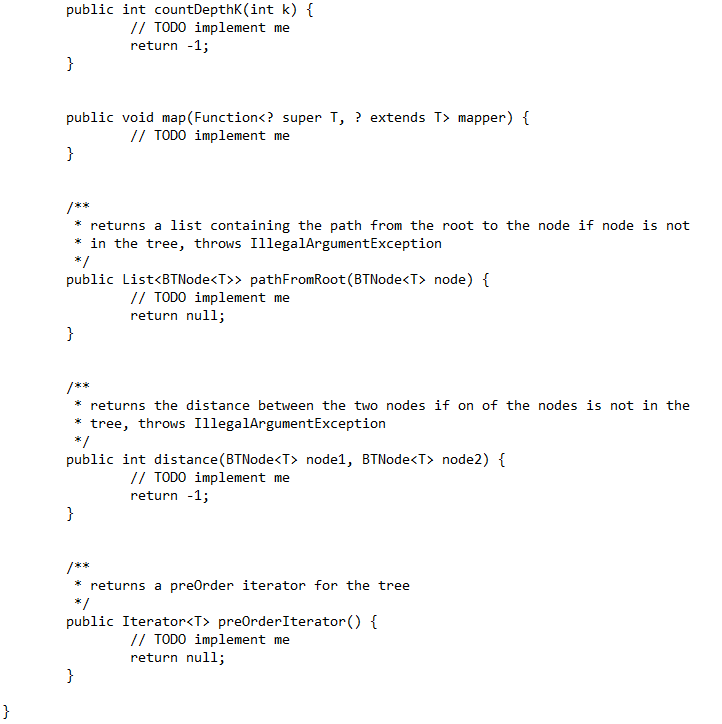 //BTNode
//BTNode



You need to implement the following classes: - binarytree.BinaryTree - binarytree.BTNode Note that all files must be under the correct package (folder). You may add more classes to your solution if necessary. Make sure your zip file can be unzipped using the command "unzip assignmen3.zip" in CSIL. The zip file needs to contain exactly one folder: src. In the src folder there must be one folder/package: binarytree. The binarytree folder needs to contain the following files (and any additional files if needed): - src/binarytree/BTNode.java - src/binarytree/BinaryTree.java References: You may use textbooks, wiki, stack overflow, geeksforgeeks, etc. If you do, specify the references in comments. Readability: Your code should be readable using the standard Java conventions. Add comments wherever is necessary. If needed, write helper functions or add classes to improve readability. Compilation: Your code MUST compile in CSIL using javac. Make sure that your code compiles without warnings/errors. If the code does not compile in CSIL the grade on that part will be 0 (zero). Even if you can't solve a problem completely, make sure it compiles. The assignment will be graded mostly automatically, with some exceptions. Do not add main() to your solutions. The main() method will be in the test files. Warnings: Warnings during compilation will reduce points. More importantly, they indicate that something is probably wrong with the code. Testing: Test your code. Examples of tests are included. Your code will be tested using the provided tests as well as additional tests. You should create more tests to check your solution. Write the following methods in the class BinaryTree. a) [10 points] int numberOfLeaves() The method returns the number of leaves in the tree. b) [15 points] int countDepthK(int k) The method returns the number of nodes in the tree with depth=k. If k is greated than the depth of the tree, the method returns 0 . c) [15 points] void map(Function super T, ? extends T> mapper) The method gets a mapper, and for each node in the tree applies it to the node.data. In order to apply the mapper on the data in a node you may use the line node.setData(mapper.apply(node.getData())) For the API see https://docs.oracle.com/iavase/8/docs/api/java/util/function/Function.html d) [15 points] List > pathFromRoot(BTNode
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


